An active multi-beam antenna design method and its application for the future 6G satellite network
2024-08-21
(Press-News.org)
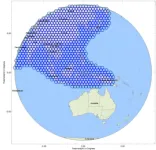
First, the payload requirements and problems faced by traditional multi-beam antenna are described. The user beam of the VHTS payload system mainly uses Ka-band multi-beam antenna for a large range of area coverage, and the number of beams in the coverage area is not less than 500, usually using 7-color frequency reuse scheme(Fig. 2). At present, the spaceborne multi-beam antenna technology applied to high-throughput communication satellites is usually divided into multi-aperture multi-beam antenna and passive multi-feed multi-beam antenna. Multi-aperture multi-beam antenna is usually composed of 3 to 4 reflector antennas, when facing the demand of super-large coverage, the edge beam gain is rapidly reduced, the beam is deformed, and the sidelobe is increased. The passive multi-feed multi-beam antenna is based on the waveguide beam forming system, which usually consists of 2 reflector antennas, and the edge beam in a large coverage area can be compensated by optimizing the amplitude and phase excitation coefficients of multiple feeds. The number of feeds of typical products of this technology is usually 2.5 to 4 times the number of beams. For the demand of more than 500 beams, the number of feeds is to huge and complicated for satellite engineering applications. Additionally, active multi-feed multi-beam antennas are widely used in mobile communication satellites. This type of multi-beam antenna usually adopts a large mesh reflector combined with multi-feed array which have been put forward to achieve primary sub-beam defocusing, thereby achieving high-level over-lap of all sub-beams. The gain and sidelobe of the beams are optimized through full array synthesis. The payload system basically adopts 12-color frequency reuse, and the C/I is about 12 dB, which cannot meet the requirements of 7-color frequency reuse and C/I≥15 dB for VHTS. Meanwhile, there are too many feeds to form a single beam, and the beam forming network is too complicated when facing the huge number of beams.
Figure 2 VHTS coverage for Asia-Pacific region(976 0.25°beams)
Then, the scholars describe the design theory and optimization method of active multi-beam antenna and propose a new design method of active multi-beam antenna based on multi-target cooperation and multi-feed amplitude and phase weighted optimization algorithms. The method takes the amplitude and phase excitation coefficient of feeds as optimization variables, establishes objective functions based on the number of synthetic feeds, the gain of synthetic beams and different C/I, and obtains a balanced optimal solution that meets the performance requirements. In order to solve the problem that it is difficult to obtain the optimal solution for complex nonlinear optimization caused by multiple objective functions solving the target coupling and the problem that the optimization speed is too slow, this paper proposes the surrogate model of convolutional self-encoder based on artificial intelligence (AI) technology for the multi-objective optimization solution, which efficiently completes the search for the optimal beam excitation coefficient. The method concludes 8 steps. Step 1: The GRASP model is carried out for the multi-beam antenna. GRASP is used to analyze the main lobe gain, sidelobe level, and beam direction results of the sub-beam pattern of each feed. Step 2: Python-GRASP is adopted to co-simulate the typical beam position parameters (ucenterMR, vcenterMR) of the synthesized beam, the number L of feeds involved in the synthesis, the amplitude/phase weights aRi and pRi of each feed, and the performance of the synthesized beam under the disturbance of parameters. Step 3: The convolutional auto-encoder proxy model is constructed experimentally, the parameters in the model are determined, and the convolutional autoencoder is trained. Step 4: Determine whether the model fits according to the test set and the surrogate model prediction results. If yes, save the above nonlinear related parameters; otherwise, repeat Step 3. Step 5: Initialize the max-min algorithm, debug the parameters in the max-min algorithm, design the optimization objective function according to the antenna optimization index, and load the trained convolutional autoencoder proxy model. Step 6: Calculate the residual value (main lobe gain, sidelobe level, and beam direction) in the 2-dimensional sampling point (u, v) of the spatial electric field corresponding to the optimal solution in the max-min algorithm, and then the algorithm performs iterative optimization. Step 7: Determine whether the residual (main lobe gain, sidelobe level, and beam pointing) values in the 2-dimensional sampling point (u, v) of the spatial electric field corresponding to the optimal solution meet the set optimization index. If the optimization index is met, the algorithm stops the iteration; otherwise, it returns to Step 6. Step 8: Put the number L of feeds and the corresponding optimal solution of amplitude/phase weights into GRASP to calculate and verify the accuracy of the optimization results of this scheme. The active multi-beam antenna designed by the proposed method can make up for the scanning loss very well (Fig. 8).
Fig. 8. Pattern of beams at different wave positions formed by an active multi-beam antenna.
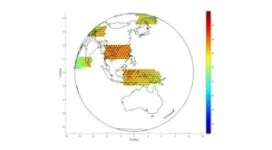
Finally, the design and simulation of active multi-beam antennas are carried out based on the technical requirements of VHTS in Table 1. The aperture and focal length of the receiving antenna are 3.2 m and 5.8 m respectively, and the aperture and focal length of the transmitting antenna are 5.0 m and 9.0 m respectively. Under the coverage of nearly a thousand beams, the antenna achieves ultra-high gain of more than 50dBi (Fig. 14) and ultra-high C/I of more than 18dB (Fig. 15), supporting the communication capacity to achieve Tbps level.
