(Press-News.org) The world’s seabeds are little explored, and the knowledge we have is patchy. Using remotely operated underwater vehicles to learn about seabeds is expensive, requires certain weather conditions, and is difficult in deep, remote, and offshore habitats.
To circumvent these challenges, researchers in Australia have now enlisted endangered Australian sea lions (Neophoca cinerea) to carry cameras. The resulting videos allowed the researchers to identify previously unmapped benthic habitats used by the sea lions on the continental shelf. They published their results in Frontiers in Marine Science.
“Using animal-borne video and movement data from a benthic predator is a really effective way of mapping diverse benthic habitats across large areas of the seabed,” said first author Nathan Angelakis, a PhD student with The University of Adelaide and the South Australian Research and Development Institute (Aquatic Sciences). “These data are useful both for mapping critical habitats for an endangered species such as the Australian sea lion, and more broadly, for mapping unexplored areas of the seabed.”
Tracking sea lions
For the project, supported with funding from The Australian Government and The Ecological Society of Australia, eight adult female Australian sea lions from Olive Island and Seal Bay colonies were equipped with small and light-weight cameras. Cameras and tracking instruments were glued to small pieces of neoprene that were then glued to the fur of the sea lions. In total, the filming and tracking equipment weighed less than 1% of the sea lions’ body weight to prevent dragging effects and allow the animals to move without restrictions. Recordings were made over two to three days.
“We deployed the instruments on adult females so we could recover the equipment a few days later when they returned to land to nurse their pups,” Angelakis explained. “We used satellite-linked GPS loggers on the sea lions, which meant we could track their position in real-time and knew when they had returned to the colony.”
Predicting ocean habitats
From the animal-borne videos – 89 hours of recordings in total – the researchers identified six benthic habitats: macroalgae reef, macroalgae meadow, bare sand, sponge/sand, invertebrate reefs, and invertebrate boulder.
The researchers then used machine learning models to predict large habitat areas across the continental shelf of southern Australia. To do so, they also incorporated oceanographic and environmental factors which may be important drivers of the structure and distribution of these habitats. The oceanographic data that was incorporated into the models was based on 21 years of observation and measurements.
“The sea lions from both locations covered quite broad areas around the colonies. In our calculations, we kept the area in which we predicted habitats small to maximize the precision of our predictions,” Angelakis said. “This allowed us to model benthic habitats across more than 5,000 square km of the continental shelf.”
As seen by sea lions
The habitats the sea lions filmed were different than in other, previously mapped regions of South Australia. This could be due to contrasting oceanographic/environmental conditions, as well as sea lions not using or traveling through certain habitats or preferring certain ones over others. Some habitats in the region might have been missed, the researchers pointed out.
The study nevertheless contributes greatly to knowledge about these seabeds and provides critical information about an endangered species, the populations of which have declined by more than 60% over the past 40 years. In addition, it can also be used to survey and assess other marine species of interest that are observed in the video.
The researchers said that exploring these habitats by way of animal-borne video does offer an efficient and cost-effective method for future mapping endeavors. Assessing marine areas from the perspective of a predator, rather than from a more traditional anthropocentric perspective can improve scientists’ understanding of benthic environments and develop more comprehensive maps of the seabed.
END
Sea lion camera crews help researchers explore previously unmapped ocean habitats
Scientists equipped Australian sea lions with cameras and used the video data to identify unknown ocean habitats in southern Australia
2024-08-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Superbugs spread to family members of recently hospitalized patients
2024-08-07
ARLINGTON, Va. (August 7, 2024) — Family members of patients recently discharged from the hospital may have a higher risk of getting an antibiotic-resistant infection, often called a superbug, even if the patient was not diagnosed with the same infection, suggesting hospitals play a role in the community spread of resistant bacteria, according to study in Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology, the journal of the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America.
When recently hospitalized patients were diagnosed with the superbug — Methicillin-resistant ...
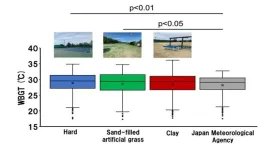
Preventing heat stroke in tennis: insights into the heat environments of tennis courts
2024-08-07
With rising global temperatures due to global warming, the risk of heat strokes has increased and is expected to grow even further. This is particularly troubling for athletes participating in competitive sports. In tennis, multiple matches are played daily, lasting up to five hours. Playing such matches in sweltering conditions could be highly detrimental.
The Tokyo Olympic Games in 2021 faced extremely hot conditions with many players calling for appropriate countermeasures. Consequently, the International Tennis Federation (ITF) formulated and issued the “Extreme Weather Policy” at the Tokyo Olympics to manage matches based ...
