(Press-News.org) The idea of electrically stimulating a brain region called the central thalamus has gained traction among researchers and clinicians because it can help arouse subjects from unconscious states induced by traumatic brain injury or anesthesia, and can boost cognition and performance in awake animals. But the method, called CT-DBS, can have a side effect: seizures. A new study by researchers at MIT and Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) who were testing the method in awake mice, quantifies the probability of seizures at different stimulation currents and cautions that they sometimes occurred even at low levels.
“Understanding production and prevalence of this type of seizure activity is important because brain stimulation-based therapies are becoming more widely used,” said co-senior author Emery N. Brown, Edward Hood Taplin Professor of Medical Engineering and Computational Neuroscience in The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory, the Institute for Medical Engineering and Science, the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences and the Center for Brains Minds and Machines (CBMM) at MIT.
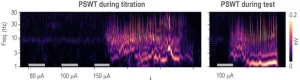
In the brain, the seizures associated with CT-DBS occur as “electrographic seizures” which are bursts of voltage among neurons across a broad spectrum of frequencies. Behaviorally, they manifest as “absence seizures” in which the subject appears to take on a blank stare and freezes for about 10-20 seconds.
In their study, the researchers were hoping to determine a CT-DBS stimulation current— in a clinically relevant range of under 200 microamps—below which seizures could be reliably avoided.
In search of that ideal current, they developed a protocol of starting brief bouts of CT-DBS at 1 microamp and then incrementally ramping the current up to 200 microamps until they found a threshold where an electrographic seizure occurred. Once they found that threshold, then they tested a longer bout of stimulation at the next lowest current level in hopes that an electrographic seizure wouldn’t occur. They did this for a variety of different stimulation frequencies. To their surprise, electrographic seizures still occurred 2.2 percent of the time during those longer stimulation trials (i.e. 22 times out of 996 tests) and in 10 out of 12 mice. At just 20 microamps, mice still experienced seizures in 3 out of 244 tests, a 1.2 percent rate.
“This is something that we needed to report because this was really surprising,” said co-lead author Francisco Flores, a research affiliate in The Picower Institute and CBMM, and an instructor in anesthesiology at MGH where Brown is also an anesthesiologist. Isabella Dalla Betta, a technical associate in The Picower Institute, co-led the study published in Brain Stimulation.
Stimulation frequency didn’t matter for seizure risk but the rate of electrographic seizures increased as the current level increased. For instance, it happened in 5 out of 190 tests at 50 microamps, and 2 out of 65 tests at 100 microamps. The researchers also found that when an electrographic seizure occurred, it did so more quickly at higher currents than at lower levels. Finally, they also saw that seizures happened more quickly if they stimulated the thalamus on both sides of the brain vs. just one side. Some mice exhibited behaviors similar to absence seizure, though others became hyperactive.
It is not clear why some mice experienced electrographic seizures at just 20 microamps while two mice did not experience the seizures even at 200. Flores speculated that there may be different brain states that change the predisposition to seizures amid stimulation of the thalamus. Notably, seizures are not typically observed in humans who receive CT-DBS while in a minimally conscious state after a traumatic brain injury or in animals who are under anesthesia. Flores said the next stage of the research would aim to discern what the relevant brain states may be.
In the meantime, the study authors wrote, “EEG should be closely monitored for electrographic seizures when performing CT-DBS, especially in awake subjects.”
The paper’s co-senior author is Matt Wilson, Sherman Fairchild Professor in The Picower Institute, CBMM, and the departments of Biology and Brain and Cognitive Sciences. In addition to Dalla Betta, Flores, Brown and Wilson, the study’s other authors are John Tauber, David Schreier, and Emily Stephen.
Support for the research came from The JPB Foundation, The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory, George J. Elbaum (MIT ‘59, SM ‘63, PhD ‘67), Mimi Jensen, Diane B. Greene (MIT, SM ‘78), Mendel Rosenblum, Bill Swanson, annual donors to the Anesthesia Initiative Fund; and the National Institutes of Health.
END
Study assesses seizure risk from stimulating thalamus
In awake mice, researchers found that even low stimulation currents could sometimes still cause electrographic seizures
2024-08-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Machine learning approach towards quality assurance, challenges and possible strategies in laboratory medicine
2024-08-21
The integration of machine learning (ML) and automation in laboratory medicine marks a significant advancement, revolutionizing diagnostic accuracy and operational efficiency. This review examines the impact of these technologies, highlighting both their potential benefits and the challenges they pose. The advent of automation combined with ML has introduced new capabilities in pattern detection, predictive analytics, and sophisticated data handling, which are crucial for navigating the complexities of biomedical data. However, these advancements also bring concerns regarding data privacy, the need for stringent validation procedures, and the integration of new technologies into existing ...
