(Press-News.org) America Makes, the National Additive Manufacturing Innovation Institute, is supporting research to revolutionize the additive manufacturing (AM) industry by significantly reducing operational qualification time and cost.
The $2 million project, titled ACCELERATE, is led by Dr. Mohsen Taheri-Andani, an assistant professor in the J. Mike Walker ’66 Department of Mechanical Engineering at Texas A&M University. To secure the funding, Dr. Taheri-Andani partnered with Dr. Yash Parikh, a process engineering consultant at EOS who graduated with a doctorate in mechanical engineering from Texas A&M in 2021.
A central aspect of this project is validating operational qualification through detailed tasks and documentation, which is vital for confirming the AM process to consistently meet material specification requirements. Additionally, the project will tackle various aspects of AM operations — from facility controls and operator training to software configuration and process monitoring. Special emphasis will be placed on feedstock control, machine calibration, and post-processing operations, ensuring thorough quality assurance.
Dr. Taheri-Andani will lead a research team supporting the project by establishing repeatable and reproducible AM operations, emphasizing installation qualification, operational qualification, and product qualification.
"Leading this groundbreaking project is a privilege. The goal is to enhance the AM landscape and substantially reduce the time and cost associated with operational qualification,” said Dr. Taheri-Andani. “Collaborating with brilliant minds, including our alumni like Yash, makes this journey even more rewarding."
Dr. Parikh will support Dr. Taheri-Andani and his research team with expert guidance on a novel data-driven operational qualification approach as well as best practices to expedite it. “Reuniting with my alma mater, Texas A&M University, for such a transformative project is an honor,” said Dr. Parikh. “This collaboration goes beyond innovation; it’s about positively impacting the industry and reinforcing the enduring bond between alumni and the university. This prestigious award is a testament to the unwavering dedication of faculties and students within the Mechanical Engineering Department who are committed to driving innovation and excellence in advanced technologies, including AM. With EOS showcasing its support through a cost-sharing pledge, I am excited to embark on this journey as one of the research partners and dedicated to demonstrating a steadfast commitment to realize the desired production results for customers and the AM community at large.”
This collaborative effort brings together a comprehensive skilled team, including research partners from the University of Michigan and two AM companies — Addiguru, LLC, and Beehive Industries — all contributing their expertise to the project.
Additionally, this project will receive support from Freemelt, a company providing Electron Powder Bed Fusion (E-PBF) equipment and services, leveraging the open-source and cutting-edge E-PBF system, FreemeltONE. Daniel Gidlund, CEO, stated, "Working together with Dr. Taheri-Andani, the project aims to push the boundaries of qualification in metal AM, which is a critical aspect for AM industrialization. We are very glad and excited to support and be engaged with Texas A&M Engineering Experiment Station under this critical America Makes project.”
“I am committed to advancing AM and highlighting the importance of collaborative research and industry-academia partnerships,” said Dr.Taheri-Andani. “This project, aimed at streamlining operational qualification, is poised to make a significant impact on the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of AM processes.”
###
END
Reducing operation qualification time and cost in additive manufacturing
America Makes supports a project led by Texas A&M Professor Dr. Mohsen Taheri-Andani and alumni Dr. Yash Parikh.
2024-08-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
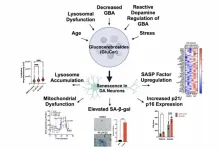
Lipid accumulation drives cellular senescence in dopaminergic neurons
2024-08-13
"These findings align with our previous results in dopaminergic neurons in highlighting a central role for lipid accumulation in the senescence of DA neurons."
BUFFALO, NY- August 13, 2024 – A new research perspective was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science), Volume 16, Issue 14 on July 19, 2024, entitled, “Lipid accumulation drives cellular senescence in dopaminergic neurons.”
As highlighted in the Abstract of this perspective, Parkinson’s disease (PD) is an age-related movement disorder caused ...
The Hastings Center awarded $1.5 million by PCORI to study organizational trustworthiness and community-engaged research
2024-08-13
A research team at The Hastings Center has been approved for $1.5 million in funding by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) to study organizational trustworthiness as it relates to community-engaged research. Led by Virginia A. Brown, PhD, a research scholar at The Hastings Center, the study will be the first to investigate the role of organizational trustworthiness in shaping research engagement processes and outcomes.
Measures to assess organizational trustworthiness as it relates to research ...
Dairy nutrition is leading the sustainability charge
2024-08-13
Philadelphia, August 13, 2024 – Research into reducing greenhouse gas emissions from livestock has increased exponentially as the dairy and agriculture sectors work together toward shared sustainability and efficiency goals. While this progress has been made in all areas of dairy science research, from genetics to animal health and welfare, dairy nutrition has emerged as a particularly impactful area for emission reduction. In a new invited review in the Journal of Dairy Science, a preeminent voice in sustainability and dairy nutrition synthesizes ...
