(Press-News.org) A computer algorithm has achieved a 98% accuracy in predicting different diseases by analysing the colour of the human tongue.
The proposed imaging system developed by Iraqi and Australian researchers can diagnose diabetes, stroke, anaemia, asthma, liver and gallbladder conditions, COVID-19, and a range of vascular and gastrointestinal issues.
Engineering researchers from Middle Technical University (MTU) and the University of South Australia (UniSA) achieved the breakthrough in a series of experiments where they used 5260 images to train machine learning algorithms to detect tongue colour.
Two teaching hospitals in the Middle East supplied 60 tongue images from patients with various health conditions. The artificial intelligence (AI) model was able to match the tongue colour with the disease in almost all cases.
A new paper published in Technologies outlines how the proposed system analyses tongue colour to provide on-the-spot diagnosis, confirming that AI holds the key to many advances in medicine.
Senior author, MTU and UniSA Adjunct Associate Professor Ali Al-Naji, says AI is replicating a 2000-year-old practice widely used in traditional Chinese medicine – examining the tongue for signs of disease.
“The colour, shape and thickness of the tongue can reveal a litany of health conditions,” he says.
“Typically, people with diabetes have a yellow tongue; cancer patients a purple tongue with a thick greasy coating; and acute stroke patients present with an unusually shaped red tongue.
“A white tongue can indicate anaemia; people with severe cases of COVID-19 are likely to have a deep red tongue; and an indigo or violet coloured tongue indicates vascular and gastrointestinal issues or asthma.”
In the study, cameras placed 20 centimetres from a patient captured their tongue colour and the imaging system predicted their health condition in real time.
Co-author UniSA Professor Javaan Chahl says that down the track, a smartphone will be used to diagnose disease in this way.
“These results confirm that computerised tongue analysis is a secure, efficient, user friendly and affordable method for disease screening that backs up modern methods with a centuries-old practice,” Prof Chahl says.
END
Say ‘aah’ and get a diagnosis on the spot: is this the future of health?
2024-08-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
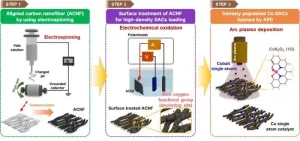
Rapid removal of emerging endocrine disruptors in wastewater using high-performance single-atom catalysts
2024-08-13
Bisphenols are widely used as the main raw material for plastics such as receipts, water bottles, water containers, and vinyl due to their heat-resistant and mechanochemical properties. Among bisphenols, bisphenol A (BPA) that we often refer to as an "endocrine-disrupting chemicals" has been linked to adverse effects on reproduction, development, intelligence, and various metabolic diseases. Bisphenol F (BPF), a recently developed alternative to BPA Bisphenol A has also been reported in the literature to cause neurological disruption and various health risks.
Dr. Jong Min Kim of the Materials Architecturing ...
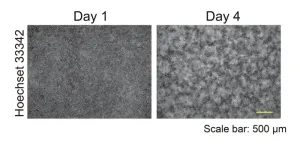
Starvation and adhesion drive formation of keratinocyte patterns in skin
2024-08-13
Cell–cell adhesion-induced patterning in keratinocytes can be explained by just starvation and strong adhesion, Hokkaido University researchers find.
Fingerprints are one of the best-recognised examples of pattern formation by epithelial cells. The primary cells in the epithelium are the keratinocytes, and they are known to form patterns at the microscopic and macroscopic levels. While factors affecting this pattern formation have been reported, the exact mechanisms underlying the process are still not fully understood.
A team of researchers, led by Associate ...
Ships now spew less sulfur, but warming has sped up
2024-08-13
RICHLAND, Wash.—Last year marked Earth’s warmest year on record. A new study finds that some of 2023’s record warmth, nearly 20 percent, likely came as a result of reduced sulfur emissions from the shipping industry. Much of this warming concentrated over the northern hemisphere.
The work, led by scientists at the Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, published today in the journal Geophysical Research Letters.
Regulations put into effect in 2020 by the International Maritime Organization required a roughly 80 percent reduction in the sulfur content of shipping ...
