(Press-News.org) DALLAS (SMU) – It’s a relevant question for business owners with few repeat customers, such as contract workers or real estate agents: Does being transparent about past business transactions change the odds of making a sale that benefits both buyer and seller?
The answer matters because mutually beneficial sales ensure that these kinds of transactions will continue, keeping the economy strong.
A new study published in the journal American Economic Review suggests the answer depends on a variety of factors.
A mutually beneficial sale is defined from two points of view: The seller values the money they receive more than the service they offer, because the price adequately reflects the time and resources needed for that task. Meanwhile, the buyer is satisfied that they received the value they were seeking for the price they paid to acquire it.
This is known by economists as market efficiency – there are no missed opportunities to make a sale from which both the seller and buyer would benefit.
Research from economists at SMU and the University of Miami demonstrates that being transparent about a high volume of past transactions improves market efficiency when a seller has the potential to earn high profits due to the high number of buyers competing to obtain their services. Examples include companies that provide specialized services, like lawyers, accountants or skilled technicians.
Buyers with no previous experience with a seller can observe how frequently the seller has conducted similar transactions and “indirectly infer some of the hidden information about a seller’s quality or the value the seller can create,” explained study co-author Santanu Roy, University Distinguished Professor of Economics at SMU.
But the situation flips when the market power shifts – when there are more sellers than buyers, Roy and his fellow researcher Ayça Kaya, an associate professor of economics at the University of Miami, determined. “It’s actually much worse when buyers observe previously sold quantities,” Roy said.
The reason? In these markets, sellers are more likely to heavily discount their services to get new buyers.
Roy said these and other study findings give useful guidance on regulation and design of markets where business owners can’t count on repeat customers.
“Should we encourage maintaining reliable records of individual market transactions and making some of this information publicly available to new market participants in the future? The paper provides a nuanced answer to this, one that depends on market competition and fundamentals,” Roy said. “Ignoring these factors can make matters much worse.”
To analyze whether such businesses benefited from transparency with their past sales, economists Kaya and Roy used what’s known as a dynamic game theoretic model with incomplete information.
These models allow economists to factor in multiple parties, when one’s outcome may depend on the actions of others. Essentially, they created an artificial world through complex mathematical equations that was simpler than the real world, yet allowed them to make some insights into what would happen in real-life.
“We assumed that the seller encountered a new cohort of buyers every period and we then compared the outcome of a transparent market (new buyers could access reliable records of the frequency or volume of past trading by this seller) with that of an opaque market (buyers had no information about past trading),” Roy said.
Two main things were looked at: how much competition a seller might face and whether buyers were optimistic or pessimistic about the quality of what was being sold.
In this study, the researchers only looked at sellers making the number of past transactions available to buyers, not how much they charged for items, Roy noted.
About SMU
SMU is the nationally ranked global research university in the dynamic city of Dallas. SMU’s alumni, faculty and more than 12,000 students in eight degree-granting schools demonstrate an entrepreneurial spirit as they lead change in their professions, communities and the world.
END
Does transparency help or hurt businesses dominated by one-time transactions
2024-08-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Insufficient evidence to recommend low-dose CT screening in never smokers lung cancer screening: new insights and ongoing debates
2024-08-05
(Denver, Colo.—August 5, 2024) – Lung cancer remains the leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. Detecting this disease in its early stages significantly improves survival rates, making low-dose CT screening an essential component in the fight against lung cancer. Recent studies, particularly from Asia, have sparked a debate on whether these screening benefits extend to non-smokers and those with minimal smoking histories.
However, according to an article published in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology, there is currently insufficient evidence to support ...
Early childhood screen use contexts and cognitive and psychosocial outcomes
2024-08-05
About The Study: The findings of this study show small to moderate effect sizes that highlight the need to consider screen use contexts (i.e., type, content, co-use, and purpose of use) when making recommendations for families, clinicians, and educators beyond screen time limits; including encouraging intentional and productive screen use, age-appropriate content, and co-use with caregivers.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Sumudu Mallawaarachchi, PhD, email sumudu@uow.edu.au.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2024.2620)
Editor’s ...
