(Press-News.org) Novel findings attend to attitudes of the stigmatized, rather than stigmatizers
Past research identified perception of promiscuity and assumptions that PrEP users are HIV-positive as key drivers of perceived stigma
Perception of stigma is highest among those who believe their sexual behavior puts them at risk for HIV
Knowing others who use PrEP does not influence one’s fear of potential discrimination
CHICAGO --- Public health messaging that drives stigma around Pre-exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP), a medication that can reduce HIV risk by up to 99%, appears to play a role in uptake of the medication. While the potential mismarketing of the drug is well-understood and has been studied extensively, few studies have examined factors associated with the perception of stigma among PrEP users.
A new study conducted by scientists at Northwestern University found that among PrEP users, many fear using PrEP puts them at risk of discrimination, even when they know other people who use the medication.
The study, published Aug. 16 in the journal Sexes, speculates about causes for self- stigma and recommends mitigation strategies to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which aims to reduce new HIV infections in the United States by 90% by 2030.
“We are among the first to explore the perception of stigma attached to PrEP use among current PrEP users,” said quantitative researcher Shahin Davoudpour, the study’s first and corresponding author. “Typically, stigma-focused studies pay attention to stigmatizers rather than the stigmatized. Our findings are also novel as they show higher stigma perception among PrEP users — the group who we would expect to express the least stigmatizing behavior.”
Davoudpour is a research assistant professor of medical social sciences at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine with a portfolio of research grounded in social stigma and HIV/AIDS.
Unlike stigma or discrimination on their own — which have been the topics of previous research — perceived stigma is a powerful social motivator, defined as the anticipation or fear of being discriminated against. By looking at the stigmatized rather than stigmatizers, the scientists hoped to gain better insight into why uptake of the medication has been slower than anticipated, as well as why PrEP users tend to be inconsistent in taking it.
Perceived stigma can be driven by several factors, often stemming from broader societal biases and misinformation about sexual practices and HIV risk. Davoudpour’s team examined two common measures of perceived stigma in PrEP use: the assumption that PrEP users are seen as promiscuous and the perception that people who use PrEP are HIV-positive.
The study used data from the baseline survey of an online study (which enrolled participants between 2017 and 2019) of a racially diverse population of over 3,000 sexual minority men, trans men and women, and non-binary individuals in the U.S. The “Keeping it LITE Study” collected data about PrEP use, persistence and attitudes, which the team ran through models to assess several stigma factors.
Davoudpour called the findings “significant and counter-intuitive,” including the conclusions that perception of stigma associated with PrEP remains high among PrEP users, and that that perceived stigma is not significantly reduced by knowing others who use PrEP.
“Current PrEP users are more likely to believe that PrEP users are promiscuous — a stigma marker — than those who have never used the medication,” Davoudpour said.
“PrEP was initially promoted for individuals most vulnerable to HIV — especially those with multiple sex partners and inconsistent condom use — thus its use has been inexorably tied to promiscuity,” said study co-author Gregory Phillips II, an associate professor of medical social sciences and preventative medicine at Feinberg. “However, PrEP can benefit a variety of people, including those in monogamous serodiscordant relationships (one partner is HIV-positive and the other is HIV-negative), but current messaging doesn't reflect the broader array of potential PrEP users.”
Current marketing campaigns involving HIV preventatives tend to repeatedly highlight benefits of PrEP. Instead, the authors argue, “public health messaging can shift its focus to decreasing the perception of PrEP stigma among those vulnerable to HIV” via sex-positive messaging that disconnects PrEP from promiscuity and emphasizes its use among vulnerable populations.
This work was in part supported by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, the National Institute of Mental Health and the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (grant numbers UH3AI133676 and UG3AI133676).
END
Current HIV prevention medication users often stigmatize other PrEP users as ‘promiscuous’
Public health campaigns for Pre-exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP) should focus on sex-positive messaging
2024-08-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How "winner and loser effects" impact social rank in animals - and humans
2024-08-19
Research has shown that in many animals, the winners of a fight are more likely to win subsequent contests, while the losers tend to lose their following fights. In experiments where male stickleback fish were randomly introduced to another fish, 65% of the winning fish won the second match, while all losing fish lost the second contest.
Such winner and loser effects can greatly influence individual behavior and fitness. This effect happens in humans as well. In "Winner and Loser Effects and Social Rank in Humans," recently published in The Quarterly Review of Biology, authors Noah M. T. Smith and Reuven ...
Research study examines Alzheimer’s disease drug on tissue samples from people with Down syndrome
2024-08-19
People with Down syndrome are likely to develop Alzheimer’s disease at a young age, with autopsy studies showing that by age 40 years, the brains of individuals with Down syndrome have amyloid plaques. Yet people with Down syndrome have been excluded from or underrepresented in clinical trials of new therapies for treating AD. Lecanemab, which has been shown to target and remove beta-amyloid plaques, has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to treat AD early in the disease’s progression. ...
