(Press-News.org) New research by the University of Liverpool has revealed how an underwater avalanche grew more than 100 times in size causing a huge trail of destruction as it travelled 2000km across the Atlantic Ocean seafloor off the North West coast of Africa.
In a study publishing in the journal Science Advances (and featured on the front cover), researchers provide an unprecedented insight into the scale, force and impact of one of nature’s mysterious phenomena, underwater avalanches.
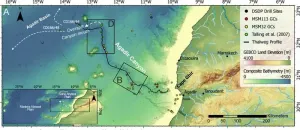
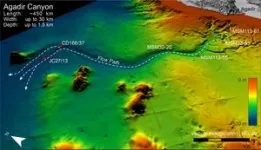
Dr Chris Stevenson, a sedimentologist from the University of Liverpool’s School of Environmental Sciences, co-led the team that for the first time has mapped a giant underwater avalanche from head to toe, which took place nearly 60,000 years ago in the Agadir Canyon.
Their analysis reveals the event, which started as a small seafloor landslide about 1.5 km3 in volume, grew over 100 times in size picking up boulders, gravel, sand and mud as it travelled through one of the largest submarine canyons in the world before travelling a further 1600km across the Atlantic Sea floor.
The avalanche was so powerful that it eroded the entire 400 km length of the canyon and several hundred metres up the sides – about 4500 km2 in total - and was so strong it carried cobbles more than 130m up the side of the canyon.
Unlike a landslide or snow avalanche, underwater avalanches are impossible to see and extremely difficult to measure. However, they are the primary mechanism for moving material such as sediments, nutrients and pollutants across the surface of the earth and present a significant geohazard to the seafloor infrastructure such as internet cables.
The research team analysed more than 300 core samples from the area taken during research cruises over the last 40 years. This, alongside seismic and bathymetry data, enabled them to map out the giant avalanche.
Dr Stevenson said: “This is the first time anyone has managed to map out an entire individual underwater avalanche of this size and calculate its growth factor.”
“What is so interesting is how the event grew from a relatively small start into a huge and devastating submarine avalanche reaching heights of 200 meters as it moved at a speed of about 15 m/s ripping out the sea floor and tearing everything out in its way.
“To put it in perspective: that’s an avalanche the size of a skyscraper, moving at more than 40 mph from Liverpool to London, which digs out a trench 30 m deep and 15 km wide destroying everything in its path. Then it spreads across an area larger than the UK burying it under about a metre of sand and mud.”
Dr Christoph Bottner, a Marie-Curie research fellow at Aarhus University in Denmark, who co-led the team, said “We calculate the growth factor to be at least 100, which is much larger compared to snow avalanches or debris flows which only grow by about 4-8 times. We have also seen this extreme growth in smaller submarine avalanches measured elsewhere, so we think this might be a specific behaviour associated with underwater avalanches and is something we plan to investigate further.”
Professor Sebastian Krastel, head of Marine Geophysics at Kiel University and chief scientist aboard the cruises that mapped the canyon, added: “Our new insight fundamentally challenges how we view these events. Before this study, we thought that big avalanches only came from big slope failures. But now, we know that they can start small and grow into extremely powerful and extensive giant events.
"These findings are of enormous importance for how we try and assess their potential geohazard risk to seafloor infrastructure like internet cables that carry almost all global internet traffic, which are critical to all aspects of our modern societies.”
The most recent cruises mapping the Agadir Canyon were led by the Institute of Geosciences, Kiel University, Leibniz Institute for Baltic Sea Research and GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research, Germany. A suite of archive core data was analysed from the British Ocean Sediment Core Repository at NOCS Southampton, which was collected aboard NERC ships over the past 40 years.
The paper ‘Extreme erosion and bulking in a giant submarine gravity low’ is published in the journal Science Advances (doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adp2584).
END
New study reveals devastating power and colossal extent of a giant underwater avalanche off the Moroccan coast
An international research team has mapped a giant underwater avalanche which took place nearly 60,000 years ago in the Agadir Canyon
2024-08-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
To kill mammoths in the Ice Age, people used planted pikes, not throwing spears, researchers say
2024-08-21
How did early humans use sharpened rocks to bring down megafauna 13,000 years ago? Did they throw spears tipped with carefully crafted, razor-sharp rocks called Clovis points? Did they surround and jab mammoths and mastadons? Or did they scavenge wounded animals, using Clovis points as a versatile tool to harvest meat and bones for food and supplies?
UC Berkeley archaeologists say the answer might be none of the above.
Instead, researchers say humans may have braced the butt of their pointed spears against the ground and angled the weapon upward in a way that would impale a charging animal. The force would have driven the spear deeper ...
Using AI to link heat waves to global warming
2024-08-21
Researchers at Stanford and Colorado State University have developed a rapid, low-cost approach for studying how individual extreme weather events have been affected by global warming. Their method, detailed in a Aug. 21 study in Science Advances, uses machine learning to determine how much global warming has contributed to heat waves in the U.S. and elsewhere in recent years. The approach proved highly accurate and could change how scientists study and predict the impact of climate change on a range of extreme weather events. The ...
The role of an energy-producing enzyme in treating Parkinson’s disease
2024-08-21
An enzyme called PGK1 has an unexpectedly critical role in the production of chemical energy in brain cells, according to a preclinical study led by researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine. The investigators found that boosting its activity may help the brain resist the energy deficits that can lead to Parkinson’s disease.
