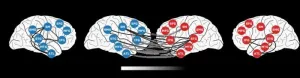
(Press-News.org) When two people interact, their brain activity becomes synchronized, but it was unclear until now to what extent this “brain-to-brain coupling” is due to linguistic information or other factors, such as body language or tone of voice. Researchers report August 2 in the journal Neuron that brain-to-brain coupling during conversation can be modeled by considering the words used during that conversation, and the context in which they are used.
“We can see linguistic content emerge word-by-word in the speaker’s brain before they actually articulate what they're trying to say, and the same linguistic content rapidly reemerges in the listener’s brain after they hear it,” says first author and neuroscientist Zaid Zada (@zaidzada) of Princeton University.
To communicate verbally, we must agree on the definitions of different words, but these definitions can change depending on the context. For example, without context, it would be impossible to know whether the word “cold” refers to temperature, a personality trait, or a respiratory infection.
“The contextual meaning of words as they occur in a particular sentence, or in a particular conversation, is really important for the way that we understand each other,” says neuroscientist and co-senior author Samuel Nastase (@samnastase) of Princeton University. “We wanted to test the importance of context in aligning brain activity between speaker and listener to try to quantify what is shared between brains during conversation.”
To examine the role of context in driving brain coupling, the team collected brain activity data and conversation transcripts from pairs of epilepsy patients during natural conversations. The patients were undergoing intracranial monitoring using electrocorticography for unrelated clinical purposes at the New York University School of Medicine Comprehensive Epilepsy Center. Compared to less invasive methods like fMRI, electrocorticography records extremely high-resolution brain activity because electrodes are placed in direct contact with the surface of the brain.
Next, the researchers used the large language model GPT-2 to extract the context surrounding each of the words used in the conversations, and then used this information to train a model to predict how brain activity changes as information flows from speaker to listener during conversation.
Using the model, the researchers were able to observe brain activity associated with the context-specific meaning of words in the brains of both speaker and listener. They showed that word-specific brain activity peaked in the speaker’s brain around 250 ms before they spoke each word, and corresponding spikes in brain activity associated with the same words appeared in the listener’s brain approximately 250 ms after they heard them.
Compared to previous work on speaker–listener brain coupling, the team’s context-based approach model was better able to predict shared patterns in brain activity.
“This shows just how important context is, because it best explains the brain data,” says Zada. “Large language models take all these different elements of linguistics like syntax and semantics and represent them in a single high-dimensional vector. We show that this type of unified model is able to outperform other hand-engineered models from linguistics.”
In the future, the researchers plan to expand on their study by applying the model to other types of brain activity data, for example fMRI data, to investigate how parts of the brain not accessible with electrocorticography operate during conversations.
“There's a lot of exciting future work to be done looking at how different brain areas coordinate with each other at different timescales and with different kinds of content,” says Nastase.
###
This research was supported by the National Institutes of Health.
Neuron, Zada et al., “A shared model-based linguistic space for transmitting our thoughts from brain to brain in natural conversations” https://cell.com/neuron/fulltext/S0896-6273(24)00460-4
Neuron (@NeuroCellPress), published by Cell Press, is a bimonthly journal that has established itself as one of the most influential and relied upon journals in the field of neuroscience and one of the premier intellectual forums of the neuroscience community. It publishes interdisciplinary articles that integrate biophysical, cellular, developmental, and molecular approaches with a systems approach to sensory, motor, and higher-order cognitive functions. Visit http://www.cell.com/neuron. To receive Cell Press media alerts, contact press@cell.com.
END
About The Study: The number of prescriptions filled for semaglutide has increased substantially, reaching 2.6 million prescriptions filled at retail pharmacies by December 2023. While Ozempic persistently accounted for most semaglutide fills, increases were considerably greater for Wegovy since its approval for weight loss in June 2021. These increases, which primarily occurred following increased awareness of weight-loss benefits in late 2022, are likely contributing to the FDA-reported shortage of Ozempic and Wegovy first issued in March 2022. Despite the disproportionate burden of obesity in Medicaid and Medicare Part D populations, and recent increases in public spending ...
About The Study: This qualitative study found that semaglutide products are actively being sold without prescription by illegal online pharmacies, with vendors shipping unregistered and falsified products. Two websites evaluated were sent FDA warning letters for unlawful sale of unapproved and misbranded semaglutide. U.S. poison centers have reported a 1500% increase in calls related to semaglutide, highlighting the need for enhanced pharmacovigilance including for online sourcing harms.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Tim K. Mackey, MAS, PhD, email tkmackey@ucsd.edu.
