(Press-News.org) About The Study: In this cross-sectional study of 13,000 pediatric emergency department visits at nine university hospitals in Italy, school opening following a COVID-19 pandemic–related school disruption was associated with an increase in acute psychiatric emergencies. The findings of this study suggest that school may be a major source of stress for youths; factors mediating school-associated mental health disturbances in youth should be investigated.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Benedetto Vitiello, MD, email benedetto.vitiello@unito.it.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.25829)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.25829?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=080524
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
COVID-19 pandemic school disruptions and acute mental health in children and adolescents
JAMA Network Open
2024-08-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Estimated exposure to 6 potentially hepatotoxic botanicals in U.S. adults
2024-08-05
About The Study: In this survey study, an estimated 15.6 million U.S. adults consumed at least one botanical product with liver liability within the past 30 days, comparable with the number of people who consumed nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and a commonly prescribed hypolipidemic drug. Turmeric was most frequently reported, followed in order by green tea, ashwagandha, Garcinia cambogia, red yeast rice, and black cohosh products. Given a lack of regulatory oversight on the manufacturing and testing of botanical products, clinicians should be aware of possible adverse events from consumption of ...
Expanding student-journalists' access to EurekAlert!
2024-08-05
In an effort to give aspiring journalists hands-on practice in the science news ecosystem and help prepare them for a successful professional career, EurekAlert! is expanding journalist-memberships to applicants working at student news publications, such as campus newspapers and radio stations.
EurekAlert! has historically granted journalist-memberships to full-time journalism students, interns, and fellowship recipients who work at accredited media outlets under the guidance of experienced members. All approved journalist-members receive the same access to embargoed materials.
"As the advisor to MIT's ...
Planting some tree species may worsen, not improve, NYC air, says new study
2024-08-05
In line with longstanding initiatives to expand its green spaces, New York City is planting tens of thousands of trees each year. They provide shade, lower surface temperatures by releasing moisture, absorb a surprising amount of airborne carbon, scrub out soot and other floating pollutants, and provide wildlife habitat along with just plain beauty. What could go wrong?
Actually, something could go wrong, according to a new study. Oaks and sweetgums, which currently account for a majority of the city’s trees, produce huge amounts of volatile compounds called isoprenes. Harmless by themselves, isoprenes interact rapidly with polluting nitrogen oxides emitted by vehicles, ...
Ben-Gurion University scientist uses state-of-the-art microscopy to discover drug candidates for cancer
2024-08-05
BEER-SHEVA, Israel, August 5, 2024 – Microscopy has been making leaps and bounds in recent years. Science that was inconceivable a few years ago has become a matter of programming state-of-the-art microscopes to process reams of data. Dr. Gabriel Frank quickly realized the potential of cryo-electron microscopy to discover the molecular structures at levels heretofore unobservable. When he joined Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, he pushed for the University to enter the field, culminating in the establishment of the Guzik Center for Advanced Microscopy and the purchase of a new more advanced electron microscope. Using this microscope, Dr. ...
Configuration design method of mega constellation for low earth orbit observation
2024-08-05
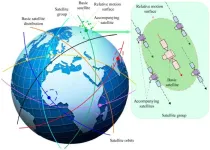
First, satellites in the mega constellation are categorized and the constellation design based on different satellite division is proposed. Satellites in the mega constellation are divided into 2 types, namely, the basic satellites and the accompanying satellites. All basic satellites that are surrounded by accompanying satellites are evenly distributed globally, and they have the same subsatellite trajectory. A basic satellite and its accompanying satellites are defined as a satellite group. The constellation is composed ...
Sometimes it hurts to think
2024-08-05
If somebody complains that it hurts to think, they may be onto something, as mental exertion appears to be associated with unpleasant feelings in many situations, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
“Managers often encourage employees, and teachers often encourage students, to exert mental effort. On the surface, this seems to work well: Employees and students do often opt for mentally challenging activities,” said senior author Erik Bijleveld, PhD, of Radboud University. “From this, you may be tempted to conclude that ...
FAU lands $1.3M NSF grant to boost dryland soil quality amid climate stressors
2024-08-05
Drylands, found across every continent, cover about 45% of the Earth's land surface and support 38% of the human population. In these regions, precipitation is low and evaporation rates are typically high, leading to an arid or semi-arid climate. Due to scarce water resources and sparse vegetation, drylands present formidable challenges for agriculture and human habitation. As the climate continues to warm, drylands are rapidly expanding.
A particularly urgent problem in drylands is climate-driven soil degradation, which affects about 33% of the planet’s land surface.
Drylands host ...
Self-powered pump harnesses light and chemistry to target, capture pollutants
2024-08-05
Dartmouth researchers have developed a self-powered pump that uses natural light and chemistry to target and remove specific water pollutants, according to a new report in the journal Science.
As water enters the pump, a wavelength of light activates a synthetic molecular receptor designed to bond to negatively charged ions, or anions, a class of pollutants linked to metabolic disruptions in plants and animals. A second wavelength deactivates the receptors as water exits the pump and causes them to release the ...
Heart transplant list doesn’t rank kids by medical need, Stanford Medicine-led study finds
2024-08-05
The method used across the United States to wait-list children for heart transplants does not consistently rank the sickest patients first, according to a new study led by Stanford Medicine experts.
The study will publish online Aug. 5 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Adding nuance to the wait-list system by accounting for more health factors could reduce children’s risk of dying while they await donor hearts, according to the study’s authors. A revision to the way donor hearts are assigned is already in process. The study adds evidence for why it is needed, they ...
Advancing towards a novel, highly accurate method for cervical cancer screening
2024-08-05
Cervical cancer is a highly prevalent cancer, with approximately 500,000 new cases diagnosed each year. Shockingly, the number of individuals diagnosed with precursor lesions in the cervix—also known as cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN)—is 20 times higher. As with many potentially malignant conditions, early diagnosis of cervical cancer can make all the difference in a patient’s life in terms of treatment outcomes. For this, developing effective, convenient, and easily available screening protocols for CIN and cervical cancer is of paramount importance.
Currently, the two ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
[Press-News.org] COVID-19 pandemic school disruptions and acute mental health in children and adolescentsJAMA Network Open