The study, published Aug. 21 in Science Advances, presented evidence that PGK1 is a “rate-limiting” enzyme in energy production in the output-signaling branches, or axons, of the dopamine neurons that are affected in Parkinson’s disease. This means that even a modest boost to PGK1 activity can have ...
Life from a drop of rain: New research suggests rainwater helped form the first protocell walls
2024-08-21
One of the major unanswered questions about the origin of life is how droplets of RNA floating around the primordial soup turned into the membrane-protected packets of life we call cells.
A new paper by engineers from the University of Chicago’s Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering (UChicago PME), the University of Houston’s Chemical Engineering Department, and biologists from the UChicago Chemistry Department, have proposed a solution.
In the paper, published today in Science Advances, UChicago PME postdoctoral researcher Aman Agrawal and his co-authors ...
Surprising mechanism for removing dead cells identified
2024-08-21
Billions of our cells die every day to make way for the growth of new ones. Most of these goners are cleaned up by phagocytes—mobile immune cells that migrate where needed to engulf problematic substances. But some dying or dead cells are consumed by their own neighbors, natural tissue cells with other primary jobs. How these cells sense the dying or dead around them has been largely unknown.
Now researchers from The Rockefeller University have shown how the sensor system operates in hair follicles, which have a well-known cycle of birth, decay, and regeneration put into motion by hair follicle stem cells (HFSCs). In a new study published in Nature, ...
UC Irvine discovery of ‘item memory’ brain cells offers new Alzheimer’s treatment target
2024-08-21
Irvine, Calif., Aug. 21, 2024 — Researchers from the University of California, Irvine have discovered the neurons responsible for “item memory,” deepening our understanding of how the brain stores and retrieves the details of “what” happened and offering a new target for treating Alzheimer’s disease.
Memories include three types of details: spatial, temporal and item, the “where, when and what” of an event. Their creation is a complex process that involves storing information based on the meanings and outcomes of different experiences and forms the foundation of our ability to recall and recount them.
The study, published ...
Study shows successful use of ChatGPT in ag education
2024-08-21
By John Lovett
University of Arkansas System Division of Agriculture
FAYETTEVILLE, Ark. — Artificial intelligence tools such as ChatGPT show promise as a useful means in agriculture to write simple computer programs for microcontrollers, according to a study published this month.
Microcontrollers are small computers that can perform tasks based on custom computer programs. They receive inputs from sensors and can be used in climate and irrigation controls, food processing systems, as well as robotic and drone applications, to name a few agricultural uses.
A recent study published with the Arkansas Agricultural ...
Early interventions may improve long-term academic achievement in young childhood brain tumor survivors
2024-08-21
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. – August 20, 2024) Children who survive a brain tumor often experience effects from both the cancer and its treatment long after therapy concludes. Scientists at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital found very young children treated for brain tumors were less prepared for school (represented by lower academic readiness scores) compared to their peers. This gap persisted once survivors entered formal schooling. Children from families of higher socioeconomic status were partially protected from the effect, suggesting that providing early developmental resources may proactively help reduce the academic achievement gap. The findings were published today in ...
Cholecystectomy not always necessary for gallstones and abdominal pain
2024-08-21
Each year, 100,000 people visit their doctor with abdominal pain, with approximately 30,000 of them diagnosed with gallstones. The standard treatment for these patients is a laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Since the 1990s, the number of surgeries has increased exponentially, despite the lack of clear international criteria. As a result, gallbladder removal is one of the most common surgeries in the Netherlands, yet it is not always effective against pain: about one-third of patients continue to experience abdominal pain after cholecystectomy. The procedure has long been an example of inappropriate care, but this is now changing.
In a 2019 study conducted by Radboud university ...
Greenhouse gas HFC-23: Abatement of emissions is achievable
2024-08-21
Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) are potent greenhouse gases (GHGs). The most potent of these compounds is trifluoromethane, also known as HFC-23. One kilogram of HFC-23 in the atmosphere contributes as much to the greenhouse effect as 12,000 kilograms of CO₂. It takes around 200 years for the gas to break down in the atmosphere. For this reason, more than 150 countries have committed to significantly reducing their emissions of HFC-23 as part of the Kigali Amendment to the Montreal Protocol.
The main source of HFC-23 ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
Modernization can increase differences between cultures
Cannabis intoxication disrupts many types of memory
Heat does not reduce prosociality
Advancing brain–computer interfaces for rehabilitation and assistive technologies
Detecting Alzheimer's with DNA aptamers—new tool for an easy blood test
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal study develops radiomics model to predict secondary decompressive craniectomy
New molecular switch that boosts tooth regeneration discovered
Jeonbuk National University researchers track mineral growth on bioorganic coatings in real time at nanoscale
Convergence in the Canopy: Why the Gracixalus weii treefrog sounds like a songbird
Subway systems are uncomfortably hot — and worsening
Granular activated carbon-sorbed PFAS can be used to extract lithium from brine
How AI is integrated into clinical workflow lowers medical liability perception
New biotech company to accelerate treatments for heart disease
One gene makes the difference: research team achieves breakthrough in breeding winter-hardy faba beans
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
[Press-News.org] New study reveals devastating power and colossal extent of a giant underwater avalanche off the Moroccan coastAn international research team has mapped a giant underwater avalanche which took place nearly 60,000 years ago in the Agadir Canyon