(Press-News.org) NEW ORLEANS, La. – Ochsner Health proudly announces that 21 Ochsner nurses have been named to the 2024 Great 100 Nurses of Louisiana list by the Great 100 Nurses Foundation. This recognition highlights the contributions and commitment to excellence demonstrated by Ochsner’s nursing staff.
The Great 100 Nurses Foundation was established to honor nurses in Louisiana, North Carolina, Texas and Oklahoma. Each year, the foundation selects 100 nurses throughout Louisiana based on their concern for humanity, contribution to nursing and mentoring of others.
“Being included among the Great 100 Nurses of Louisiana is a testament to the unwavering dedication and hard work these nurses exhibit daily. Their commitment to providing high-quality patient care sets a standard of excellence that resonates throughout our organization,” said Tiffany Murdock, senior vice president and chief nursing officer, Ochsner Health.
Congratulations to the following outstanding nurses:
Leonard J. Chabert Medical Center
Jana Semere, RN
Ochsner Baptist – A Campus of Ochsner Medical Center
Kimberly Route, RN
Megan Seay, RN
Ochsner Health Center – Elmwood
Paula Landry, RN
Ochsner Health Center for Children – New Orleans
Catina Gordon-Oates, RN
Ochsner LSU Health Shreveport – Academic Medical Center
David Dupree, RN
Susan Fourcade, RN
Betsy Harris, RN
Twala Hernandez, RN
Anthony Jenkins, RN
Krystal Player Jackson, RN
Ochsner LSU Health Shreveport – St. Mary Medical Center
Mary Gallagher, RN
Ochsner Medical Center – Baton Rouge
Carlos Williams, RN
Ochsner Medical Center – New Orleans
Toni Brousse, RN
Tracy Bynum, RN
Erin Goodrow, RN
Nicholle Scholl, RN
Ashley Wertz, RN
Ochsner St. Anne Hospital
Jamie Grayson, RN
Ochsner St. Mary
Sharon Terrebonne, RN
Float Pool
Denise Campbell, RN
Honorees will be celebrated at the Great 100 Nurses Celebration of Louisiana on October 16 at the Pontchartrain Center in Kenner. Nurses will be presented with accolades for their outstanding service and dedication to the nursing profession.
For more information about Ochsner and nursing careers, visit www.ochsner.org/nursing.
###
About Ochsner Health
Ochsner Health is the leading nonprofit healthcare provider in the Gulf South, delivering expert care at its 46 hospitals and more than 370 health and urgent care centers. For 13 consecutive years, U.S. News & World Report has recognized Ochsner as the No. 1 hospital in Louisiana. Additionally, Ochsner Children’s has been recognized as the No. 1 hospital for kids in Louisiana for three consecutive years. Ochsner inspires healthier lives and stronger communities through a combination of standard-setting expertise, quality and connection not found anywhere else in the region. In 2023, Ochsner Health cared for more than 1.5 million people from every state in the nation and 65 countries. Ochsner’s workforce includes more than 38,000 dedicated team members and over 4,700 employed and affiliated physicians. To learn more about how Ochsner empowers people to get well and stay well, visit https://www.ochsner.org/.
END
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. – August 5, 2024) Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T–cell immunotherapy re-engineers a patient’s immune cells to target cancer cells. While successful in some types of leukemia, the approach has yet to realize its potential against pediatric solid tumors. Scientists at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital have identified a way to improve CAR T–cell homing – a T cell’s ability to navigate effectively to a tumor – for osteosarcoma. Improved homing is a necessary step in designing more successful CAR T–cell therapies. The results were published today in Clinical Cancer ...
In Brazil, climate and other human-made environmental changes threaten decades-long efforts to fight a widespread and debilitating parasitic disease. Now, a partnership between researchers from Stanford and Brazil is helping to proactively predict these impacts.