Survival tactics: AI-driven insights into chromatin changes for winter dormancy in axillary buds
2024-08-21
Evolution has enabled plants to survive under adverse conditions. The winter bud of a plant is a crucial structure that establishes adaptability. Depending on environmental and intrinsic conditions, buds can transition between growth and dormancy. The three dormancy phases are determined by signals triggering each phase: ecodormancy, influenced by environmental factors; paradormancy, promoted by other plant organs; and endodormancy, maintained by internal signals within the bud. Paradormant buds enter endodormancy in response to changes in day length and/or low temperature in autumn, while endo-and eco-dormant phases occur ...
New molecules from IOCB Prague decrease appetite and protect the brain against Alzheimer’s-type diseases
2024-08-21
Scientists on the team of Dr Lenka Maletínská have developed a promising new compound derived from one of the peptides naturally occurring in the brain. Its application may contribute to the addressing of two major health challenges of the modern days: obesity and Alzheimer's disease. The neuropeptide CART is primarily associated with the regulation of food intake. Its modified version, created at the Institute of Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry of the Czech Academy of Sciences, shows better stability and is more effective. It suppresses appetite and protects the brain by reducing the pathogenicity of the tau protein, which is associated with ...
More academic freedom leads to more innovation
2024-08-21
The innovative strength of a society depends on the level of academic freedom. An international team involving the Technical University of Munich (TUM) has now proven this relationship for the first time. The researchers analyzed patent applications and patent citations in a sample from around 160 countries over the 1900–2015 period in relation to indicators used in the Academic Freedom Index. In view of the global decline in academic freedom over the past 10 years, the researchers predict a loss ...
Facts alone fall short in correcting science misinformation
2024-08-21
SPOKANE, Wash. – Just the facts may not be enough to overcome misinformation, a recent study indicates.
In an experiment, 152 college students who had been exposed to misinformation read one of two articles intended to give them the correct, scientifically backed information. Those who read an expository article that had “just the facts” retained more misconceptions than those who read an article with a refutation—meaning it specifically called out the false claims before presenting the facts.
The ...
Chalk-based coating creates a cooling fabric
2024-08-21
DENVER, Aug. 21, 2024 — In the scorching heat of summer, anyone who spends time outside — athletes, landscapers, kids at the park or beachgoers — could benefit from a cooling fabric. While there are some textiles that reflect the sun’s rays or transfer heat away from the body, current options require boutique fibers or complex manufacturing processes. But now, researchers report a durable chalk-based coating that cools the air underneath treated fabric by up to 8 degrees Fahrenheit.
Evan D. Patamia, ...
Pilot study uses recycled glass to grow plants for salsa ingredients
2024-08-21
DENVER, Aug. 21, 2024 — Tortilla chips and fresh salsa are tasty in themselves, but they could be even more appealing if you grow the ingredients in a sustainable way. Researchers report that cilantro, bell pepper and jalapeño can be cultivated in recycled glass from discarded, pulverized bottles like those from beer or soda. The pilot study found that partially substituting soil in a planter with recycled glass fragments speeds up plant development and reduces unwanted fungal growth.
The researchers will present their results at the fall meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ACS Fall 2024 is ...
MIT engineers’ new theory could improve the design and operation of wind farms
2024-08-21
The blades of propellers and wind turbines are designed based on aerodynamics principles that were first described mathematically more than a century ago. But engineers have long realized that these formulas don’t work in every situation. To compensate, they have added ad hoc “correction factors” based on empirical observations.
Now, for the first time, engineers at MIT have developed a comprehensive, physics-based model that accurately represents the airflow around rotors even under extreme conditions, such as when the blades are operating at high forces and speeds, or are angled in certain directions. The model could improve the way rotors themselves ...
Proposed risk factor tool finds heart failure rates are higher among American Indian adults
2024-08-21
Research Highlights:
An analysis based on a proposed heart failure risk prediction tool reveals that the incidence of heart failure may be 2- to 3-fold higher among American Indian adults compared to people in other population groups.
The risk prediction equation focused on diabetes control and kidney damage indicates that smoking, Type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, previous heart attack and diabetes-related kidney damage are associated with increased risk of developing heart failure among American Indian adults.
The findings suggest a need to develop population-level preventive strategies in American Indian communities, researchers said.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 ...
Breakthrough in cost-effective production of cultivated meat
2024-08-21
A groundbreaking study demonstrates the first cost-effective method for producing cultivated meat. The study shows that continuous manufacturing addresses the key challenges of scalability and cost, potentially making cultivated meat accessible to everyday consumers and contributing to a more sustainable and ethical food system.
In an extraordinary stride for cellular agriculture, Professor Yaakov Nahmias, founder of Believer Meats, and a multidisciplinary team at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem and the cultivated meat industry unveiled a pioneering continuous manufacturing process ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
[Press-News.org] Study assesses seizure risk from stimulating thalamusIn awake mice, researchers found that even low stimulation currents could sometimes still cause electrographic seizures