mTORC1 in classical monocytes: Links to human size variation & neuropsychiatric disease
"This report suggests that a simple assay may allow cost-effective prediction of medication response."
2024-08-07
(Press-News.org)
"This report suggests that a simple assay may allow cost-effective prediction of medication response."
BUFFALO, NY- August 7, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science), Volume 16, Issue 14 on July 26, 2024, entitled, “mTORC1 activation in presumed classical monocytes: observed correlation with human size variation and neuropsychiatric disease.”
In this new study, researchers Karl Berner, Naci Oz, Alaattin Kaya, Animesh Acharjee, and Jon Berner from Woodinville Psychiatric Associates, Virginia Commonwealth University, University of Birmingham, University Hospitals Birmingham, and MRC Health Data Research UK, aimed to measure phosphorylated p70S6K, a marker for mTORC1 activity, in individuals with psychiatric disease to determine whether phosphorylated p70S6K could predict medication response.
Their results showed that mTORC1 activity correlated highly with classical biometrics (height, macrocephaly, pupil distance) and specific neuropsychiatric disease profiles (anxiety and autism).
“Our data suggest that human variability of mTORC1 gain of function observed during the differentiation of stem-like monocytes into vascular tissue-resident macrophages correlates with physical size, subsets of neuropsychiatric disease, and clinical ketamine or rapamycin response.”
Read the full paper: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.206033
Corresponding Author: Jon Berner
Corresponding Email: jonbernermd@gmail.com
Keywords: aging, ketamine, lithium, monocyte, mTORC1, rapamycin
Click here to sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article.
About Aging:
The journal Aging aims to promote 1) treatment of age-related diseases by slowing down aging, 2) validation of anti-aging drugs by treating age-related diseases, and 3) prevention of cancer by inhibiting aging. (Cancer and COVID-19 are age-related diseases.)
Aging is indexed by PubMed/Medline (abbreviated as “Aging (Albany NY)”), PubMed Central, Web of Science: Science Citation Index Expanded (abbreviated as “Aging‐US” and listed in the Cell Biology and Geriatrics & Gerontology categories), Scopus (abbreviated as “Aging” and listed in the Cell Biology and Aging categories), Biological Abstracts, BIOSIS Previews, EMBASE, META (Chan Zuckerberg Initiative) (2018-2022), and Dimensions (Digital Science).
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
Facebook
X
Instagram
YouTube
LinkedIn
Reddit
Pinterest
Spotify, and available wherever you listen to podcasts
Click here to subscribe to Aging publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker Str., Suite 1B
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-08-07
MINNEAPOLIS – There’s some good news for people with Parkinson’s disease: The risk of developing dementia may be lower than previously thought, or dementia may occur later in the course of the disease than previously reported, according to a study published in the August 7, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
“The development of dementia is feared by people with Parkinson’s, and the combination of both a movement disorder and a cognitive disorder can be devastating to them and their loved ones,” said study author Daniel Weintraub, MD, ...
2024-08-07
Long-term exposure to contaminants such as arsenic and nitrate in water is linked to an increased risk of various diseases, including cancers, cardiovascular diseases, developmental disorders and birth defects in infants. In the United States, there is a striking disparity in exposure to contaminants in tap water provided by community water systems (CWSs), with historically marginalized communities at greater risks compared to other populations. Often, CWSs that distribute water with higher contamination levels exist in areas that lack adequate public infrastructure or sociopolitical and financial resources.
In ...
2024-08-07
Living less than about one-third of a mile from pesticide use prior to conception and during early pregnancy could increase the risk of stillbirths, according to new research led by researchers at the Mel and Enid Zuckerman College of Public Health and Southwest Environmental Health Sciences Center.
Researchers found that during a 90-day pre-conception window and the first trimester of pregnancy, select pesticides, including organophosphates as a class, were associated with stillbirth.
The paper, “Pre-Conception ...
2024-08-07
Affective sensitivity to air pollution (ASAP) describes the extent to which affect, or mood, fluctuates in accordance with daily changes in air pollution, which can vary between individuals, according to a study published August 7, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Michelle Ng from Stanford University, USA, and colleagues.
Individuals’ sensitivity to climate hazards is a central component of their vulnerability to climate change. Building on known associations between air pollution exposure and ...
2024-08-07
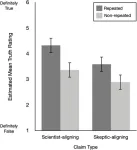
Climate science supporters rated climate-skeptical statements as “truer” after just a single repetition, according to a study published August 7, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE led by Mary Jiang from The Australian National University, Australia, and coauthored by Norbert Schwarz from the University of Southern California, USA, and colleagues. The results held true even for the strongest climate science supporters surveyed.
Amidst the influx of content that a person consumes each day, the principle of motivated ...
2024-08-07
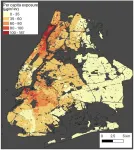
New York City subway commuters who are economically disadvantaged or belong to racial minority groups have the highest exposure to fine particulate matter during their commutes, according to a new study published August 7, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Shams Azad of New York University, USA.
Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) is a type of air pollution that, due to its small size, when inhaled by a person can enter the bloodstream. PM2.5 is known to cause short- and long-term health complications. For the last few decades, cities have promoted public transportation to reduce traffic congestion and improve ambient outdoor air quality. Subway systems reduce pollution by decreasing ...
2024-08-07
Women who spend a lot of time on TikTok — especially those seeing a lot of pro-anorexia content — feel worse about their appearance, a new study shows. The results suggest that high TikTok exposure could harm mental health, reducing body image satisfaction and increasing the risk for disordered eating behavior. Madison Blackburn and Rachel Hogg from Charles Sturt University in Australia present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on August 7, 2024.
Since its launch, the short-form video app TikTok has had more than 2 billion downloads. The app’s algorithm curates content on a “For ...
2024-08-07
In a new survey study, Dutch employees who worked from home tended to report higher levels of productivity and less burnout if they were more satisfied with their home office setup. The study also linked more air ventilation in the home office to higher self-reported productivity. Martijn Stroom and colleagues at Maastricht University in the Netherlands report these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on August 7, 2024.
In recent years, thanks in large part to the COVID-19 pandemic and technological advancements, ...
2024-08-07
Trained dogs can sniff out CWD, a disease of major concern, in the droppings of farmed and wild deer, offering potential for non-invasive surveillance
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0303225
Article Title: Biodetection of an odor signature in white-tailed deer associated with infection by chronic wasting disease prions
Author Countries: USA
Funding: TWRA AP-14839 Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service and WILDLIFE RESOURCES AGENCY, TENNESSEE https://www.aphis.usda.gov/aphis/ourfocus/business-services/financial-management-division/financial_services_branch/agreements_service_center/terms-conditions-for-aphis-awards ...
2024-08-07
Ice cream made from mare's milk blended with cow's cream not only tastes good, but may have beneficial probiotic qualities
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0304692
Article Title: The use of mare’s milk for yogurt ice cream and synbiotic ice cream production
Author Countries: Poland
Funding: The author(s) received no specific funding for this work. END ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] mTORC1 in classical monocytes: Links to human size variation & neuropsychiatric disease
"This report suggests that a simple assay may allow cost-effective prediction of medication response."