(Press-News.org) GRAND RAPIDS, Mich. (Aug. 1, 2024) — Humans and baker’s yeast have more in common than meets the eye, including an important mechanism that helps ensure DNA is copied correctly, reports a pair of studies published in the journals Science and Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
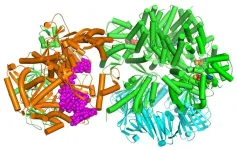
The findings visualize for the first time a molecular complex — called CTF18-RFC in humans and Ctf18-RFC in yeast — that loads a “clamp” onto DNA to keep parts of the replication machinery from falling off the DNA strand.
It is the latest discovery from longtime collaborators Huilin Li, Ph.D., of Van Andel Institute, and Michael O’Donnell, Ph.D., of The Rockefeller University, to shed light on the intricate mechanisms that enable the faithful passage of genetic information from generation to generation of cells.
“The accurate copying of DNA is fundamental to the propagation of life,” Li said. “Our findings add key pieces to the puzzle of DNA replication and could improve understanding of DNA replication-related health conditions.”
DNA replication is a tightly controlled process that copies the genetic code, allowing its instructions to be conveyed from one generation of cells to the next. In diseases like cancer, these mechanisms can fail, leading to uncontrolled or faulty replication with devastating consequences.
To date, at least 40 diseases, including many cancers and rare disorders, have been linked to problems with DNA replication.
The process begins by unzipping DNA’s ladder-like structure, resulting in two strands called the leading and lagging strands. A molecular construction crew then assembles the missing halves of the strands, turning a single DNA helix into two. Much of this work falls to enzymes called polymerases, which assemble the building blocks of DNA.
On their own, however, polymerases aren’t good at staying on the DNA strand. They require CTF18-RFC in humans and Ctf18-RFC in yeast to thread a ring-shaped clamp onto the DNA leading strand, and another clamp loader called RFC in both human and yeast to thread the clamp onto the lagging strand. The clamp then closes and signals to the polymerases that they can begin replicating DNA.
Using high-powered cryo-electron microscopes, Li, O’Donnell and their teams revealed previously unknown facets of the leading strand clamp loaders’ structures, including a “hook” that forces the leading strand polymerase to let go of the new DNA strand so it can be recognized by the clamp loader. This distinction represents a key difference between the functions of the leading strand clamp loader (CTF18-RFC) and the lagging strand clamp loader (RFC) and illuminates an important aspect of varying DNA duplication mechanisms on the leading and lagging strands.
Lastly, the study identified shared features between the yeast and human leading strand clamp loaders, which demonstrate an evolutionary link between the two. This finding underscores the value of yeast as powerful yet simple models for studying genetics.
Other authors of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences paper include Qing He, Ph.D., and Feng Wang, Ph.D., of VAI. Other authors of the Science paper include Zuanning Yuan, Ph.D., of VAI; and Roxana Georgescu, Ph.D., Nina Y. Yao, Ph.D., and Olga Yurieva, Ph.D., of The Rockefeller University.
Research reported in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences study and the Science study was supported by Van Andel Institute (Li); the National Institute of General Medical Sciences of the National Institutes of Health under award nos. R01GM148159 (O’Donnell) and R35GM131754 (Li); and the Howard Hughes Medical Institute (O’Donnell). The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health or other funders.
###
ABOUT VAN ANDEL INSTITUTE
Van Andel Institute (VAI) is committed to improving the health and enhancing the lives of current and future generations through cutting edge biomedical research and innovative educational offerings. Established in Grand Rapids, Michigan, in 1996 by the Van Andel family, VAI is now home to more than 500 scientists, educators and support staff, who work with a growing number of national and international collaborators to foster discovery. The Institute’s scientists study the origins of cancer, Parkinson’s and other diseases and translate their findings into breakthrough prevention and treatment strategies. Our educators develop inquiry-based approaches for K–12 education to help students and teachers prepare the next generation of problem-solvers, while our Graduate School offers a rigorous, research-intensive Ph.D. program in molecular and cellular biology. Learn more at vai.org.
END
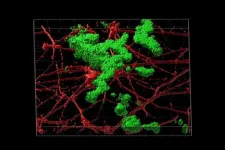
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have developed a way to capture the effects of aging in the development of Alzheimer’s disease. They have devised a method to study aged neurons in the lab without a brain biopsy, an advancement that could contribute to a better understanding of the disease and new treatment strategies.
