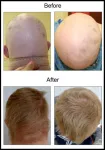
Drawing upon their 2016 discovery that the interferon response is constantly activated in people with Down syndrome, the team designed the trial to focus on the autoimmune and inflammatory skin conditions that are very common in people with Down syndrome including alopecia areata, psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, and hidradenitis suppurativa, and employed the JAK inhibitor tofacitinib (marketed as XELJANZ®, Pfizer). The study also monitored effects on co-occurring autoimmune conditions, such as autoimmune thyroid disease, celiac disease, and arthritis.
“Individuals with Down syndrome are at a high risk of developing autoimmune skin conditions, which are often hard to treat and cause significant discomfort and decrease their quality of life,” explains Dr. Emily Gurnee, assistant professor of dermatology, one of the dermatologists involved in the study, and a principal investigator in the trial. “Limited data exist to guide conversations about treatment options for skin conditions common to individuals with Down syndrome. The findings from scientists at the Crnic Institute support the notion that JAK inhibitors are a valuable treatment not only for skin conditions but may benefit other autoimmune conditions prevalent in this population.”
The study team observed important improvements in skin pathology, with the most striking results observed for those affected by alopecia areata, as well as improvements in arthritis and decreased biomarkers of autoimmune thyroid disease. Most study participants chose to remain on the medicine, often through off-label prescriptions, after completion of trial activities.
“Most importantly, we observed that major inflammatory markers elevated in Down syndrome that are known to cause autoimmunity were brought down to the normal range with this medicine, indicating that the immune system is being calmed down by this JAK inhibitor, while preserving strong immune function,” explains Dr. Joaquín Espinosa, executive director of the Crnic Institute, professor of pharmacology, and one of the principal investigators in the clinical trial. “More data will be needed to define the safety profile of JAK inhibitors in Down syndrome, and we look forward to the completion of the trial and analysis of the full dataset.”
The study also reports the deepest characterization of the immune system dysregulation characteristic of Down syndrome to date through analysis of clinical data and biospecimens collected by the ongoing Human Trisome Project study.
The Crnic Institute team analyzed clinical data and blood samples to characterize the pattern of autoimmune conditions and accompanying inflammatory processes in hundreds of research participants in the Human Trisome Project using so called multi-omics technologies. They observed that triplication of chromosome 21, or trisomy 21, the genetic abnormality underlying Down syndrome, leads to rapid onset of diverse autoimmune conditions during childhood, along with increased levels of many inflammatory factors and strong dysregulation of multiple immune cell types.
“One key observation is that elevation of multiple inflammatory markers and dysregulation of all branches of the immune system occurs from a very early age, even before any clinical manifestations of autoimmunity,” says Dr. Matthew Galbraith, assistant research professor of pharmacology, director of the Data Sciences Program of the Crnic Institute and co-author of the study. “This points to a constitutive state of immune dysregulation triggered by the extra chromosome that eventually leads to the appearance of multiple autoimmune conditions, with variations in timing and severity among individuals.”
“Since 2016 we have been hypothesizing that the class of medicines known as JAK inhibitors will provide therapeutic benefits in this population,” explains Dr. Angela Rachubinski, assistant research professor of pediatrics, director of the Clinical and Translational Sciences Program at the Crnic Institute, lead author of the paper, and one of the principal investigators in the trial. “Although JAK inhibitors have been approved for a range of autoimmune and inflammatory conditions in the general population, this clinical trial, which started activities back in 2020, provides the first systematic investigation of the effects of a JAK inhibitor in people with Down syndrome."
The Crnic Institute study team is already overseeing a second trial testing the safety and efficacy of the JAK inhibitor relative to other medicines for treating the condition known as Down Syndrome Regression Disorder, and a third trial focused on children with Down syndrome is expected to start recruitment in late 2024.
“We are very grateful to the scientists and physicians at the Crnic Institute for their transformative research that is already translating into improved medical care and health outcomes for the amazing people with Down syndrome who we serve,” says Michelle Sie Whitten, president & CEO of Global Down Syndrome Foundation, a partner and an affiliate organization of the Crnic Institute. “We are proud that GLOBAL’s advocacy work with Congress and with the National Institutes of Health (NIH) has led to the establishment of the trans-NIH Down syndrome funding project, INCLUDE, that underwrites this and numerous other groundbreaking studies and clinical trials.”
About the Linda Crnic Institute for Down Syndrome
The Linda Crnic Institute for Down Syndrome is one of the only academic research centers fully devoted to improving the lives of people with Down syndrome through advanced biomedical research, spanning from basic science to translational and clinical investigations. Founded through the generous support and partnership of the Global Down Syndrome Foundation, the Anna and John J. Sie Foundation, and the University of Colorado, the Crnic Institute supports a thriving Down syndrome research program involving over 50 research teams across four campuses on the Colorado Front Range. To learn more, visit www.crnicinstitute.org or follow us on Facebook and Twitter @CrnicInstitute.
About the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus
The University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus is a world-class medical destination at the forefront of transformative science, medicine, education and patient care. The campus encompasses the University of Colorado health professional schools, more than 60 centers and institutes, and two nationally ranked independent hospitals - UCHealth University of Colorado Hospital and Children's Hospital Colorado – which see more than 2 million adult and pediatric patient visits yearly. Innovative, interconnected and highly collaborative, the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus delivers life-changing treatments, patient care and professional training and conducts world-renowned research fueled by $705 million in research grants. For more information, visit www.cuanschutz.edu.
About Global Down Syndrome Foundation
The Global Down Syndrome Foundation (GLOBAL) is the largest non-profit in the U.S. working to save lives and dramatically improve health outcomes for people with Down syndrome. GLOBAL has donated more than $32 million to establish the first Down syndrome research institute supporting over 400 scientists and over 2,500 patients with Down syndrome from 33 states and 10 countries. Working closely with Congress and the National Institutes of Health, GLOBAL is the lead advocacy organization in the U.S. for Down syndrome research and care. GLOBAL has a membership of over 100 Down syndrome organizations worldwide, and is part of a network of Affiliates – the Crnic Institute for Down Syndrome, the Sie Center for Down Syndrome, and the University of Colorado Alzheimer’s and Cognition Center – all on the Anschutz Medical Campus.
GLOBAL’s widely circulated medical publications include Global Medical Care Guidelines for Adults with Down Syndrome, Prenatal & Newborn Down Syndrome Information, and the award-winning magazine Down Syndrome World TM. GLOBAL also organizes the Be Beautiful Be Yourself Fashion Show, the largest Down syndrome fundraiser in the world. Visit globaldownsyndrome.org and follow us on social media Facebook, X and Instagram.
###
END