(Press-News.org) Recent large-scale epidemiologic studies have increasingly suggested that aberrant brain development and psychiatric disorders may share common mechanisms. The interplay between genetic variants and environmental stress has been shown to significantly impact genome integrity, reshaping brain development. This can result in changes to neural networks, which are linked to neurodevelopmental and psychiatric disorders—areas where many questions remain unresolved.
For more information, visit: bit.ly/4ddJSV0
For contributing article to this research topic, visit: bit.ly/4crNG41
Please use the Hot-Topic Code: BMS-CMP-2024-HT-33 when prompted during the article submission.
In a new Special Issue, we aim to present a comprehensive overview of the latest research in neurodevelopmental and psychiatric diseases. We welcome submissions that explore these complex topics from various perspectives, including original research, review articles, innovative treatment methods, case reports, and brain imaging studies. While the interplay with therapeutic psychoactive drugs is of interest, it is not mandatory.
Key topics include identifying novel molecules and signaling pathways involved in neural development, exploring gene-environment interactions that influence neurochemistry, and translating findings from model organisms to human health. We also encourage studies that investigate the central nervous system's interaction with the peripheral body and the lived experience of those with neurodevelopmental or psychiatric conditions.
END
Common mechanisms underpinning neurodevelopmental disorders and psychiatric diseases
Published by Dr. Bing Lang in the journal, Current Molecular Pharmacology
2024-08-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Department of Energy announces 2024 Office of Science Distinguished Scientist Fellows and lecture series
2024-08-12
WASHINGTON, D.C. – Four of the nation’s top scientists have each been awarded $1 million in direct funding via the Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science Distinguished Scientist Fellows program.
The program was established to develop, sustain, and promote scientific and academic excellence in Office of Science (SC) research through collaborations between universities and national laboratories.
The awards, authorized by the America COMPETES act, are bestowed on senior national laboratory scientists. The United States has ...
Mary Bishai named Distinguished Scientist Fellow
2024-08-12
UPTON, N.Y. — Physicist Mary Bishai of the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory has been named a 2024 DOE Office of Science Distinguished Scientist Fellow. The honor recognizes her “enduring contributions at the intensity frontier of high energy physics in unraveling fundamental properties of neutrinos, extraordinary leadership and service to the particle physics community, and deep commitment to broadening participation through mentoring next generation scientists.”
As described in a DOE Office of Science press release issued today, the ...
Can meditation and stretching relieve cramping caused by cirrhosis?
2024-08-12
People suffering from cirrhosis may find some symptom relief from two accessible activities: stretching and meditation.
A study from the University of Michigan compared the two therapies as a means to relieve nocturnal muscle cramps and found both effective.
The resulting paper, “The RELAX randomized controlled trial: Stretching versus meditation for nocturnal muscle cramps,” appeared in Liver International.
The study
Two out of every three people with cirrhosis experience muscle cramps at night that wake them from sleep.
Since ...
Study reveals oleoyl-ACP-hydrolase underpins lethal respiratory viral disease
2024-08-12
Respiratory infections can be severe, even deadly, in some individuals, but not in others. Scientists at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity and other collaborators have gained new understanding of why this is the case by uncovering an early molecular driver that underpins fatal disease. Oleoyl-ACP-hydrolase (OLAH) is an enzyme involved in fatty acid metabolism. A study, published today in Cell, shows that OLAH drives severe disease outcomes.
The important role of OLAH in immune response has gone unrecognized for several reasons, including a lack of noticeable expression in healthy ...
Advances in drug delivery carrier microwave-assisted reactions for enhanced therapeutics and diagnostic purposes
2024-08-12
Microwave irradiation technology is emerging as a powerful tool in the fields of organic synthesis, pharmaceuticals, and nanocarrier development. Recently, microwave-assisted reactions have gained significant attention for their effectiveness in synthesizing drug delivery carriers. This technology offers notable advantages, including high yield, shorter reaction times, and improved compound purity, making it a promising approach for developing nanoparticles with enhanced physicochemical properties and bioavailability.
For more information, please visit: bit.ly/3SFk4cf
For contributing article in this research topic, visit: bit.ly/3WXyoza
Use ...
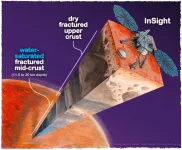
Presence of liquid water most probable explanation for data collected by mars lander
2024-08-12
Data about Mars’ planetary crust gathered from the Mars InSight lander are best explained by the conclusion that the crust has stores of liquid water.
Analysis led by Vashan Wright, a geophysicist at UC San Diego’s Scripps Institution of Oceanography, provides the best evidence to date that the planet still has liquid water in addition to that frozen at its poles. If that conclusion is true, it sets the stage for new research considering the planet’s habitability and continuing a search for life that exists on a place other than Earth. The potential presence of liquid water on Mars has tantalized scientists for decades. Water is essential for a habitable planet.
