(Press-News.org) LA JOLLA, CA—In a struggle that probably sounds familiar to dieters everywhere, the less a Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) worm eats, the more slowly it loses fat. Now, scientists at Scripps Research have discovered why: a small molecule produced by the worms’ intestines during fasting travels to the brain to block a fat-burning signal during this time.
Although the exact molecule they identified in the worms has not yet been studied in humans, the new work helps scientists better understand the complex crosstalk between the gut and the brain. It also may shed light on why fasting—not eating for set periods of time—has benefits that are independent from the number of calories a person eats. The new study was published in Nature Communications on August 11, 2024.
“We’ve found for the first time that fasting is conveying information to the brain beyond just caloric withdrawal,” says Scripps Research Professor of Neuroscience Supriya Srinivasan, PhD, the senior author of the new study. “These findings make me wonder whether there are molecules made in the guts of other animals, including mammals, that explain some of the health outcomes associated with fasting.”
Researchers have long known that the brain controls the production and breakdown of fats in humans, other mammals and model organisms such as C. elegans. In 2017, Srinivasan’s group identified FLP-7, a brain hormone that triggers fat burning in the roundworm’s gut. However, C. elegans do not have sensory nerves in their intestines, so scientists have struggled to pin down the reverse communication pathway: How does the gut signal the brain?
“We knew that altering the metabolic state of the gut could change the properties of neurons in the brain, but it was very mysterious how this actually happened,” says Srinivasan.
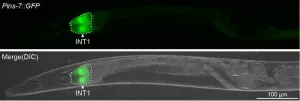
In the new work, Srinivasan and her colleagues removed more than 100 signaling molecules from C. elegans intestines, one at a time, and measured their impact on the brain’s production of FLP-7. They found one molecule that had a large effect on FLP-7: a form of insulin known as INS-7. In humans, insulin is most known as the hormone produced by the pancreas that control blood sugar levels. But this insulin molecule was instead being made by gut cells and also impacting fat metabolism via the brain.
“When we first found that this was an insulin, we thought it was paradoxical,” recalls Srinivasan. “Insulin is so well studied in mammals, and there was no precedent for an insulin molecule having this role.”
However, when the group probed how INS-7 was impacting FLP-7-producing brain cells, they found that it was not activating insulin receptors—as all previously discovered insulin molecules do—but by blocking the insulin receptor. In turn, this blockade set off a cascade of other molecular events that eventually made the brain cells stop producing FLP-7.
“INS-7 is basically a signal coming from the intestines that tells the brain not to burn any more fat stores right now because there’s no food coming in,” explains Srinivasan.
Studies have previously shown that periods of fasting can influence the body in a variety of ways, but the mechanisms of those changes have been unclear. The new study points toward one way that an empty gut can signal the brain, which could potentially lead to a variety of health impacts beyond fat.
The new results, Srinivasan says, help explain how the brain and digestive system communicate in both directions to control metabolism based on the availability of food. More research is needed to uncover which specific pathways are involved in new gut-to-brain signals in mammals. Compounds that mimic gut hormones—such as semaglutide, commonly known under brand names such as Ozempic, Wegovy and Rybelus—have recently emerged as popular ways to control obesity and diabetes, so new gut peptides could add to this drug class. Srinivasan is also planning experiments to probe how C. elegans gut cells are triggered to produce INS-7 during fasting and which types of brain cells are affected by the molecule.
In addition to Srinivasan, authors of the study, “A homeostatic gut-to-brain insulin antagonist restrains neuronally stimulated fat loss,” are Chung-Chih Liu, Ayub Khan, Nicolas Seban, Nicole Littlejohn, and Aayushi Shah of Scripps Research.
This work was supported by funding from the National Institutes of Health (R01 DK124706 and R01 AG056648).
//
About Scripps Research
Scripps Research is an independent, nonprofit biomedical institute ranked one of the most influential in the world for its impact on innovation by Nature Index. We are advancing human health through profound discoveries that address pressing medical concerns around the globe. Our drug discovery and development division, Calibr, works hand-in-hand with scientists across disciplines to bring new medicines to patients as quickly and efficiently as possible, while teams at Scripps Research Translational Institute harness genomics, digital medicine and cutting-edge informatics to understand individual health and render more effective healthcare. Scripps Research also trains the next generation of leading scientists at our Skaggs Graduate School, consistently named among the top 10 US programs for chemistry and biological sciences. Learn more at www.scripps.edu.