International Society of Biomechanics recommendations for wearables-based motion capture
2024-08-19
Dr. Reed Gurchiek, an Assistant Professor in the Department of Bioengineering, Clemson University, and an Early-stage Investigator, was a co-first author of a recent publication in the Journal of Biomechanics titled “International Society of Biomechanics recommendations on the definition, estimation, and reporting of joint kinematics in human motion analysis applications using wearable inertial measurement technology”. A collaborative effort that incorporated feedback from the biomechanics community has produced recommendations in five categories: sensor characteristics ...
Rutgers researchers discover new way to control the sense of touch
2024-08-19
Rutgers researchers have found a new way to manage the receptors that control the sense of touch, which could lead to treating chronic pain more effectively.
“Identifying a natural molecule that specifically reduces pain sensitivity offers hope for new therapeutic strategies in the management of pain,” said Tibor Rohacs, a professor in the Department of Pharmacology, Physiology and Neuroscience at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School and a member of the Rutgers Brain Health Institute. “Our goal is to translate these findings into effective treatments that improve the quality of life for people suffering from chronic ...
New UH study targets early signs of vision loss in diabetic patients
2024-08-19
A $3.3 million study at the University of Houston College of Optometry will track the health of patients with prediabetes and diabetes to find out who might develop eye problems and be at risk for future vision loss. The study is being led by Wendy Harrison, associate professor, and is underwritten by the National Eye Institute.
Vision loss in type 2 diabetes results from diabetic retinopathy, caused by damage to blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive layer of tissue in the back of your eye. The disease can appear without warning.
“The ...
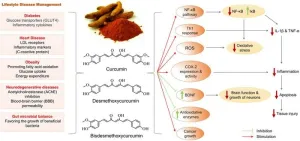
Herbal-based nutraceuticals in management of lifestyle diseases: Experience from Indian population
2024-08-19
Lifestyle diseases, also known as non-communicable diseases (NCDs), have emerged as a major health burden globally, including in India. These diseases, such as obesity, diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, and metabolic disorders, are primarily caused by unhealthy lifestyle choices like sedentary behavior, poor dietary habits, and stress. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), NCDs are responsible for 41 million deaths annually, accounting for 74% of all global deaths. Notably, 86% of these premature deaths occur in low- and middle-income countries.
The increasing prevalence of lifestyle diseases ...
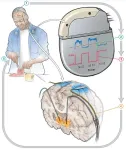
Taming Parkinson’s disease with intelligent brain pacemakers
2024-08-19
Media Contact: Robin.Marks@ucsf.edu, (415) 502-6397
Subscribe to UCSF News
Taming Parkinson’s Disease with Intelligent Brain Pacemakers
UCSF studies show personalized, self-adjusting, neuromodulation has the potential to enhance movement and sleep.
Two new studies from UC San Francisco are pointing the way toward round-the-clock personalized care for people with Parkinson’s disease through an implanted device that can treat movement problems during the day and insomnia at night.
The approach, called adaptive deep brain stimulation, or aDBS, uses methods derived from AI to ...
Self-adjusting brain pacemaker may help reduce Parkinson’s disease symptoms
2024-08-19
A small feasibility study funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) found that an implanted device regulated by the body’s brain activity could provide continual and improved treatment for the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease (PD) in certain people with the disorder. This type of treatment, called adaptive deep brain stimulation (aDBS), is an improvement on a technique that has been used for PD and other brain disorders for many years. The study found aDBS was markedly more effective at controlling PD symptoms compared to conventional DBS treatments.
“This study marks a big step forward towards ...
Florida’s red flag gun law and firearm and nonfirearm homicide and suicide rates
2024-08-19
About The Study: Although firearm homicide mortality increased after Florida’s red flag law enactment (permitting the temporary removal of firearms by law enforcement officers from individuals posing a danger to themselves or others), this increase was lower than expected compared with its synthetic control, resulting in an 11% rate reduction (0.73 fewer deaths per 100,000). There were no differences from expected mortality rates for nonfirearm homicide, firearm suicide, or nonfirearm suicide.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Catherine Gimbrone, MPH, email c.gimbrone@columbia.edu.
To ...
Number of pediatric inpatient psychiatric beds in the U.S. did not increase 2017-2020 despite youth mental health crisis
2024-08-19
U.S. pediatric inpatient psychiatric bed capacity did not change 2017 – 2020, despite increases in pediatric mental health emergency visits, according to a study published in JAMA Pediatrics. Researchers also found substantial geographic variation in inpatient psychiatric bed capacity per 100,000 children, ranging from zero in Alaska to 75 in Arkansas. Over 90 percent of pediatric inpatient beds are in urban centers, raising concerns for youth living in rural areas.
“Access to psychiatric inpatient care for youth is insufficient to meet the growing demand, forcing patients to wait for hours or even days in emergency departments or on medical units until a psychiatric bed becomes ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
Digital microsteps as scalable adjuncts for adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
[Press-News.org] Current HIV prevention medication users often stigmatize other PrEP users as ‘promiscuous’Public health campaigns for Pre-exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP) should focus on sex-positive messaging