(Press-News.org) Light technology is at the heart of many cutting-edge innovations, from high-speed internet to advanced medical imaging. However, transmitting light through challenging environments, such as turbulent atmospheres or deformed optical systems, has always posed a significant hurdle. These complexities can distort and disrupt the light field, making it difficult to achieve clear and reliable results. Scientists have long sought ways to overcome these limitations, and a new breakthrough may hold the key to advance practical applications.
As reported in Advanced Photonics, researchers at Soochow University have made a significant advancement in understanding how light behaves as it travels through complex and fluctuating media. This breakthrough could revolutionize various applications ranging from optical communications to advanced imaging techniques.
In the realm of optics, the deformation, flicker, and drift of light fields caused by complex media have historically limited practical applications. The Soochow University team introduced a novel approach to tackling this problem by leveraging a concept known as coherence entropy.
Coherence entropy, a measure of the statistical property of light known as coherence, provides a global characterization of light fields subjected to random fluctuations. Traditionally, characterizing the coherence of light has been complex and difficult to quantify. The research team has successfully applied orthogonal modal decomposition to partially coherent beams, leading to the introduction of coherence entropy as a reliable metric.
Their study revealed that coherence entropy remains stable during the propagation of light through a unitary system, even when faced with complex and deformed optical environments. This consistency suggests that coherence entropy can be a robust indicator of light field behavior in non-ideal conditions.
The team demonstrated the practical utility of coherence entropy by examining its effectiveness in partially coherent beams as they moved through various deformed optical systems and turbulent media. The results show that coherence entropy is resilient and remains a dependable measure for evaluating the performance of light fields in challenging conditions.
“This research represents a major leap forward in our ability to predict and control light propagation through complex environments,” said corresponding author Dr. Chengliang Zhao, the lead researcher. “The introduction of coherence entropy as a global coherence characteristic opens up new possibilities for customizing light fields to improve their performance in real-world applications.”
The implications of this study are far-reaching. From enhancing optical communication systems that must operate through atmospheric turbulence, to advancing imaging technologies that rely on light fields traveling through distorted media, coherence entropy could become a crucial tool for scientists and engineers alike.
By providing a more reliable way to assess and manage light fields in less-than-ideal conditions, this research paves the way for broader and more effective use of low-coherence light fields across various scientific and practical domains.
For details, see the original Gold Open Access article by X. Lu, Z. Wang, et al., “Coherence entropy during propagation through complex media,” Adv. Photon. 6(4), 046002 (2024), doi 10.1117/1.AP.6.4.046002.
END
Coherence entropy unlocks new insights into light-field behavior
Global coherence metric offers a reliable way to assess and manage light fields in less-than-ideal conditions
2024-08-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Mizzou scientists achieve more than 98% efficiency removing nanoplastics from water
2024-08-13
COLUMBIA, Mo. — University of Missouri scientists are battling against an emerging enemy of human health: nanoplastics. Much smaller in size than the diameter of an average human hair, nanoplastics are invisible to the naked eye.
Linked to cardiovascular and respiratory diseases in people, nanoplastics continue to build up, largely unnoticed, in the world’s bodies of water. The challenge remains to develop a cost-effective solution to get rid of nanoplastics while leaving clean water behind.
That’s where Mizzou comes in. Recently, researchers at the university created a new liquid-based solution that eliminates more than 98% of these microscopic ...
Electric scooter–related injuries are becoming more frequent and costly
2024-08-13
August 13, 2024 — The introduction of publicly shared electric scooters (“e-scooters”) in Denver, Colorado has resulted in a steady increase in injuries and hospital admissions, according to research led by Alexander Lauder, MD, an orthopedic surgeon at Denver Health Medical Center. The findings are presented in Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research® (CORR®), a publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons®. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"International ...
Children born prematurely fall into three groups
2024-08-13
About thirteen million babies each year are born prematurely, with preterm birth linked to increases in risk for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), problems with social development, and lower grades.
A problem with past analyses of prematurity, however, is that they do not capture the variety seen in children born pre-term, including some with outcomes better than the average results for full- term children. Pre-term means birth before 37 weeks of gestation, with full term being 40 weeks.
The tendency to lump preterm babies into one group hinders efforts to tailor care for any one child, researchers say. Now a new study, published online August 13 ...