END
Gut molecule slows fat burning during fasting
Scripps Research scientists discovered a molecule produced by roundworm intestines that signals the brain to slow fat loss when food is not available.
2024-08-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The Lancet Public Health: Climate change and ageing populations to drive greater disparities in deaths from hot and cold temperatures across Europe, modelling study suggests
2024-08-22
Modelling study using data on 854 European cities is the first to estimate current and future deaths from hot and cold temperatures at this level of regional detail for the entire continent.
Study suggests existing regional disparities in death risk from hot and cold temperatures among adults will widen in the future due to climate change and ageing populations.
A slight decline in cold-related deaths is projected by 2100, while deaths from heat will increase in all parts of Europe, most significantly in southern regions. Areas worst affected will include Spain, Italy, Greece and parts of France.
Currently, around eight times ...
Suicide rates among doctors have declined, but female doctors still at high risk
2024-08-22
Suicide rates among doctors have declined over time, but are still significantly higher for female doctors compared with the general population, finds an analysis of evidence from 20 countries published by The BMJ today.
The researchers acknowledge that physician suicide risk varies across different countries and regions, but say the results highlight the ongoing need for continued research and prevention efforts, particularly among female physicians.
According to some estimates, one doctor dies by suicide every day in the US, and ...
New study provides further support for psilocybin’s potential to treat depressive symptoms
2024-08-22
High doses of psilocybin - the active ingredient in magic mushrooms - appears to have a similar effect on depressive symptoms as the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) drug escitalopram, suggests a systematic review and meta-analysis published in The BMJ today.
The findings show that patients treated with high dose psilocybin showed better responses than those treated with placebo in antidepressant trials, although the effect size was small.
The researchers point out that flaws in study designs may have overestimated the effectiveness ...
Calls for cold water swimming to be made safer for women
2024-08-22
Cold water swimming is growing in popularity amongst women, but more support is needed to make many wild swimming sites in the UK safer and more accessible, finds a new study led by UCL researchers.
The research, published in Women’s Health, explored the habits of women who enjoy cold water swimming and was carried out in collaboration with researchers from the University of Portsmouth, University of Sussex, University Hospitals Sussex NHS Foundation Trust, University of Plymouth and Bournemouth University.
The team surveyed 1,114 women in the UK aged 16 to 80 years ...
Wounds are common among people who use illicit opioids, but proper wound care is hard to find
2024-08-22
The animal tranquilizer xylazine is increasingly found in the illicit opioid supply nationwide, leading to severe wounds among people who use drugs. New research led by a University of Pittsburgh physician-scientist and published in Drug and Alcohol Dependence seeks to understand wound care experiences of this population.
A cross-sectional survey of people who use drugs identified through three syringe service providers in Massachusetts found the vast majority had experienced xylazine wounds in the prior year. As the need for comprehensive, low barrier wound care grows, access to such care continues to lag behind the demand. As a result, these wounds often lead to serious ...
Even as COVID raged, spikes in homicide were a significant drag on life expectancy for Black men
2024-08-22
MADISON — While the COVID-19 pandemic quickly reversed decades of progress in closing the gap between life expectancies for Black and white people in the United States, the disease’s toll may have obscured the impact of another significant public health concern — a sharp increase in homicide rates — on the life expectancy of Black men, according to researchers at the University of Wisconsin–Madison.
In 2019, Black men in the U.S. were expected to live an average of 71.4 years, ...
MD Anderson receives over $21.4 million in CPRIT funding to support research and launch new core facilities
2024-08-22
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center today was awarded nine grants totaling over $21.4 million from the Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas (CPRIT) in support of two new core facilities, faculty recruitment and groundbreaking cancer research across all areas of the institution.
“We are enormously appreciative of CPRIT’s support of impactful cancer research initiatives at MD Anderson,” said Peter WT Pisters, M.D., president of MD Anderson. “These new core facilities will help advance important areas of research in spatial biology and decision ...
