(Press-News.org) Researchers from the RIKEN Center for Brain Science (CBS) in Japan have discovered a region of the brain that encodes where an animal is planning to be in the near future. Linked to internal maps of spatial locations and past movements, activity in the newly discovered grid cells accurately predicts future locations as an animal travels around its environment. Published in Science on August 15, the study helps explain how planned spatial navigation is possible.
It might seem effortless, but navigating the world requires quite a bit of under-the-hood brain activity. For example, simply walking around a supermarket picking up groceries requires internalized maps of the outside world, information about one’s own changing position and speed, and memories about where one has been and what one is trying to buy.
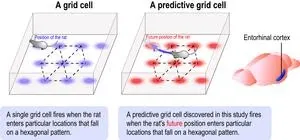
Much of this kind of information is contained in cells within two connected parts of the brain – the hippocampus and the medial entorhinal cortex, or MEC for short – which are extremely similar in all mammals, from rats to humans. In particular, the MEC contains maps of an animal’s current location in space, a discovery that won the Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine in 2014.
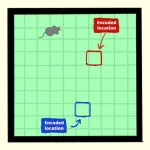
The new study focuses on the MEC, but not on the stored information needed for spatial navigation or an animal’s current location. Instead, the experiments performed by Shigeyoshi Fujisawa and Ayako Ouchi from RIKEN CBS concentrate on how this brain region creates maps of future positions, which are continuously updated as animals move. While rats traversed an open square field in search of freely available water that was moved around to different locations, the researchers recorded all movements, which included hundreds of trajectories. At the same time, they recorded the activity from individual brain cells in the MEC. Afterward, they checked how well the brain activity over time matched the rats’ changing positions.
They found that the activity of some brain cells in the MEC created an internal grid that mapped future positions within the field. For example, an MEC cell might encode a certain location in the field, but only when a rat reached a spot 30 cm to 40 cm earlier in a route that eventually crossed that location—regardless of which direction the rat was coming from. This is very different from the grid cells that helped win the Nobel Prize, which become active only when an animal is currently in a particular location. The authors call the newly discovered neurons “predictive grid cells”, and conducted several follow up experiments to get a better idea of what exactly they encode.
First, they tested whether the newly discovered grid cells predicted the future location in terms of distance or time from the present. They found that both were encoded, although the “gridness” of the cells was higher when considering distance. They also found that future positions were faithfully encoded in different situations, whether the rats were trying to go to specific targets or if they were randomly foraging for food. This means that the function of the predictive grid cells is not limited to goal-directed behavior.
“This study provides important insights into the mechanisms of spatial navigation and episodic memory formation in hippocampal and entorhinal cortical circuits,” says Fujisawa. “In the future, we would like to clarify the mechanism by which such predictive grid cells are organized.”
END
Navigating the future: brain cells that plan where to go
2024-08-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The brain creates three copies for a single memory
2024-08-15
The ability to turn experiences into memories allows us to learn from the past and use what we learned as a model to respond appropriately to new situations. For this reason, as the world around us changes, this memory model cannot simply be a fixed archive of the good old days. Rather, it must be dynamic, changing over time and adapting to new circumstances to better help us predict the future and select the best course of action. How the brain could regulate a memory’s dynamics was a mystery – until multiple memory copies ...
Breakthrough addresses sex-related weight gain and disease
2024-08-15
ITHACA, N.Y. -- A decline in estrogen during menopause causes changes in body fat distribution and associated cardiovascular and metabolic disease, but a new study identifies potential therapies that might one day reverse these unhealthy shifts.
The study, “Cxcr4 Regulates a Pool of Adipocyte Progenitors and Contributes to Adiposity in a Sex-Dependent Manner,” was published Aug. 5 in Nature Communications.
The researchers discovered that a receptor called Cxcr4, when blocked in mice, reduced the tendency of fat stem cells to develop into white fat, also called white adipose tissue. This treatment could potentially be combined with low doses of estrogen therapy to cut ...
As human activities expand in Antarctica, scientists identify crucial conservation sites
2024-08-15
A team of scientists led by the University of Colorado Boulder has identified 30 new areas critical for conserving biodiversity in the Southern Ocean surrounding Antarctica. In a study published Aug. 15 in the journal Conservation Biology, the researchers warn that without greater protection to limit human activities in these areas, native wildlife could face significant population declines.
