(Press-News.org) How would you summarize your study for a lay audience?
Some proteins, such as programmed cell death protein 1 (PD1), can stop the immune system from attacking cancer cells and, therefore, support the growth of cancer. Therapies targeting these proteins can be highly effective, but tumors can become resistant.
We applied a method to detect proteins on a single–cell level to uncover human carcinoembryonic antigen cell adhesion molecule 1 (CEACAM1) patterns in melanoma. We found that increased CEACAM1 expression levels on multiple different immune cell types was associated with tumors resistant to cancer therapy. This points us to a new potential target for therapy for patients with melanoma resistant to treatment.
What knowledge gaps does your study help to fill?
It is important for researchers to identify factors involved in anti-tumor resistance to develop effective cancer therapies. Previous research has revealed that CEACAM1 inhibits an immune response and its levels have been associated with poor patient outcomes.
How did you conduct your study and what did you find?
By using mass cytometry, we created and used a human CEACAM1-specific antibody to provide global insights into the potential cellular basis for CEACAM1’s immune role in melanoma, its association with the state of treatment and its expression relative to PD1 and PD-L1. We discovered that CEACAM1 is found on specific groups of immune cells (including subsets of B cells, monocytic cells, dendritic cells and T cells) in the tumor microenvironment and its presence is associated with treatment-resistant cancer.
What are the implications?
We now understand how CEACAM1 is connected to the immune system’s response to melanoma and how it compares to other proteins involved in immune regulation. Our work highlights CEACAM1 as a potential therapeutic target for melanoma patients whose tumors are resistant to other therapies, such as immune checkpoint inhibitors.
What are the next steps?
We are eager to understand the immune cell-type specific mechanisms by which CEACAM1 operates in the tumor microenvironment.
Paper cited: Huang, Y-H, Yoon, CH et al. “High-dimensional mapping of human CEACAM1 expression on immune cells and association with melanoma drug resistance.” Nature Communication Medicine DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s43856-024-00525-8
END
Research spotlight: Identifying potential new protein targets for melanoma therapeutics
2024-08-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Damon Runyon Cancer Research Foundation awards $5.2 million to top clinical investigators
2024-08-06
Damon Runyon Cancer Research Foundation awards $5.2 million to top clinical investigators
The Damon Runyon Cancer Research Foundation has named six new Damon Runyon Clinical Investigators. The recipients of this prestigious award are outstanding, early-career physician-scientists conducting patient-oriented cancer research at major research centers under the mentorship of the nation's leading scientists and clinicians.
The Clinical Investigator Award program was designed to increase the number of physicians capable of translating scientific discoveries into new treatments for cancer patients. Each Awardee will receive $600,000 over three years, ...
Good outcomes 10 years after surgery for ectopic bone in thoracic spine
2024-08-06
August 6, 2024 — Thoracic ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament (TOPLL) is a rare condition associated with ectopic bone formation in the thoracic spine. A long-term follow-up study from Japan shows significant and lasting improvement in outcomes with posterior decompression and fixation surgery for patients with T-OPLL, reports The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"Surgical treatment of T-OPLL is effective in improving neurological function, quality ...
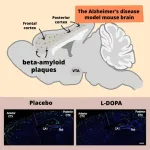
Dopamine treatment alleviates symptoms in Alzheimer’s disease
2024-08-06
A new way to combat Alzheimer’s disease has been discovered by Takaomi Saido and his team at the RIKEN Center for Brain Science (CBS) in Japan. Using mice with the disease, the researchers found that treatment with dopamine could alleviate physical symptoms in the brain as well as improve memory. Published in the scientific journal Science Signaling on August 6, the study examines dopamine’s role in promoting the production of neprilysin, an enzyme that can break down the harmful plaques in the brain that are the ...
Do your supplements contain potentially hepatoxic botanicals?
2024-08-06
Millions of Americans consume supplements that contain potentially hepatoxic botanical ingredients, according to a study from University of Michigan researchers.
Over a 30-day period, 4.7% of the adults surveyed in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey conducted from 2017 to 2020 took herbal and dietary supplements containing at least one of the botanicals of interest: turmeric; green tea; ashwagandha; black cohosh; garcinia cambogia; and red yeast rice containing products.
The resulting paper, “Estimated Exposure ...
No room for nuance in polarized political climate: SFU study
2024-08-06
Sometimes you just can’t win, and that goes double for people navigating the increasingly polarized political landscape in the United States.
Having nuanced opinions of politics in the U.S. turns out to be a very lonely, and unpopular, road, according to a recent study from a research team that includes assistant professor Aviva Phillipp-Muller from Simon Fraser University’s Beedie School of Business.
Published in the Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, the study found that people who express ambivalence about political topics – ranging from COVID-19 mask mandates, immigration and the death ...
What happens to your brain when you drink with friends?
2024-08-06
EL PASO, Texas (Aug. 6, 2024) – Grab a drink with friends at happy hour and you’re likely to feel chatty, friendly and upbeat. But grab a drink alone and you may experience feelings of depression. Researchers think they now know why this happens.
“Social settings influence how individuals react to alcohol, yet there is no mechanistic study on how and why this occurs,” said Kyung-An Han, Ph.D., a biologist at The University of Texas at El Paso who uses fruit flies to study alcoholism.
Now, Han and a team of UTEP faculty and students have taken a key step in understanding the neurobiological process behind social drinking and how it boosts ...
University of Houston researchers create new treatment and vaccine for flu and various coronaviruses
2024-08-06
A team of researchers, led by the University of Houston, has discovered two new ways of preventing and treating respiratory viruses. In back-to-back papers in Nature Communications, the team - from the lab of Navin Varadarajan, M.D. Anderson Professor of William A. Brookshire Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering - reports the development and validation of NanoSTING, a nasal spray, as a broad-spectrum immune activator for controlling infection against multiple respiratory viruses; and the development of NanoSTING-SN, a pan-coronavirus nasal vaccine, that can protect against infection and disease by all members of the coronavirus family.
NanoSTING ...
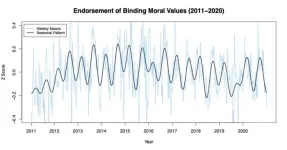
People's moral values change with the seasons
2024-08-06
A new UBC study has revealed regular seasonal shifts in people’s moral values.
The finding has potential implications for politics, law and health—including the timing of elections and court cases, as well as public response to a health crisis.
The research published this week in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) analyzed survey responses from more than 230,000 people in the U.S. over 10 years and revealed that people’s embrace of certain moral ...
Researchers reveal atomic-scale details of catalysts’ active sites
2024-08-06
The chemical and energy industries depend upon catalysts to drive the reactions used to create their products. Many important reactions use heterogeneous catalysts — meaning that the catalysts are in a different phase of matter than the substances they are reacting with, such as solid platinum reacting with gases in an automobile’s catalytic converter.
Scientists have investigated the surface of well-defined single crystals, illuminating the mechanisms underlying many chemical reactions. However, there is much more to be learned. For heterogeneous catalysts, their 3D atomic structure, their chemical composition and the nature of ...
The prescription for a healthier democracy
2024-08-06
When we’re sick, the first step on the road to recovery is a visit to the doctor’s office.
It turns out the same may also be true for breathing life into America’s democracy.
A Rutgers University–New Brunswick study published in the journal JAMA Health Forum finds that physicians can play a crucial role in strengthening political inclusion of marginalized groups by aiding patients in voter registration.
“Hospitals aren’t the first place we think of when it comes to voter registration,” said Katherine McCabe, an associate professor of American politics at Rutgers University-New Brunswick and lead ...