Lehigh University is a core institution of new $26 Million NSF Engineering Research Center
2024-08-21
The U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) has awarded $26 million to establish a new Gen-4 Engineering Research Center (ERC) named Environmentally Applied Refrigerant Technology Hub (EARTH) to create a sustainable and circular refrigerant economy.
The University of Kansas is the lead institution, joined by partners at Lehigh University, University of Notre Dame, University of Maryland, University of Hawai'i and University of South Dakota. David Vicic, the Howard S. Bunn Distinguished Professor of Chemistry, will lead Lehigh’s team. Mark Shiflett, University of Kansas Foundation Distinguished Professor in the Department of Chemical & Petroleum Engineering, will be the ERC EARTH ...
NJIT biologist awarded $680,000 federal grant to save North Atlantic right whale
2024-08-21
Brooke Flammang, a biologist at New Jersey Institute of Technology (NJIT), has been awarded nearly $680,000 from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) as part of a growing nationwide effort to save the critically endangered North Atlantic right whale (Eubalaena glacialis).
NOAA Fisheries recently unveiled a more than $9 million initiative funded by the Inflation Reduction Act to support a coalition of universities, nonprofits and scientific organizations engaged in the recovery of the species, which has seen its numbers dwindle to roughly 360 individuals ...
University of Kansas awarded $26 million for new Engineering Research Center from National Science Foundation
2024-08-21
LAWRENCE — The National Science Foundation (NSF) has awarded the University of Kansas $26 million to establish a new Gen-4 Engineering Research Center (ERC) —Environmentally Applied Refrigerant Technology Hub (EARTH) — that will create a sustainable and circular refrigerant economy.
NSF’s Engineering Research Centers bring universities and businesses together to strengthen the competitive position of American industry in the global marketplace.
“NSF's Engineering Research Centers ask big questions in order to catalyze ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How stepping into nature affects the brain
Study: Cancer’s clues in the bloodstream reveal the role androgen receptor alterations play in metastatic prostate cancer
FAU Harbor Branch awarded $900,000 for Gulf of America sea-level research
Terminal ileum intubation and biopsy in routine colonoscopy practice
Researchers find important clue to healthy heartbeats
Characteristic genomic and clinicopathologic landscape of DNA polymerase epsilon mutant colorectal adenocarcinomas
Start school later, sleep longer, learn better
Many nations underestimate greenhouse emissions from wastewater systems, but the lapse is fixable
The Lancet: New weight loss pill leads to greater blood sugar control and weight loss for people with diabetes than current oral GLP-1, phase 3 trial finds
Pediatric investigation study highlights two-way association between teen fitness and confidence
Researchers develop cognitive tool kit enabling early Alzheimer's detection in Mandarin Chinese
New book captures hidden toll of immigration enforcement on families
New record: Laser cuts bone deeper than before
Heart attack deaths rose between 2011 and 2022 among adults younger than age 55
Will melting glaciers slow climate change? A prevailing theory is on shaky ground
New treatment may dramatically improve survival for those with deadly brain cancer
Here we grow: chondrocytes’ behavior reveals novel targets for bone growth disorders
Leaping puddles create new rules for water physics
Scientists identify key protein that stops malaria parasite growth
Wildfire smoke linked to rise in violent assaults, new 11-year study finds
New technology could use sunlight to break down ‘forever chemicals’
Green hydrogen without forever chemicals and iridium
Billion-DKK grant for research in green transformation of the built environment
For solar power to truly provide affordable energy access, we need to deploy it better
Middle-aged men are most vulnerable to faster aging due to ‘forever chemicals’
Starving cancer: Nutrient deprivation effects on synovial sarcoma
Speaking from the heart: Study identifies key concerns of parenting with an early-onset cardiovascular condition
From the Late Bronze Age to today - Old Irish Goat carries 3,000 years of Irish history
Emerging class of antibiotics to tackle global tuberculosis crisis
Researchers create distortion-resistant energy materials to improve lithium-ion batteries
[Press-News.org] Gut molecule slows fat burning during fastingScripps Research scientists discovered a molecule produced by roundworm intestines that signals the brain to slow fat loss when food is not available.