To ...
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that for older adults with diabetes, maintaining hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) stability in individualized target ranges over time is associated with a lower risk of Alzheimer disease and related dementias. Lower HbA1c time in range may identify patients at increased risk of Alzheimer disease and related dementias.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Paul R. Conlin, MD, email paul.conlin@va.gov.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this ...
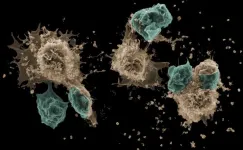
Inflammation is the body's response to harmful stimuli, characterized by heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of tissue function. When balanced, inflammation protects the body by clearing harmful agents and initiating tissue repair. However, excessive inflammation can cause tissue destruction and disease. Key players in this process are various immune cells, which work together during inflammation. The type of immune cells involved often varies depending on the harmful stimulus, influencing the outcome of the inflammatory response.
Immune cell trapping during allergic responses
Mast cells, residing in tissues and critical for initiating ...
A new USC study suggests that publicly insured individuals who are most likely to benefit from new drugs for diabetes and obesity are less likely to get them than those with private insurance.
Prescription fills for the drug best known as Ozempic or Wegovy — semaglutide — increased by more than 400% between January 2021 and December 2023, according to research out today in JAMA Health Forum.
Approved first for type 2 diabetes, then for weight loss, studies show that semaglutide also improves blood pressure and reduces cardiovascular disease — problems that plague millions of Americans. Yet the lion’s share of prescriptions ...
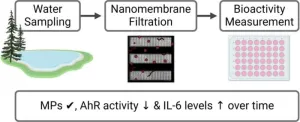
A new study reveals the bioactivity of microplastics in Lake Ontario using cutting-edge nanomembrane filtering technology. Researchers found all samples contained microplastics ranging between 8 and 20 µm. The study highlights varying bioactivity levels, such as aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) activity and IL-6 levels, indicating potential health risks. These findings underscore the urgent need for further research to comprehend the impact of microplastics on human health and the environment. This pioneering approach offers fresh insights into tackling the challenges posed by microplastic pollution.
Microplastics ...
The origins of life remain a major mystery. How were complex molecules able to form and remain intact for prolonged periods without disintegrating? A team at ORIGINS, a Munich-based Cluster of Excellence, has demonstrated a mechanism that could have enabled the first RNA molecules to stabilize in the primordial soup. When two RNA strands combine, their stability and lifespan increase significantly.
In all likelihood, life on Earth began in water, perhaps in a tide pool that was cut off from seawater at low tide but flooded by waves at high tide. Over billions of years, complex molecules like DNA, RNA and proteins ...
Why does the universe contain matter and (virtually) no antimatter? The BASE international research collaboration at the European Organisation for Nuclear Research (CERN) in Geneva, headed by Professor Dr Stefan Ulmer from Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf (HHU), has achieved an experimental breakthrough in this context. It can contribute to measuring the mass and magnetic moment of antiprotons more precisely than ever before – and thus identify possible matter-antimatter asymmetries. BASE has developed a trap, which can cool individual antiprotons much more rapidly ...
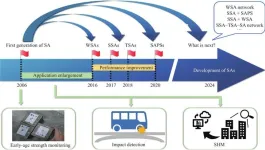
The proliferation of concrete infrastructure worldwide has been met with growing concerns over its durability and safety. Concrete structures are increasingly subjected to dynamic forces from natural disasters like earthquakes and environmental degradation, such as corrosion. These factors, coupled with the saturation of infrastructure projects, amplify the risks associated with structural failure. Consequently, there is a pressing need for effective structural health monitoring (SHM) systems that can preemptively identify and address these vulnerabilities. The ...
In recent years, microwave technology has dramatically progressed, marked by the arrival of the 5G era, owing to the advantages of electromagnetic waves in long-distance, wireless, and high-speed transmissions. However, electromagnetic wave pollution problems such as electromagnetic wave interference and electromagnetic wave radiation are becoming increasingly serious. Electromagnetic wave pollution not only affects the normal operation of electronic equipment, greatly threatens the information security of the scientific community, but also endangers human health and is a possible cause of cancer ...