A new method for protection from plant pathogens could help support global food security.
2024-08-13
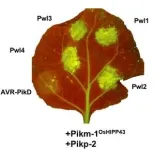
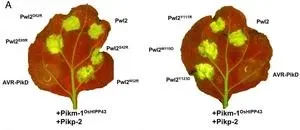
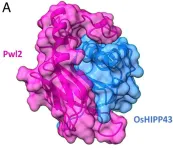
By modifying a plant intracellular immune receptor (NLR), researchers have developed a potential new strategy for resistance to rice blast disease, one of the most important diseases threatening global food security. The collaborative team from the UK and Japan have recently published their research in PNAS. This could have implications for future approaches to crop protection and ultimately global food supply stability.
The research was led from the Department of Biochemistry and Metabolism at the John Innes Centre, with partners at The Sainsbury Laboratory, University of East Anglia, and the Division of Genomics and Breeding, Iwate Biotechnology Research Center, Japan. For a ...
Halogen bonding for selective electrochemical separation, path to sustainable chemical processing demonstrated
2024-08-13
With a new polymer that only attracts certain substances from solutions when electrically activated, researchers have taken a major step towards sustainable chemical separation.
A team based at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign has reported the first demonstration of selective electrochemical separation driven by halogen bonding in the journal JACS Au. This was achieved by engineering a polymer that modulates the charge density on a halogen atom when electricity is applied. The polymer then attracts only certain targets – such as halides, oxyanions, and even organic molecules – from organic solutions, ...
Study reveals urban trees suffer more from heat waves and drought than their rural counterparts
2024-08-13
NEW YORK, August 13, 2024 — A recently published study in Ecological Applications details how trees in New York City and Boston are more negatively impacted by heat waves and drought than trees of the same species in nearby rural forests. The finding, made by researchers at the Advanced Science Research Center at the CUNY Graduate Center (CUNY ASRC), highlights the challenges urban trees face in the context of climate change and underscores the importance of tailored urban forestry management as ...
New $7.7 million grant to propel search for medications for brain disorders
2024-08-13
JUPITER, Fla. — Children born with a damaged gene needed for healthy brain development, SYNGAP1, experience seizures, sensory processing disorders, difficulty speaking, intellectual disability, and autism-like behaviors. It’s a condition without any treatments, one that’s hard both on parents and children, said Gavin Rumbaugh, Ph.D., a neuroscientist at The Herbert Wertheim UF Scripps Institute for Biomedical Innovation & Technology.
Rumbaugh and a team of scientists from the institute have been awarded a five-year grant from the National Institute of Mental Health worth $7.7 million to work toward a treatment. Their goal is to ...
National Cancer Institute awards grant to Hollings researchers focused on depression among cancer survivors
2024-08-13
Depression is common among people with likely incurable cancer – understandably so. But studies have shown that it can be treated, and if the goal is for individuals to be able to engage as much as possible with family, friends, hobbies or whatever gives them joy and purpose in whatever amount of time they have, then treating depression becomes imperative.
That’s not so easy, though, as patients may face a shortage of mental health workers, difficulties with transportation and continuing stigma around mental health issues.
Evan Graboyes, M.D., a head and neck surgical oncologist and director of Survivorship ...
MSK Research Highlights, August 13, 2024
2024-08-13
New research from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK) found patients with non-small cell lung cancer brain metastases may benefit from up-front stereotactic radiosurgery; identified a connection between antibiotic use and autoimmune diseases; and uncovered a previously unknown structural role for messenger RNAs in the cytoplasm of cells.
Patients with non-small cell lung cancer brain metastases may benefit from upfront stereotactic radiosurgery
For patients with non-small cell lung cancer that has spread to the brain, targeted therapies called ...
Study finds that dopaminergic medication improves sleep quality in Parkinson’s disease patients
2024-08-13
A study involving 22 Parkinson’s disease (PD) patients has shown that use of the dopaminergic drug levodopa improves sleep quality. When the patients took the drug, the number of times they woke up during the night fell 25% and the amount of time they remained awake fell 30% on average.
The investigation was conducted with FAPESP’s support by researchers at São Paulo State University (UNESP) in Brazil, and the University of Grenoble Alpes (UGA) in France. An article reporting the results is published in ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
[Press-News.org] Reducing operation qualification time and cost in additive manufacturingAmerica Makes supports a project led by Texas A&M Professor Dr. Mohsen Taheri-Andani and alumni Dr. Yash Parikh.