Rice-built reactor yields green ammonia and purified water
2024-08-13
HOUSTON – (Aug. 12, 2024) – Ammonia plays a critical role in sustaining food production for the world’s growing population, but making it accounts for about 2% of global energy consumption and 1.4% of carbon dioxide emissions. Rice University engineers have developed a revolutionary reactor design that could decarbonize ammonia production while also mitigating water pollution.
In a study published in Nature Catalysis, a team of Rice engineers led by Haotian Wang described the development of a new reactor system that converts nitrates — common pollutants found in industrial wastewater and ...
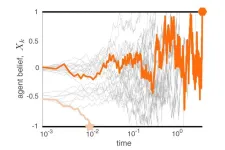
Think fast — or not: FSU research describes mathematics behind decision making
2024-08-13
New research from a Florida State University professor and colleagues explains the mathematics behind how initial predispositions and additional information affect decision making.
The research team’s findings show that when decision makers quickly come to a conclusion, the decision is more influenced by their initial bias, or a tendency to err on the side of one of the choices presented. If decision makers wait to gather more information, the slower decision will be less biased. The work was published today in Physical Review E.
“The basic result might ...
Largest study of its kind finds common lab tests aren’t reliable for diagnosing Long COVID
2024-08-13
A new study found that most routine laboratory tests are not reliable for diagnosing Long COVID, also known as Post-Acute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC).
The study, published today in Annals of Internal Medicine, found no reliable biomarker among 25 routine clinical laboratory values for prior infection, PASC or specific types of PASC clusters. This suggests none of these routine labs can serve as a clinically useful biomarker of PASC.
"Our study shows patients can have severe Long COVID with normal lab results. This ...
Engineers make tunable, shape-changing metamaterial inspired by vintage toys
2024-08-12
Common push puppet toys in the shapes of animals and popular figures can move or collapse with the push of a button at the bottom of the toys’ base. Now, a team of UCLA engineers has created a new class of tunable dynamic material that mimics the inner workings of push puppets, with applications for soft robotics, reconfigurable architectures and space engineering.
Inside a push puppet, there are connecting cords that, when pulled taught, will make the toy stand stiff. But by loosening these cords, the “limbs” of the toy will go limp. Using the same cord tension-based principle that controls a puppet, researchers have developed a new type of metamaterial, a material ...
Start-up Whisper Aero uses the ORNL Summit supercomputer to test concepts for an ultraquiet electric airplane
2024-08-12
From a nondescript industrial building in the small town of Crossville, Tennessee, the team of engineers at Whisper Aero is planning a revolution in aviation technology.
Previously home to a publisher of magazines — including, coincidentally, Trade-A-Plane, an airplane sales publication started in 1937 — the long-empty property’s cavernous spaces are now filled with multidisciplinary activities that include the creation of a new electric aircraft engine.
In January 2024, employees of the 3-year-old start-up moved into their new headquarters, refurbishing its dusty rooms into a 21st century aerospace technology facility with areas ...
New study unveils 16,000 years of climate history in the tropical Andes
2024-08-12
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — A new study that explores ancient temperatures and rainfall patterns in the tropical Andes of South America has revealed how 16,000 years of climate history in this part of the world was driven by carbon dioxide levels and ocean currents from global climate events.
Led by Brown University researchers, the study marks the first high-resolution temperature record covering the past 16,000 years in the tropical Andes and could help scientists predict and mitigate future climate impacts in tropical regions of the planet. The work is described in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Science.
“Usually ...
The Society of Huntsman Translational Scholars welcomes two more members
2024-08-12
Huntsman Cancer Institute and the University of Utah (the U) are proud to announce the induction of two physician-scientists, Heloisa Soares, MD, PhD, and Skyler Johnson, MD, as members of The Society of Huntsman Translational Scholars.
The Society of Huntsman Translational Scholars supports scientists who focus on translating research discoveries made in the lab into innovations that improve outcomes for cancer patients. Scholars receive financial support for their scientific work, have opportunities for mentorship, and collaborate with other society members in advancing scientific discoveries.
“The Society of Huntsman Translational Scholars ...