COVID-19 pandemic school disruptions and acute mental health in children and adolescents
2024-08-05
About The Study: In this cross-sectional study of 13,000 pediatric emergency department visits at nine university hospitals in Italy, school opening following a COVID-19 pandemic–related school disruption was associated with an increase in acute psychiatric emergencies. The findings of this study suggest that school may be a major source of stress for youths; factors mediating school-associated mental health disturbances in youth should be investigated.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Benedetto Vitiello, ...
Estimated exposure to 6 potentially hepatotoxic botanicals in U.S. adults
2024-08-05
About The Study: In this survey study, an estimated 15.6 million U.S. adults consumed at least one botanical product with liver liability within the past 30 days, comparable with the number of people who consumed nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and a commonly prescribed hypolipidemic drug. Turmeric was most frequently reported, followed in order by green tea, ashwagandha, Garcinia cambogia, red yeast rice, and black cohosh products. Given a lack of regulatory oversight on the manufacturing and testing of botanical products, clinicians should be aware of possible adverse events from consumption of ...
Expanding student-journalists' access to EurekAlert!
2024-08-05
In an effort to give aspiring journalists hands-on practice in the science news ecosystem and help prepare them for a successful professional career, EurekAlert! is expanding journalist-memberships to applicants working at student news publications, such as campus newspapers and radio stations.
EurekAlert! has historically granted journalist-memberships to full-time journalism students, interns, and fellowship recipients who work at accredited media outlets under the guidance of experienced members. All approved journalist-members receive the same access to embargoed materials.
"As the advisor to MIT's ...
Planting some tree species may worsen, not improve, NYC air, says new study
2024-08-05
In line with longstanding initiatives to expand its green spaces, New York City is planting tens of thousands of trees each year. They provide shade, lower surface temperatures by releasing moisture, absorb a surprising amount of airborne carbon, scrub out soot and other floating pollutants, and provide wildlife habitat along with just plain beauty. What could go wrong?
Actually, something could go wrong, according to a new study. Oaks and sweetgums, which currently account for a majority of the city’s trees, produce huge amounts of volatile compounds called isoprenes. Harmless by themselves, isoprenes interact rapidly with polluting nitrogen oxides emitted by vehicles, ...
Ben-Gurion University scientist uses state-of-the-art microscopy to discover drug candidates for cancer
2024-08-05
BEER-SHEVA, Israel, August 5, 2024 – Microscopy has been making leaps and bounds in recent years. Science that was inconceivable a few years ago has become a matter of programming state-of-the-art microscopes to process reams of data. Dr. Gabriel Frank quickly realized the potential of cryo-electron microscopy to discover the molecular structures at levels heretofore unobservable. When he joined Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, he pushed for the University to enter the field, culminating in the establishment of the Guzik Center for Advanced Microscopy and the purchase of a new more advanced electron microscope. Using this microscope, Dr. ...
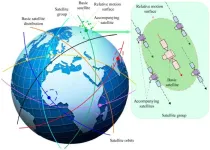
Configuration design method of mega constellation for low earth orbit observation
2024-08-05
First, satellites in the mega constellation are categorized and the constellation design based on different satellite division is proposed. Satellites in the mega constellation are divided into 2 types, namely, the basic satellites and the accompanying satellites. All basic satellites that are surrounded by accompanying satellites are evenly distributed globally, and they have the same subsatellite trajectory. A basic satellite and its accompanying satellites are defined as a satellite group. The constellation is composed ...
Sometimes it hurts to think
2024-08-05
If somebody complains that it hurts to think, they may be onto something, as mental exertion appears to be associated with unpleasant feelings in many situations, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
“Managers often encourage employees, and teachers often encourage students, to exert mental effort. On the surface, this seems to work well: Employees and students do often opt for mentally challenging activities,” said senior author Erik Bijleveld, PhD, of Radboud University. “From this, you may be tempted to conclude that ...
FAU lands $1.3M NSF grant to boost dryland soil quality amid climate stressors
2024-08-05
Drylands, found across every continent, cover about 45% of the Earth's land surface and support 38% of the human population. In these regions, precipitation is low and evaporation rates are typically high, leading to an arid or semi-arid climate. Due to scarce water resources and sparse vegetation, drylands present formidable challenges for agriculture and human habitation. As the climate continues to warm, drylands are rapidly expanding.
A particularly urgent problem in drylands is climate-driven soil degradation, which affects about 33% of the planet’s land surface.
Drylands host ...