(Press-News.org) The failure to co-ordinate legal, policy and scientific thinking risks “a squandering of opportunity” to improve air quality, concludes new environmental law research, co-led by a UCL academic.
In their Science paper, ‘Harnessing science, policy and law to deliver clean air’, Professors Eloise Scotford (UCL Faculty of Laws), Alastair Lewis (University of York) and Delphine Misonne (UCLouvain Saint-Louis, Brussels) review recent research and highlight significant risks to achieving clean air globally.
Despite significant achievements in air quality law and policy in some parts of the world in recent decades, scientific evidence points to health harms arising from air pollution at ever-lower concentrations, making clean air increasingly urgent yet ever more difficult to achieve.
Research shows that, for many national regulatory regimes, elevating the ambition of air-quality policies and outcomes is not just a matter of increasing legal standards to the level of World Health Organisation Air Quality Guidelines.
Recognising this complexity, the researchers highlight the need to shift from policy ambition to policy deliverability, through the agile integration of scientific, policymaking and legal knowledge.
“Once-in-a-generation transitions, if not accompanied by a consideration of the air quality impacts, and a coordinated regulatory refresh, could lead to a squandering of opportunity,” they say in their paper.
The researchers point to several areas where co-ordinated action is needed: around setting standards; deciding which pollutants to legislate for; setting targets to reduce pollution as well as for it not to exceed certain levels; urban planning including considering the impact of air pollution on deprived communities and minority ethnic groups; and co-ordinating policymaking at a local, national and supranational level.
One of these issues – deciding which pollutants to regulate – concerns the fact that a relatively small number of pollutants have been the focus of air quality laws for the past four decades, but these may need expanding to better represent the current state of the science in terms of toxicology and harms.
The problem, they say, is that “legally embedded standards are generally only created when the scientific evidence of harms is considered compelling by lawmakers”, leading to “criteria pollutants” such as the very fine particles known as PM2.5 being commonly regulated today. Being cheap and easy to measure, PM2.5 has become the “de facto variable” in health studies, they say.
But they add that: “There is likely merit in limit values for black carbon, ultrafine particles, formaldehyde or subcomponents of Particulate Matter such as secondary organic aerosol; however, each has yet to accumulate weight of evidence to become legal obligations.”
To help counter this bias, the researchers are calling for “exploratory” air-pollution observations, following the precautionary principle, “ideally” coupled with research funding to incentivise them.
Another key issue in ensuring that clean air policies are deliverable and delivered is the coordination of policymaking.
The benefits of reducing air pollution and climate emissions have “long been articulated by the scientific community, but there is an under-recognised need for legal and regulatory coordination as well”, the researchers say in their paper.
They cite the example of low-carbon fuels for aviation, saying that carbon regulation alone “does not guarantee better air quality”.
Climate commitment for the adoption of low-carbon fuels can only succeed in reducing pollution if there are “parallel, internationally agreed regulatory requirements for reduced engine emissions of nitrogen oxide and Particulate Matter”, they say.
In their conclusion to their paper, the researchers say: “To move the debate forward, we argue that growing the space for dynamic regulatory development at the science-law-policy interface is an important avenue for accelerating the delivery of global clean-air goals.”
Ends
For more information or to speak to the researchers, please contact Nick Hodgson, UCL Media Relations. +44 (0)7769 240209 / nick.hodgson@ucl.ac.uk
END
Air quality regimes around the world are playing catch up as science evolves and policy ambitions are too blunt, researchers say
Peer reviewed / Literature review
2024-08-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Engineers develop general, high-speed technology to model, understand catalytic reactions
2024-08-05
AMES, Iowa – Researchers have been studying the industrial production of ammonia for a century. But they’ve struggled to find ways to improve the low-yield, low-efficiency process.
Atmospheric nitrogen, with the aid of an iron catalyst, reacts with hydrogen to produce ammonia. That reaction produces lots of ammonia – worldwide production is 160 million tons every year. Most is used in agriculture, especially as nitrogen fertilizer. It’s also used in many industries, including refrigeration ...
New $1.9 million PSU grant aims to improve outcomes for students with disabilities
2024-08-05
Improving outcomes for students with disabilities as they transition from high school to postsecondary education and employment starts with effective training and development opportunities for the secondary educators who support them.
Portland State University (PSU) has received a $1.9 million grant to redesign, implement and test a professional development model that aims to provide essential training for secondary educators. The grant, awarded by the U.S. Department of Education’s prestigious Institute of Education Sciences, will fund a four-year project titled "Transition Coalition Self-Study Plus (TCSS+): A ...
