(Press-News.org) FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Aug. 1, 2024
Media Contact:
Monica McDonald
(404) 365-2162
mmcdonald@rheumatology.org
American College of Rheumatology Opens Press Registration for ACR Convergence 2024
ATLANTA – Complimentary press registration is now open for journalists to cover research presented at ACR Convergence 2024, taking place Nov. 14-19 at the Walter E. Washington Convention Center in Washington, D.C. A listing of sessions for the meeting can be found in the online program.
Approved journalists will receive an all-access pass to the meeting, discounted housing (while supplies last), access to an embargoed digital press center, assistance scheduling interviews with speakers, on-demand access to recorded sessions through Oct. 31, 2025, and access to an onsite newsroom equipped with a printer, computers and refreshments.
Early press registration will end on Oct. 25. The ACR public relations team will process requests received before this time and will continue accepting requests through the end of the meeting. Still, delayed responses should be expected after the early registration deadline, as staff support the event's execution.
Details about eligibility requirements and how to apply for press credentials are on the ACR website. For questions about the registration process or the press policies, email pr@rheumatology.org.
###
About ACR Convergence
ACR Convergence, the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology, is where rheumatology meets to collaborate, celebrate, congregate, and learn. With hundreds of sessions and thousands of abstracts, it offers a superior combination of basic science, clinical science, business education and interactive discussions to improve patient care and advance the specialty. For more information about the meeting, visit https://rheumatology.org/annual-meeting, or join the conversation on X by following the official hashtag (#ACR24).
About the American College of Rheumatology
Founded in 1934, the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) is a not-for-profit, professional association committed to advancing the specialty of rheumatology that serves 9,100 physicians, health professionals, researchers and scientists worldwide. In doing so, the ACR offers education, research, advocacy and practice management support to help its members continue their innovative work and provide quality patient care. Rheumatology professionals are experts in the diagnosis, management and treatment of more than 100 different types of arthritis and rheumatic diseases. For more information, visit rheumatology.org.
END
American College of Rheumatology opens press registration for ACR Convergence 2024
2024-08-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Half a billion-year-old spiny slug reveals the origins of mollusks
2024-08-01
UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL 19:00 BST / 14:00 ET THURSDAY 1 AUGUST 2024
Images available via link in the notes section
Exceptional fossils with preserved soft parts reveal that the earliest molluscs were flat, armoured slugs without shells.
The new species, Shishania aculeata was covered with hollow, organic, cone-shaped spines.
The fossils preserve exceptionally rare detailed features which reveal that these spines were produced using a sophisticated secretion system that is shared with annelids (earthworms and relatives).
A team of researchers including scientists from the University of Oxford have made an astonishing discovery of ...
Award-winning research maps the body’s internal sensory communication highway
2024-08-01
When the question is “how are you feeling on the inside?,” it’s our vagus nerve that offers the answer.
But how does the body’s longest cranial nerve, running from brain to large intestine, encodes sensory information from the visceral organs? For his work investigating and mapping this internal information highway, Qiancheng Zhao is the 2024 grand prize winner of the Science & PINS Prize for Neuromodulation.
Interoception—the body’s ability to sense its internal state in a timely and precise manner—facilitated by the vagus plays a key role in respiratory, gastrointestinal, cardiovascular, endocrine and immune ...
Current Andean glacier loss is unprecedented in the Holocene
2024-08-01
Andean tropical glaciers are experiencing unprecedented retreat, according to a new study that reveals their current sizes are the smallest in over 11,700 years. “Our finding … identifies this region as a hot spot in our understanding of the changing state of the cryosphere,” say the authors. Glaciers act as important indicators of climate change, with their global retreat accelerating over recent decades. Examining this retreat in the context of the previous 11,700 years of the Holocene interglacial highlights the impact of modern global warming. Although many glaciers worldwide are smaller today compared to ...