“Many animals are only found in the Southern Ocean, and they all play an important role in its ecosystem,” said Cassandra Brooks, the paper’s senior author and associate professor in the Department of Environmental Studies and a fellow of the ...
Solutions to Nigeria’s newborn mortality rate might lie in existing innovations, finds review
2024-08-15
The review, led by Imperial College London’s Professor Hippolite Amadi, argues that Nigeria’s own discoveries and technological advancements of the past three decades have been “abandoned” by policymakers.
The authors argue that too many Nigerian newborns, clinically defined as infants in the first 28 days of life, die of causes that could have been prevented had policymakers adopted recent in-country scientific breakthroughs.
Led by Professor Amadi of Imperial’s Department of Bioengineering, who received the Nigeria Prize ...
Study highlights sex differences in notified infectious disease cases across Europe
2024-08-15
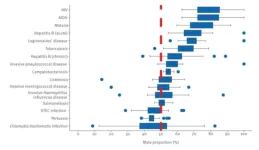
A study published in Eurosurveillance analysing 5.5 million cases of infectious diseases in the European Union/European Economic Area (EU/EEA) over 10 years has found important differences in the relative proportion of notified male versus female cases for several diseases. The proportion of males ranged on average from 40-45% for pertussis and Shiga toxin-producing Escherischia coli (STEC) infections to 75-80% for HIV/AIDS.
“Although this study was not able to fully explain the differences observed across countries and diseases, it offers some interesting leads,” said Julien Beauté, principal expert in general surveillance at the European ...
Nanobody inhibits metastasis of breast tumor cells to lung in mice
2024-08-15
“In the present study we describe the development of an inhibitory nanobody directed against an extracellular epitope present in the native V-ATPase c subunit.”
BUFFALO, NY- August 15, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on August 14, 2024, entitled, “A nanobody against the V-ATPase c subunit inhibits metastasis of 4T1-12B breast tumor cells to lung in mice.”
The vacuolar H+-ATPase (V-ATPase) is an ATP-dependent proton pump that functions to control the pH of intracellular compartments ...
Detecting machine-generated text: An arms race with the advancements of large language models
2024-08-15
Machine-generated text has been fooling humans for the last four years. Since the release of GPT-2 in 2019, large language model (LLM) tools have gotten progressively better at crafting stories, news articles, student essays and more, to the point that humans are often unable to recognize when they are reading text produced by an algorithm. While these LLMs are being used to save time and even boost creativity in ideating and writing, their power can lead to misuse and harmful outcomes, which are already ...
Nearly 25% of European landscape could be rewilded
2024-08-15
Europe's abandoned farmlands could find new life through rewilding, a movement to restore ravaged landscapes to their wilderness before human intervention. A quarter of the European continent, 117 million hectares, is primed with rewilding opportunities, researchers report August 15 in the Cell Press journal Current Biology. They provide a roadmap for countries to meet the 2030 European Biodiversity Strategy's goals to protect 30% of land, with 10% of those areas strictly under conservation.
The team ...
Emergency departments could help reduce youth suicide risk
2024-08-15
A study of over 15,000 youth with self-inflicted injury treated in Emergency Departments (EDs) found that around 25 percent were seen in the ED within 90 days before or 90 days after injury, pointing to an opportunity for ED-based interventions, such as suicide risk screening, safety planning, and linkage to services. Nearly half of ED visits after the self-inflicted injury encounter were for mental health issues.
“Self-inflicted injury is an important predictor of suicide risk,” said Samaa Kemal, MD, MPH, emergency medicine physician at Ann & Robert H. Lurie ...
Uterus transplant in women with absolute uterine-factor infertility
2024-08-15
About The Study: Uterus transplant was technically feasible and was associated with a high live birth rate following successful graft survival. Adverse events were common, with medical and surgical risks affecting recipients as well as donors. Congenital abnormalities and developmental delays have not occurred to date in the live-born children.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Liza Johannesson, MD, PhD, email Liza.Johannesson@bswhealth.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.11679)
Editor’s ...