Schistosomiasis, spread by freshwater snails, affects more than 200 million people in many tropical regions of the world. It can cause stomach pain and irreversible consequences such as enlarged liver and cancer. Public health officials worry that deforestation, rapid urban sprawl, and changing rainfall patterns – such as ...
Since the first immunotherapy drug to boost the body’s immune response against advanced lung cancer was introduced in the United States in 2015, survival rates of patients with the disease have improved significantly. That’s the conclusion of a recent real-world study published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
For the research, a team led by Dipesh Uprety, MD, FACP, of the Barbara Ann Karmanos Cancer Institute and the Wayne State University School of Medicine, analyzed data from the National Cancer Institute Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database, which compiles cancer-related data ...
The failure to co-ordinate legal, policy and scientific thinking risks “a squandering of opportunity” to improve air quality, concludes new environmental law research, co-led by a UCL academic.
In their Science paper, ‘Harnessing science, policy and law to deliver clean air’, Professors Eloise Scotford (UCL Faculty of Laws), Alastair Lewis (University of York) and Delphine Misonne (UCLouvain Saint-Louis, Brussels) review recent research and highlight significant risks to achieving clean air globally.
Despite significant achievements in air quality law and policy in some parts of the world ...
AMES, Iowa – Researchers have been studying the industrial production of ammonia for a century. But they’ve struggled to find ways to improve the low-yield, low-efficiency process.
Atmospheric nitrogen, with the aid of an iron catalyst, reacts with hydrogen to produce ammonia. That reaction produces lots of ammonia – worldwide production is 160 million tons every year. Most is used in agriculture, especially as nitrogen fertilizer. It’s also used in many industries, including refrigeration ...
Improving outcomes for students with disabilities as they transition from high school to postsecondary education and employment starts with effective training and development opportunities for the secondary educators who support them.
Portland State University (PSU) has received a $1.9 million grant to redesign, implement and test a professional development model that aims to provide essential training for secondary educators. The grant, awarded by the U.S. Department of Education’s prestigious Institute of Education Sciences, will fund a four-year project titled "Transition Coalition Self-Study Plus (TCSS+): A ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A new study is the first to shed light on the high prevalence of head injuries, and related mental health symptoms, in a previously overlooked population when it comes to concussion surveillance: law enforcement officers.
The survey of Ohio law enforcement officers found that 74% reported a lifetime history of one or more head injuries, and 30% had a head injury that happened on the job. Many more of these injuries went unreported than were treated by a health care professional. And further analysis showed post-traumatic stress disorder and depressive symptoms were higher in those who had experienced one or more head injuries.
“This ...
A new national multicenter study offers hope for women who have undergone allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (alloHCT). The results of the study, recently published in the renowned journal Blood, show that successful pregnancies are possible under certain conditions, especially in younger women, patients with non-malignant diseases, and those who received no or only low doses of total body irradiation (TBI).
For many benign hematologic disorders, allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (alloHCT) is the only ...
LEXINGTON, Ky. (Aug. 2, 2024) – The University of Kentucky’s Sanders-Brown Center on Aging has introduced a groundbreaking initiative, Brain Health Activities, aimed at supporting individuals with dementia and their caregivers. The program was developed with extensive collaboration across the UK campus, offering a variety of resources designed to enhance brain health and quality of life for those affected by dementia and their caregivers.
The idea for ...
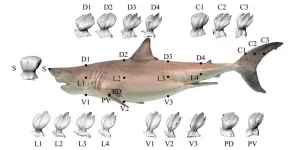
New findings on how sharks achieve drag reduction could inspire the design of riblets for more efficient aircraft and boats. In their investigation of great white shark denticles, researchers from Tokyo Tech found that ridge height and spacing play crucial roles in drag reduction at different swimming speeds. Higher middle ridges aid sharks in efficient cruising at slower speeds, while the lower side ridges become more critical for drag reduction during high-speed hunting bursts. The analysis also suggests that the speeds of an extinct giant ...