(Press-News.org) PITTSBURGH - Carnegie Mellon University will be a core partner in a new multi-institutional collaboration that has received $26 million from the National Science Foundation to launch an Engineering Research Center (ERC) dedicated to revolutionizing the ability of robots to amplify human labor.
Nine Carnegie Mellon University faculty members, with expertise ranging from Softbotics, engineering, and computer science to psychology, and diversity and inclusion, will help to develop highly dexterous robotic hands, user-friendly interfaces, and accessible training materials to empower diverse workforces to implement robotic solutions quickly and reliably.
The NSF grant will fund the new center across five years, with the ability to renew for another $26 million for an additional five years. It marks the first ERC led by Northwestern. Core partners include Carnegie Mellon University, Florida A&M and Texas A&M with additional faculty support from Syracuse University, the University of Wisconsin-Madison and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Called Human AugmentatioN via Dexterity (HAND), the new ERC will build robot hands with the ability to assist humans with manufacturing, caregiving, handling precious or dangerous materials, and more. The center aims to build technological tools that are versatile and easy-to-integrate, creating robots capable of intelligent and versatile grasping, fine motor skills, and hand-eye coordination.
An expert in Softbotics, Carmel Majidi, professor of mechanical engineering at Carnegie Mellon University, will lead the research thrust focused on developing robust, mass-manufacturable robot hands that achieve breakthrough capability via soft-yet-durable sensing skins, advanced actuators, and novel designs optimized for versatility and robustness.
“It’s an exciting time for Softbotics,” said Majidi. “We will be solving major challenges to build the artificial muscles, responsive skin-like material, and motor-powered tendons needed for user-friendly robots with dexterous capabilities to empower tomorrow’s workforce.”
This research is an extension of his 2020 moonshot project, Intelligent Symbiotic Systems, which pioneered new classes of intelligent programmable matter for transformative impacts on robotics and human-machine interactions.
“Our moonshot project was all about creating a new paradigm in bio-inspired engineering in which autonomous robotic functionality—with integrated sensing, actuation, learning, decision making, self-repair, and energy storage—is intrinsically achieved at the materials level with limited dependency on traditional motors or electronic hardware. These novel materials are critical to the development of lightweight yet mechanically robust and versatile robot hands,” said Majidi.
Other CMU collaborators include Alaine Allen and Gary Fedder from The College of Engineering; Roberta Klatzky from the Department of Psychology and Human Computer Interaction Institute; Nancy Pollard, Oliver Kroemer, and Melisa Orta Martinez from the Robotics Institute; and Katharine Needham from the School of Computer Science.
The interdisciplinary team will work to ensure new robotic hands are inexpensive, easy to operate without expertise, robust, durable, and mass-manufacturable. They will help to develop and prepare a diverse workforce for an entirely new field of study focused on dexterous robots and foster a culture that nourishes inclusivity and ensures equitable access to new technologies. Potential outcomes will include increased worker productivity, improved job opportunities, reshoring of manufacturing, reduced supply chain vulnerability, enhanced food safety, improved quality of life and democratization of the benefits of robotics.
Since its founding in 1985, the ERC program has supported convergent research, education, and technology translation at U.S. universities. Each ERC unites members from academia, industry, and government to produce transformational engineered systems along with engineering graduates who are adept at innovation and primed for leadership in the global economy.
"NSF's Engineering Research Centers ask big questions in order to catalyze solutions with far-reaching impacts," said NSF Director Sethuraman Panchanathan. "NSF Engineering Research Centers are powerhouses of discovery and innovation, bringing America's great engineering minds to bear on our toughest challenges. By collaborating with industry and training the workforce of the future, ERCs create an innovation ecosystem that can accelerate engineering innovations, producing tremendous economic and societal benefits for the nation."
###
About the College of Engineering: The College of Engineering at Carnegie Mellon University is a top-ranked, engineering college that is known for our intentional focus on cross-disciplinary collaboration in research. The College is well known for working on problems of both scientific and practical importance. Our acclaimed faculty have a focus on innovation management and engineering to yield transformative results that will drive the intellectual and economic vitality of our community, nation and world. The College offers graduate and undergraduate degree programs in biomedical engineering, chemical engineering, civil and environmental engineering, electrical and computer engineering, engineering and public policy, information networking, materials science and engineering and mechanical engineering. Our “maker” culture is ingrained in all that we do, leading to novel approaches and transformative results.
END
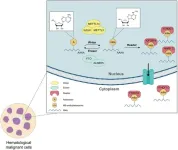
Epigenetics, the modification of chromosomes without altering DNA sequences, serves as a crucial regulatory mechanism for gene expression. Among the various epigenetic marks, N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modifications on RNA have gained significant attention in recent years for their role in various biological processes, including cancer development and progression. This article reviews the latest advances in understanding the role of m6A modifications in leukemia, a heterogeneous group of hematological malignancies.