Dozing at the wheel? Not with these fatigue-detecting earbuds
2024-08-07
Everyone gets sleepy at work from time to time, especially after a big lunch. But for people whose jobs involve driving or working with heavy machinery, drowsiness can be extremely dangerous — if not outright deadly. Drowsy driving contributes to hundreds of fatal vehicle accidents in the U.S. each year, and the National Safety Council has cited drowsiness as a critical hazard in construction and mining.
To help protect drivers and machine operators from the dangers of drifting off, engineers at the University of California, Berkeley, have created prototype earbuds that can detect the signs of drowsiness ...
FDA approves new therapy for glioma patients for first time in decades
2024-08-07
Boston – Vorasidenib has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for patients with Grade 2 gliomas with IDH1 or IDH2 mutations.
Based on evidence from the INDIGO clinical trial, a global phase 3, double-blinded, randomized clinical trial, vorasidenib more than doubled progression-free survival and delayed the need for treatment with radiation and chemotherapy for patients with Grade 2 IDH-mutant glioma after surgery to remove the tumor. INDIGO was the first phase 3 clinical trial of a molecularly targeted therapy for IDH-mutant glioma.
“The INDIGO trial ...
Think about banning kitchen worktop favourite to ward off incurable lung disease, urge doctors
2024-08-07
It may now be time to ban artificial stone—a firm favourite for kitchen worktops in the UK— to ward off the incurable lung disease caused by its manufacturing and fitting, say a team of doctors in the journal Thorax after treating the first 8 cases of artificial stone silicosis reported in the UK.
Silicosis is caused by breathing in crystalline silica dust, and millions of people around the world are at risk of developing it as a result of their jobs in mining, quarrying, stone-cutting ...
Follow Australia’s lead and ban artificial stone, researchers urge European governments
2024-08-07
The UK and the European Union should follow Australia’s lead and ban the kitchen worktop favourite and cause of irreversible and rapidly progressive lung disease—artificial stone siliicosis—urge researchers in an editorial, published online in Occupational & Environmental Medicine.
And until a ban comes into force, all possible control measures should be legally enforced to minimise workers’ exposure to the harmful crystalline silica dust generated during its manufacture and fitting, insist the authors.
Artificial stone (also known as engineered stone) is widely used for surfaces ...
Reducing child poverty in England would significantly boost child health and narrow health inequalities
2024-08-07
Renewed efforts to reduce child poverty in England between now and 2033, such as removing the 2-child limit on child benefit, would significantly boost several aspects of child health and narrow health inequalities across the country, finds research published online in the Journal of Epidemiology & Community Health.
Tackling it would substantially cut the number of infant deaths and children in care, as well as rates of childhood nutritional anaemia and emergency admissions, with the most deprived regions, especially ...
Cut ties with Coca Cola in interests of athletes, spectators, and the planet, IOC urged
2024-08-07
The International Olympic Committee (IOC) should cut its ties with Coca Cola in the best interests of athletes, spectators, and the planet, urge Trish Cotter and Sandra Mullin of the international public health organisation, Vital Strategies, in an editorial to be published shortly in the open access journal BMJ Global Health.*
The company’s sponsorship forces athletes to implicitly endorse unhealthy sugary drinks and provides Coca Cola with elite access to political and corporate leaders to exert its influence, insist the authors.
Coca Cola has sponsored the Olympic Games for almost 100 years, they note. And there’s ...
Bloomberg Philanthropies makes founding gift to Xavier Ochsner College of Medicine
2024-08-07
Today, Bloomberg Philanthropies announced a gift of $5 million in seed funding to support the creation of the Xavier Ochsner College of Medicine (XOCOM), a newly established medical school in New Orleans founded by Xavier University of Louisiana and Ochsner Health.
Earlier this year, Xavier University of Louisiana, a historically Black college and university (HBCU) with a strong track record of sending graduates into the medical field, and Ochsner Health, the Gulf South’s leading not-for-profit health system with a long academic ...
Domestication causes smaller brian size in dogs than in the wolf, but such an evolutionary change is not unusual in wild animals
2024-08-07
A recent study by László Zsolt Garamszegi from the Institute of Ecology and Botany, Centre for Ecological Research, Hungary, and Niclas Kolm from the Department of Zoology, Stockholm University, Sweden, challenges the long-held notion that domestication is the primary driver of reduced brain size in domesticated animals, specifically dogs. The study employs a phylogenetic comparative method to analyze whether the domesticated dog (Canis familiaris) exhibits a uniquely small brain relative to its body size compared to other canid species.
The prevailing belief has been that domestication leads to a significant ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Sea lion camera crews help researchers explore previously unmapped ocean habitatsScientists equipped Australian sea lions with cameras and used the video data to identify unknown ocean habitats in southern Australia