In law enforcement, a link between head injuries and depression, PTSD
2024-08-05
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A new study is the first to shed light on the high prevalence of head injuries, and related mental health symptoms, in a previously overlooked population when it comes to concussion surveillance: law enforcement officers.
The survey of Ohio law enforcement officers found that 74% reported a lifetime history of one or more head injuries, and 30% had a head injury that happened on the job. Many more of these injuries went unreported than were treated by a health care professional. And further analysis showed post-traumatic stress disorder and depressive symptoms were higher in those who had experienced one or more head injuries.
“This ...
Successful pregnancies after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation – results of a national study
2024-08-05
A new national multicenter study offers hope for women who have undergone allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (alloHCT). The results of the study, recently published in the renowned journal Blood, show that successful pregnancies are possible under certain conditions, especially in younger women, patients with non-malignant diseases, and those who received no or only low doses of total body irradiation (TBI).
For many benign hematologic disorders, allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (alloHCT) is the only ...
Sanders-Brown Center on Aging launches innovative Brain Health Activities program
2024-08-05
LEXINGTON, Ky. (Aug. 2, 2024) – The University of Kentucky’s Sanders-Brown Center on Aging has introduced a groundbreaking initiative, Brain Health Activities, aimed at supporting individuals with dementia and their caregivers. The program was developed with extensive collaboration across the UK campus, offering a variety of resources designed to enhance brain health and quality of life for those affected by dementia and their caregivers.
The idea for ...
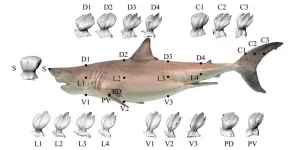
Nature's design marvel: How shark skin's denticles adapt to wide speed
2024-08-05
New findings on how sharks achieve drag reduction could inspire the design of riblets for more efficient aircraft and boats. In their investigation of great white shark denticles, researchers from Tokyo Tech found that ridge height and spacing play crucial roles in drag reduction at different swimming speeds. Higher middle ridges aid sharks in efficient cruising at slower speeds, while the lower side ridges become more critical for drag reduction during high-speed hunting bursts. The analysis also suggests that the speeds of an extinct giant ...
Ultrafine particles linked to over 1,000 deaths per year in Canada’s two largest cities
2024-08-05
A first-of-its kind study conducted in Canada’s two largest cities by McGill-led researchers has linked about 1,100 premature deaths per year to an unregulated air pollutant.
Ultrafine particles (UFPs) primarily come from vehicle emissions and industrial activities. Canada’s federal and provincial governments have not set concentration limits for UFPs, as they have for larger fine particles known as PM2.5.
“Ultrafine particles are incredibly small, allowing them to penetrate deep into the lungs and enter the bloodstream. Increasing evidence suggests these pollutants may contribute to heart and lung diseases, as well as certain forms of cancer,” ...
Physicists develop new method to combine conventional internet with the quantum internet
2024-08-05
Four researchers from the Institute of Photonics at Leibniz University Hannover have developed a new transmitter-receiver concept for transmitting entangled photons over an optical fiber. This breakthrough could enable the next generation of telecommunications technology, the quantum Internet, to be routed via optical fibers. The quantum Internet promises eavesdropping-proof encryption methods that even future quantum computers cannot decrypt, ensuring the security of critical infrastructure.
"To make the quantum Internet a reality, we need to transmit entangled photons via fiber optic networks,” says Prof. Dr. Michael Kues, Head of the Institute ...
Don't drink raw milk. But what about raw milk cheese? (video)
2024-08-05
WASHINGTON, Aug. 5, 2024 — A lot of people on the internet have been telling our host Alex to drink raw milk. This is a bad idea — a particularly bad one actually. So she wanted to make a video about why it’s such a bad idea to consume raw milk, then she realized she’s been eating raw milk without even knowing it via cheese. That’s when things got complicated.
Reactions is a video series produced by the American Chemical Society and PBS Digital Studios. Subscribe to Reactions and follow us on X, formerly Twitter @ACSReactions.
The American Chemical Society ...
Does transparency help or hurt businesses dominated by one-time transactions
2024-08-05
DALLAS (SMU) – It’s a relevant question for business owners with few repeat customers, such as contract workers or real estate agents: Does being transparent about past business transactions change the odds of making a sale that benefits both buyer and seller?
The answer matters because mutually beneficial sales ensure that these kinds of transactions will continue, keeping the economy strong.
A new study published in the journal American Economic Review suggests the answer depends on a variety of factors.
A mutually beneficial sale is defined from two points of view: The seller values the money they receive more than ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
[Press-News.org] Air quality regimes around the world are playing catch up as science evolves and policy ambitions are too blunt, researchers sayPeer reviewed / Literature review