Role of m6A Modification in Leukemia
m6A Writers and Erasers
m6A modifications ...
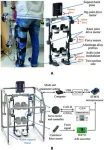
In an era where technology increasingly merges with healthcare to enhance patient outcomes, a groundbreaking study conducted by Fuyang Yu and his colleagues introduces an innovative approach to lower limb rehabilitation. Their research, published in Cyborg Bionic Systems, outlines the development of a lower limb rehabilitation robot designed to significantly improve the safety and effectiveness of gait training through a novel method based on human-robot interaction force measurement.
Rehabilitation robots are ...
There may be a way to slow the growth of endometrial cancer through targeted cancer cell therapy, according to new research from the University of Missouri School of Medicine.
This year, around 65,000 women are expected to be diagnosed with endometrial cancer, the most common cancer of the female reproductive organs. An increased risk in development for multiple human cancers is associated with mutations in the PTEN protein, which normally regulates cell division and growth. The mutation allows cells to multiply uncontrollably.
Using mice models, Krystina Dunston, research lab manager and NextGen Precision Health researchers Tae Hoon Kim and Jae-Wook Jeong, studied the ...
Québec City, August 21, 2024 – A research team from Université Laval has shown the benefits of camu-camu on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, which affects over seven million people in Canada. This exotic fruit reduces liver fat levels.
Over 12 weeks, thirty participants took either camu-camu extract or a placebo at different times in this randomized clinical trial. Participants underwent magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to determine fat levels in the liver. Scientists observed a 7.43% reduction in liver lipids when study participants took camu-camu extract. With the ...
Inside the next generation of fusion vessels known as spherical tokamaks, scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) envisioned a hot region with flowing liquid metal that is reminiscent of a subterranean cave. Researchers say evaporating liquid metal could protect the inside of the tokamak from the intense heat of the plasma. It’s an idea that dates back several decades and is tied to one of the Lab’s strengths: working with liquid metals.
“PPPL’s expertise in using liquid metals, ...
A new study on songbirds sheds light on the power of social interaction to facilitate learning, insights that potentially apply to human development.
McGill University researchers discovered that zebra finches deprived of early social experiences could still form strong bonds with a partner later in life. Once placed into cohabitation with a male, females that had never heard a mating song before could quickly develop a preference for his melody.
The findings, published in Proceedings of the Royal Society ...
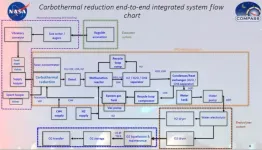
First, lunar ISPP is analyzed from aspects of lunar resources, near-term lunar processes, carbothermal process, polar ice, and reduction of iron oxides. There are basically 4 potential lunar resources: (1) Silicates in regolith containing typically >40% oxygen. (2) Regolith containing FeO for hydrogen reduction. FeO content may vary from 5% to 14%, leading to recoverable oxygen content in the 1 to 3% range. (3) Imbedded atoms in regolith from solar wind (typically parts per million). (4) Water ice in regolith pores in permanently shadowed craters near the poles (unknown percentage but ...
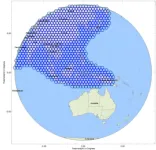
First, the payload requirements and problems faced by traditional multi-beam antenna are described. The user beam of the VHTS payload system mainly uses Ka-band multi-beam antenna for a large range of area coverage, and the number of beams in the coverage area is not less than 500, usually using 7-color frequency reuse scheme(Fig. 2). At present, the spaceborne multi-beam antenna technology applied to high-throughput communication satellites is usually divided into multi-aperture multi-beam antenna and passive multi-feed ...
Contact NEJM Group Media Relations (mediarelations@nejm.org) if you’d like to receive full-text articles and author contact information for the articles listed below.
Embargoed Until 9 AM ET on Wednesday, August 21
The African American Transplant Access Program: Mitigating Disparities in Solid Organ Transplantation
D. Simpson
The Journey to an Incentive-Based Health Equity Quality Index (Embargo lifted August 14)
E. Cheng
A Physician-Created Platform to Speed Clinical Decision-Making and Referral Workflow
E. Cunningham
How a Robust Community ...
WASHINGTON—The Endocrine Society today announced it has chosen 14 leading endocrinologists as winners of its prestigious 2025 Laureate Awards, the top honors in the field.
Endocrinologists are scientists and medical doctors who specialize in unraveling the mysteries of hormone disorders to care for patients and cure diseases. These professionals have achieved breakthroughs in scientific discoveries and clinical care benefiting people with hundreds of conditions, including diabetes, thyroid disorders, ...