Figure 14 Transmitting beam gain pattern (partial area)
Figure 15 Transmitting beam C/I (partial area
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-08-21
Contact NEJM Group Media Relations (mediarelations@nejm.org) if you’d like to receive full-text articles and author contact information for the articles listed below.
Embargoed Until 9 AM ET on Wednesday, August 21
The African American Transplant Access Program: Mitigating Disparities in Solid Organ Transplantation
D. Simpson
The Journey to an Incentive-Based Health Equity Quality Index (Embargo lifted August 14)
E. Cheng
A Physician-Created Platform to Speed Clinical Decision-Making and Referral Workflow
E. Cunningham
How a Robust Community ...
2024-08-21
WASHINGTON—The Endocrine Society today announced it has chosen 14 leading endocrinologists as winners of its prestigious 2025 Laureate Awards, the top honors in the field.
Endocrinologists are scientists and medical doctors who specialize in unraveling the mysteries of hormone disorders to care for patients and cure diseases. These professionals have achieved breakthroughs in scientific discoveries and clinical care benefiting people with hundreds of conditions, including diabetes, thyroid disorders, ...
2024-08-21
The United States National Science Foundation (NSF) and the Paul G. Allen Family Foundation have announced a $1.3 million collaborative grant to the College of Engineering and Computer Science at Florida Atlantic University, Mote Marine Laboratory & Aquarium, and Old Dominion University, for a project designed to cost-effectively identify and track wildlife using artificial intelligence.
Xingquan “Hill” Zhu, Ph.D., principal investigator and a professor in the FAU Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, is spearheading the project in collaboration with FAU’s Harbor Branch Oceanographic Institute and Charles ...
2024-08-21
Individuals with diabetes and obesity may have nutritional deficiencies that go undiagnosed and untreated, which can impact overall health
Providing health care professionals with nutrition tools is key to supporting patient care
Abbott’s grant to the American Diabetes Association will fund evidence generation on the nutritional needs and impact of nutrition formulas on people with diabetes and those living with obesity
ARLINGTON, Va. and ABBOTT, Ill., August 20, 2024 — The American Diabetes Association® (ADA) and Abbott recently announced a collaboration to better understand the nutritional needs of people ...
2024-08-21
The idea of electrically stimulating a brain region called the central thalamus has gained traction among researchers and clinicians because it can help arouse subjects from unconscious states induced by traumatic brain injury or anesthesia, and can boost cognition and performance in awake animals. But the method, called CT-DBS, can have a side effect: seizures. A new study by researchers at MIT and Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) who were testing the method in awake mice, quantifies the probability of seizures at different stimulation currents and cautions that they sometimes occurred even at low ...
2024-08-21
The integration of machine learning (ML) and automation in laboratory medicine marks a significant advancement, revolutionizing diagnostic accuracy and operational efficiency. This review examines the impact of these technologies, highlighting both their potential benefits and the challenges they pose. The advent of automation combined with ML has introduced new capabilities in pattern detection, predictive analytics, and sophisticated data handling, which are crucial for navigating the complexities of biomedical data. However, these advancements also bring concerns regarding data privacy, the need for stringent validation procedures, and the integration of new technologies into existing ...
2024-08-21
Evolution has enabled plants to survive under adverse conditions. The winter bud of a plant is a crucial structure that establishes adaptability. Depending on environmental and intrinsic conditions, buds can transition between growth and dormancy. The three dormancy phases are determined by signals triggering each phase: ecodormancy, influenced by environmental factors; paradormancy, promoted by other plant organs; and endodormancy, maintained by internal signals within the bud. Paradormant buds enter endodormancy in response to changes in day length and/or low temperature in autumn, while endo-and eco-dormant phases occur ...
2024-08-21
Scientists on the team of Dr Lenka Maletínská have developed a promising new compound derived from one of the peptides naturally occurring in the brain. Its application may contribute to the addressing of two major health challenges of the modern days: obesity and Alzheimer's disease. The neuropeptide CART is primarily associated with the regulation of food intake. Its modified version, created at the Institute of Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry of the Czech Academy of Sciences, shows better stability and is more effective. It suppresses appetite and protects the brain by reducing the pathogenicity of the tau protein, which is associated with ...
2024-08-21
The innovative strength of a society depends on the level of academic freedom. An international team involving the Technical University of Munich (TUM) has now proven this relationship for the first time. The researchers analyzed patent applications and patent citations in a sample from around 160 countries over the 1900–2015 period in relation to indicators used in the Academic Freedom Index. In view of the global decline in academic freedom over the past 10 years, the researchers predict a loss ...
2024-08-21
SPOKANE, Wash. – Just the facts may not be enough to overcome misinformation, a recent study indicates.
In an experiment, 152 college students who had been exposed to misinformation read one of two articles intended to give them the correct, scientifically backed information. Those who read an expository article that had “just the facts” retained more misconceptions than those who read an article with a refutation—meaning it specifically called out the false claims before presenting the facts.
The ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] An active multi-beam antenna design method and its application for the future 6G satellite network