(Press-News.org) More than 1 in 5 Californians who are impacted by climate events report negative effects on their mental health, with young, white women and those who’ve experienced property damage being especially affected.
####
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/climate/article?id=10.1371/journal.pclm.0000387
Article Title: Exposure to climate events and mental health: Risk and protective factors from the California Health Interview Survey
Author Countries: United States
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work.
END
More than 1 in 5 Californians who are impacted by climate events report negative effects on their mental health
2024-08-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New compound effective against flesh-eating bacteria
2024-08-02
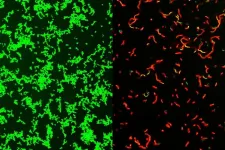
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have developed a novel compound that effectively clears bacterial infections in mice, including those that can result in rare but potentially fatal “flesh-eating” illnesses. The compound could be the first of an entirely new class of antibiotics, and a gift to clinicians seeking more effective treatments against bacteria that can’t be tamed easily with current antibiotics.
The research is published Aug. 2 in Science Advances.
The compound targets gram-positive bacteria, which can cause drug-resistant staph infections, toxic shock syndrome and ...
We should think twice before calling 911 for people experiencing a mental health crisis, advocated Harvard-trained psychiatrist Dr. Rupinder Legha
2024-08-02
We should think twice before calling 911 for people experiencing a mental health crisis, advocated Harvard-trained psychiatrist Dr. Rupinder Legha, who describes the potential risks of relying on emergency services in the US for mental health crisis management.
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/mentalhealth/article?id=10.1371/journal.pmen.0000084
Article Title: Reconsidering calling 911: Is it time to set a new standard for mental health crisis response?
Author Countries: United States
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
Coinfecting viruses impede each other’s ability to enter cells
2024-08-02
The process by which phages—viruses that infect and replicate within bacteria—enter cells has been studied for over 50 years. In a new study, researchers from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and Texas A&M University have used cutting-edge techniques to look at this process at the level of a single cell.
“The field of phage biology has seen an explosion over the last decade because more researchers are realizing the significance of phages in ecology, evolution, and biotechnology,” said Ido Golding (CAIM/IGOH), a professor of physics. “This work is unique ...
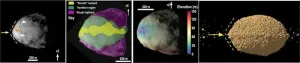
DART forward: Five papers shed new light on asteroids from world’s first planetary defense test
2024-08-02
In the months that followed NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) mission, which sent a spacecraft to intentionally collide with an asteroid moonlet, the science team verified that kinetic impact was a viable deflection technique, proving one effective method of preventing future asteroid strikes on Earth.
Since then, researchers have continued studying data collected from the successful experiment, focusing specifically on surface features of the binary asteroid system, composed of moonlet Dimorphos and parent asteroid Didymos.
In recently published papers in Nature Communications, the team explored the geology of the asteroid system encountered in 2022 to characterize its ...
Feeling judged by your doctor? You might be right
2024-08-02
When an individual visits their doctor, they aren’t supposed to keep secrets. Unless patients are forthcoming about their symptoms, behaviors, and health-related beliefs, it’s hard for healthcare professionals to effectively diagnose and treat illnesses—or to advise and educate patients about how to take better care of themselves in the future.
There’s only one problem: new research from Stevens Institute of Technology shows that many people believe they may be judged if they share mistaken beliefs with their care team—and that doctors really do take strongly negative views of patients who disclose incorrect ...
nTIDE July 2024 Jobs Report: People with disabilities hold steady in labor market despite federal reserve's attempts to slow economy
2024-08-02
East Hanover, NJ – August 2, 2024 – Following significant gains since the post-pandemic lockdown, employment rates for people with disabilities have plateaued, remaining near historic high levels over the past year despite the Federal Reserve’s efforts to slow the economy, according to today’s National Trends in Disability Employment – semi-monthly update (nTIDE) issued by Kessler Foundation and the University of New Hampshire’s Institute on Disability (UNH-IOD).
Year-to-Year nTIDE Numbers (comparing July 2023 to July 2024)
Based on data from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics ...
Dopamine physiology in the brain unveiled through cutting-edge brain engineering!
2024-08-02
□ DGIST (President Lee Kunwoo) Department of Brain Sciences Professor Lee Kwang and his team have discovered a new correlation between neural signaling in the brain and dopamine signaling in the striatum. The human brain requires fast neural signal processing in a short period of less than a second. Dopamine is known to have the strongest effect on brain neural signals, but the research team’s newly developed “optical neural chip-based multiple brain signal monitoring technology” shows that changes in dopamine signals within the physiological range do not affect brain neural signal ...
Precise package delivery in cells? Successful observation of endosome behavior provides new clues for disease treatment
2024-08-02
□ A team led by Professor Seo Dae-ha of the Department of Physics and Chemistry at DGIST (President Lee Kun-woo) has developed new real-time microscopy technology and successfully observed the behavior of “motor proteins”[1], which may hold the key to unraveling the efficient material transport strategy of cells. The research team used nanoparticle probe, high-resolution microscopy, and Fourier transform algorithm technologies to develop “Fourier transform-based plasmonic dark-field microscopy” (FT-pdf microscopy) with positional and angular accuracy comparable to electron microscopy, achieving the highest level of existing ...
Sustainable green energy innovation! Development of new technology for energy device that heals itself from damage incurred while generating electricity
2024-08-02
□ A team led by Professor Lee Joo-hyuk of the Department of Energy Engineering at DGIST (President Lee Kunwoo) has developed an ionic polyurethane-based triboelectric generator[1]with self-healing, biodegradable[2], and high electro-positive properties. The device has been designed as a green energy device that can minimize the impact on the environment by facilitating self-healing and biodegradability, while significantly enhancing power output performance through the use of ionic liquid. Based on these properties, it is expected to be used as a sustainable power source in next-generation soft electronic devices and wearable devices.
- ...
White Matter May Aid Recovery From Spinal Cord Injuries: Study
2024-08-02
Injuries, infection and inflammatory diseases that damage the spinal cord can lead to intractable pain and disability. Some degree of recovery may be possible. The question is, how best to stimulate the regrowth and healing of damaged nerves.
At the Vanderbilt University Institute of Imaging Science (VUIIS), scientists are focusing on a previously understudied part of the brain and spinal cord — white matter. Their discoveries could lead to treatments that restore nerve activity through the targeted delivery of electromagnetic stimuli or drugs.
As in the brain, the spinal cord is made up nerve cell bodies (gray matter), which process sensation and control voluntary movement, and ...