“Understanding ...
Scientists find oceans of water on Mars. It's just too deep to tap.
2024-08-12
Using seismic activity to probe the interior of Mars, geophysicists have found evidence for a large underground reservoir of liquid water — enough to fill oceans on the planet's surface.
The data from NASA's Insight lander allowed the scientists to estimate that the amount of groundwater could cover the entire planet to a depth of between 1 and 2 kilometers, or about a mile.
While that’s good news for those tracking the fate of water on the planet after its oceans disappeared more than 3 billion years ago, the reservoir won't be of much use to anyone trying to tap into it to supply a future Mars colony. It's ...
UMass Amherst researchers ID body’s ‘quality control’ regulator for protein folding
2024-08-12
AMHERST, Mass. – Anyone who’s tried to neatly gather a fitted sheet can tell you: folding is hard. Get it wrong with your laundry and the result can be a crumpled, wrinkled mess of fabric, but when folding fails among the approximately 7,000 proteins with an origami-like complexity that regulate essential cellular functions, the result can lead to one of a multitude of serious diseases ranging from emphysema and cystic fibrosis to Alzheimer’s disease. Fortunately, our bodies have a quality-control system ...
Forest restoration can boost people, nature and climate simultaneously
2024-08-12
Forest restoration can benefit humans, boost biodiversity and help tackle climate change simultaneously, new research suggests.
Restoring forests is often seen in terms of “trade-offs” – meaning it often focuses on a specific goal such as capturing carbon, nurturing nature or supporting human livelihoods.
The new study, by the universities of Exeter and Oxford, found that restoration plans aimed at a single goal tend not to deliver the others.
However, “integrated” plans would deliver over 80% of the benefits in all three areas at once.
It also found that ...
Pre-surgical antibody treatment might prevent heart transplant rejection
2024-08-12
A new study from scientists at Cincinnati Children’s suggests there may be a way to further protect transplanted hearts from rejection by preparing the donor organ and the recipient with an anti-inflammatory antibody treatment before surgery occurs.
The findings, published online in PNAS, focus on blocking an innate immune response that normally occurs in response to microbial infections. The same response has been shown to drive dangerous inflammation in transplanted hearts.
In the new study – in mice -- transplanted hearts functioned for longer periods when the organ recipients ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How some skills become second nature
SFU study sheds light on clotting risks for female astronauts
UC Irvine chemists shed light on how age-related cataracts may begin
Machine learning reveals Raman signatures of liquid-like ion conduction in solid electrolytes
Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia researchers emphasize benefits and risks of generative AI at different stages of childhood development
Why conversation is more like a dance than an exchange of words
With Evo 2, AI can model and design the genetic code for all domains of life
Discovery of why only some early tumors survive could help catch and treat cancer at very earliest stages
Study reveals how gut bacteria and diet can reprogram fat to burn more energy
Mayo Clinic researchers link Parkinson's-related protein to faster Alzheimer's progression in women
Trends in metabolic and bariatric surgery use during the GLP-1 receptor agonist era
Loneliness, anxiety symptoms, depressive symptoms, and suicidal ideation in the all of us dataset
A decision-support system to personalize antidepressant treatment in major depressive disorder
Thunderstorms don’t just appear out of thin air - scientists' key finding to improve forecasting
Automated CT scan analysis could fast-track clinical assessments
New UNC Charlotte study reveals how just three molecules can launch gene-silencing condensates, organizing the epigenome and controlling stem cell differentiation
Oldest known bony fish fossils uncover early vertebrate evolution
High‑performance all‑solid‑state magnesium-air rechargeable battery enabled by metal-free nanoporous graphene
Improving data science education using interest‑matched examples and hands‑on data exercises
Sparkling water helps keep minds sharp during long esports sessions
Drone LiDAR surveys of abandoned roads reveal long-term debris supply driving debris-flow hazards
UGA Bioinformatics doctoral student selected for AIBS and SURA public policy fellowship
Gut microbiome connected with heart disease precursor
Nitrous oxide, a product of fertilizer use, may harm some soil bacteria
FAU lands $4.5M US Air Force T-1A Jayhawk flight simulator
SimTac: A physics-based simulator for vision-based tactile sensing with biomorphic structures
Preparing students to deal with ‘reality shock’ in the workplace
Researchers develop beating, 3D-printed heart model for surgical practice
Black soldier fly larvae show promise for safe organic waste removal
People with COPD commonly misuse medications
[Press-News.org] Common mechanisms underpinning neurodevelopmental disorders and psychiatric diseasesPublished by Dr. Bing Lang in the journal, Current Molecular Pharmacology