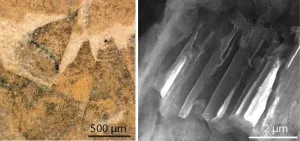
New fossil resembling a bristly durian fruit reveals insights into the origin of molluscan skeletons
2024-08-01
The early evolution of mollusks has been hard to pin down, but now a newly discovered fossil – of a shell-less, soft-bodied, spiny mollusk from the early Cambrian – provides crucial insights, researchers report. The findings suggest that this fossil, of a creature called Shishania aculeata, is a stem mollusk – representative of an intermediate between early members of the superphylum lophotrochozoans and more derived mollusks. Mollusks are one of the most diverse groups of animals, encompassing various well-known forms such as clams, ...
CLEAR: a new approach to 3D printing materials with highly entangled polymer networks
2024-08-01
Researchers have developed a novel approach to three-dimensional (3D) printing they call “CLEAR,” which significantly improves the strength and durability of materials by using a combination of light and dark chemical reactions to create densely entangled polymer chains. The authors used their approach to print structures with special features, such as the ability to adhere to wet tissues. Incorporation of polymer chain entanglements as reinforcements within 3D printed materials can significantly enhance their mechanical properties. However, traditional vat photopolymerization-based 3D printing techniques, such as digital ...
Genetic insights into how prickles develop across different plants, despite evolutionary separation
2024-08-01
The evolutionary gain and loss of plant prickles – sharp pointed epidermal outgrowths – are controlled by a shared genetic program involving cytokinin biosynthesis, researchers report. The study sheds light on the genetic basis of the emergence of similar traits in distantly related organisms and reveals genomic targets for prickle removal for crop improvement. The genetic basis of trait convergence is a central question in evolutionary biology, and the extent to which it is driven by ...
Climate anomalies may play a major role in driving cholera pandemics
2024-08-01
New research suggests that an El Niño event may have aided the establishment and spread of a novel cholera strain during an early 20th-century pandemic, supporting the idea that climate anomalies could create opportunities for the emergence of new cholera strains. Xavier Rodo of Instituto de Salud Global de Barcelona, Spain, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases.
Since 1961, more than 1 million people worldwide have died in an ongoing cholera pandemic, the seventh cholera ...
Study shows link between asymmetric polar ice sheet evolution and global climate
2024-08-01
Recent joint research led by Professor AN Zhisheng from the Institute of Earth Environment of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has revealed the pivotal role of the growth of the Antarctic ice sheet and associated Southern Hemisphere sea ice expansion in triggering the mid-Pleistocene climate transition (MPT). It has also shown how asymmetric polar ice sheet evolution affects global climate.
The MPT refers to a shift in Earth’s climate system between about ~1.25–0.7 million years ago, marking a shift to more pronounced and regular ...
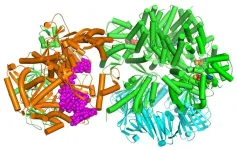
When it comes to DNA replication, humans and baker’s yeast are more alike than different
2024-08-01
GRAND RAPIDS, Mich. (Aug. 1, 2024) — Humans and baker’s yeast have more in common than meets the eye, including an important mechanism that helps ensure DNA is copied correctly, reports a pair of studies published in the journals Science and Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The findings visualize for the first time a molecular complex — called CTF18-RFC in humans and Ctf18-RFC in yeast — that loads a “clamp” onto DNA to keep parts of the replication machinery from falling off the DNA strand.
It is the latest discovery from longtime collaborators Huilin Li, Ph.D., of Van Andel Institute, ...
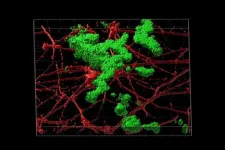
Aging-related genomic culprit found in Alzheimer’s disease
2024-08-01
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have developed a way to capture the effects of aging in the development of Alzheimer’s disease. They have devised a method to study aged neurons in the lab without a brain biopsy, an advancement that could contribute to a better understanding of the disease and new treatment strategies.
The scientists transformed skin cells taken from patients with late-onset Alzheimer’s disease into brain cells called neurons. Late-onset Alzheimer’s ...