Reducing operation qualification time and cost in additive manufacturing
2024-08-13
America Makes, the National Additive Manufacturing Innovation Institute, is supporting research to revolutionize the additive manufacturing (AM) industry by significantly reducing operational qualification time and cost.
The $2 million project, titled ACCELERATE, is led by Dr. Mohsen Taheri-Andani, an assistant professor in the J. Mike Walker ’66 Department of Mechanical Engineering at Texas A&M University. To secure the funding, Dr. Taheri-Andani partnered with Dr. Yash Parikh, a process engineering consultant at EOS who graduated with a doctorate in mechanical ...
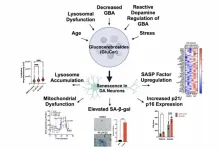
Lipid accumulation drives cellular senescence in dopaminergic neurons
2024-08-13
"These findings align with our previous results in dopaminergic neurons in highlighting a central role for lipid accumulation in the senescence of DA neurons."
BUFFALO, NY- August 13, 2024 – A new research perspective was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science), Volume 16, Issue 14 on July 19, 2024, entitled, “Lipid accumulation drives cellular senescence in dopaminergic neurons.”
As highlighted in the Abstract of this perspective, Parkinson’s disease (PD) is an age-related movement disorder caused ...
The Hastings Center awarded $1.5 million by PCORI to study organizational trustworthiness and community-engaged research
2024-08-13
A research team at The Hastings Center has been approved for $1.5 million in funding by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) to study organizational trustworthiness as it relates to community-engaged research. Led by Virginia A. Brown, PhD, a research scholar at The Hastings Center, the study will be the first to investigate the role of organizational trustworthiness in shaping research engagement processes and outcomes.
Measures to assess organizational trustworthiness as it relates to research ...
Dairy nutrition is leading the sustainability charge
2024-08-13
Philadelphia, August 13, 2024 – Research into reducing greenhouse gas emissions from livestock has increased exponentially as the dairy and agriculture sectors work together toward shared sustainability and efficiency goals. While this progress has been made in all areas of dairy science research, from genetics to animal health and welfare, dairy nutrition has emerged as a particularly impactful area for emission reduction. In a new invited review in the Journal of Dairy Science, a preeminent voice in sustainability and dairy nutrition synthesizes ...
A new method for protection from plant pathogens could help support global food security.
2024-08-13
By modifying a plant intracellular immune receptor (NLR), researchers have developed a potential new strategy for resistance to rice blast disease, one of the most important diseases threatening global food security. The collaborative team from the UK and Japan have recently published their research in PNAS. This could have implications for future approaches to crop protection and ultimately global food supply stability.
The research was led from the Department of Biochemistry and Metabolism at the John Innes Centre, with partners at The Sainsbury Laboratory, University of East Anglia, and the Division of Genomics and Breeding, Iwate Biotechnology Research Center, Japan. For a ...
Halogen bonding for selective electrochemical separation, path to sustainable chemical processing demonstrated
2024-08-13
With a new polymer that only attracts certain substances from solutions when electrically activated, researchers have taken a major step towards sustainable chemical separation.
A team based at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign has reported the first demonstration of selective electrochemical separation driven by halogen bonding in the journal JACS Au. This was achieved by engineering a polymer that modulates the charge density on a halogen atom when electricity is applied. The polymer then attracts only certain targets – such as halides, oxyanions, and even organic molecules – from organic solutions, ...
Study reveals urban trees suffer more from heat waves and drought than their rural counterparts
2024-08-13
NEW YORK, August 13, 2024 — A recently published study in Ecological Applications details how trees in New York City and Boston are more negatively impacted by heat waves and drought than trees of the same species in nearby rural forests. The finding, made by researchers at the Advanced Science Research Center at the CUNY Graduate Center (CUNY ASRC), highlights the challenges urban trees face in the context of climate change and underscores the importance of tailored urban forestry management as ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
Researchers develop AI tools for early detection of intimate partner violence
Researchers develop AI tool to predict patients at risk of intimate partner violence
New research outlines pathway to achieve high well-being and a safe climate without economic growth
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
[Press-News.org] Coherence entropy unlocks new insights into light-field behaviorGlobal coherence metric offers a reliable way to assess and manage light fields in less-than-ideal conditions