The scientists transformed skin cells taken from patients with late-onset Alzheimer’s disease into brain cells called neurons. Late-onset Alzheimer’s ...
Chestnut Hill, Mass (8/1/2024) – Rocks recently exposed to the sky after being covered with prehistoric ice show that tropical glaciers have shrunk to their smallest size in more than 11,700 years, revealing the tropics have already warmed past limits last seen earlier in the Holocene age, researchers from Boston College report today in the journal Science.
Scientists have predicted glaciers would melt, or retreat, as temperatures warm in the tropics – those regions bordering the Earth’s ...
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. — A Purdue University invention that may shorten construction timelines and increase long-term durability of concrete highways, bridges and other transportation infrastructure is emerging as a viable alternative to methods that have been used for decades to estimate when newly poured concrete is mature enough to withstand heavy loads such as those from trucks and other vehicles.
The American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials’ Committee on Materials and Pavements (AASHTO COMP) has approved the Purdue-developed method as a new national ...
BOSTON—Plant-based proteins have major health advantages over animal-based proteins, according to a New England Journal of Medicine letter to the editor by Neal D. Barnard, MD, published Aug. 1, 2024. New findings show that all plants contain all essential amino acids, in contrast to the common but mistaken belief that plants lack one or more amino acids. Of the 20 amino acids that are the building blocks of protein, nine cannot be produced by the human body. All are found in plant sources.
“In addition, plant-based ...
WASHINGTON, D.C., Aug. 1, 2024 — The latest issues of three American Psychiatric Association journals, The American Journal of Psychiatry, Psychiatric Services, and Focus are now available online.
The August issue of The American Journal of Psychiatry brings together research on PTSD, phobias, suicide attempts, and psychiatric vulnerabilities. Highlights include:
Neurobiology and Treatment of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder.
Testing Quantitative and Qualitative Sex Effects in a National Swedish Twin-Sibling Study of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder.
Sexual Identity Continuity and Change in a U.S. National Probability Sample of Sexual Minority Adults: Associations ...
By Jade Boyd
Special to Rice News
Rice University’s Angel Martí has been elected a fellow of the American Chemical Society (ACS), one of his discipline’s highest honors.
Martí, professor and department chair of chemistry, is among 37 newly elected fellows announced by ACS this week. With more than 200,000 members in 140 countries, ACS is one of the largest scientific organizations. Fewer than 1% of its members are fellows, a distinction reserved for those with exemplary records of both service to the society and outstanding scientific or professional achievement.
Martí joined ...
HOUSTON – (August 1, 2024) – Materials behave differently in different size regimes, and researchers tend to cluster their efforts either at the nanoscale, examining materials in atom-level detail, or at the microscale, looking at structures between three and five orders of magnitude greater.
However, less is known about what happens in the “in-between” realm spanning from 10 billionths to 1 millionth of a meter.
“We call this the mesoscale,” said Rice University materials scientist Lane Martin, who together with collaborators at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory and Lawrence Berkeley National ...
ACM, the Association for Computing Machinery, has recently published the first issue of Proceedings of the ACM on Software Engineering (PACSME), a new Gold Open Access journal publishing top-quality, original research on all aspects of software engineering, from requirements elicitation to quality assessment, design, maintenance, evolution, and deployment. PACMSE covers a broad range of topics and methods that help conceive, create, and maintain better software be it embedded, cloud-based, mobile and ubiquitous, or runs on conventional computers.
“The overarching goal of the new PACSME journal is to make ...
An estimated 16% of people worldwide live with a significant disability that impacts their daily life. Of this population, only about 40% engage in aerobic activity. Due to this lack of exercise, people with disabilities (PWD) are more likely to suffer from chronic conditions such as heart disease, stroke, diabetes, or cancer and are at higher risk of mental illnesses like depression and anxiety.
“Many PWD struggle with psychological issues such as low self-esteem and negative body image, which can further reduce their motivation to participate in exercise activities, especially in public places ...
As the Venezuelan crisis intensifies, researchers and policy experts have worked to understand its ramifications on the country’s politics, economics, health services, water security, infrastructure and more.
Now, Northwestern University computer scientists have comprehensively examined the effects of the crisis on a previously unexplored area: the Internet.
In a new study, the researchers found the crisis has significantly — and negatively — affected Venezuela’s Internet infrastructure and connectivity. Compared to the ...