Physicist Hollen honored as Moore Foundation Experimental Physics Investigator
2024-08-22
(Press-News.org) Shawna Hollen, associate professor of physics, has been named to The Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation’s 2024 cohort of Experimental Physics Investigators. The prestigious honor, which is accompanied by $1.25 million in funding over the next five years, will advance understanding of the link between charge density waves and quantum dots, two physical phenomena that could lead to improvements in quantum computing.
“The ideas that I put forward [in my proposal] haven’t been demonstrated. It’s not something that anyone else is doing,” said Hollen. “It’s a huge honor to receive an award from the Moore Foundation.”
Charge density waves are regular patterns of charge that form in some crystals and can lead to some intriguing behavior, including superconductivity — a state in which current can flow with zero resistance, but only at extremely low temperatures. Hollen’s work will manipulate these nanoscale charge patterns to potentially create a new class of engineerable qubits — basic units of information in quantum computing — that could operate near room temperature.
Hollen will use the award to advance her research by increasing her staff—funding a postdoctoral researcher and Ph.D. student—and purchasing some equipment necessary for characterizing and manipulating the two-dimensional materials they study: an atomic force microscope and state-of-the-art glove boxes that use a nitrogen atmosphere.
“These materials are air-sensitive so we need to be able to manipulate them in air-free environment,” said Hollen.
Hollen is grateful to the Moore Foundation for supporting work she says is “riskier and more creative” than research generally funded by federal agencies. The Experimental Physics Investigator honor specifically supports “novel and potentially high-payoff projects that will advance the field of physics but might be hard to fund through traditional funding sources.”
The University of New Hampshire inspires innovation and transforms lives in our state, nation and world. Nearly 16,000 students from 50 states and 87 countries engage with an award-winning faculty in top-ranked programs in business, engineering, law, health and human services, liberal arts and the sciences across more than 200 programs of study. A Carnegie Classification R1 institution, UNH partners with NASA, NOAA, NSF, and NIH, and received over $210 million in competitive external funding in FY23 to further explore and define the frontiers of land, sea and space.
###
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-08-22
In 2011, UNESCO issued The UNESCO Recommendation on the Historic Urban Landscape (“The Recommendation” hereafter), introducing the concept of “historic urban landscape” (HUL). HUL is defined as “the urban context and its geographical setting taking into consideration the historical layering of cultural and natural values and attributes”. It is noteworthy that ancient towns or historic cities, as an important subclass of HUL, have garnered increasing attention. In recent years, public perception and emotional experience of physical environments have become ...
2024-08-22
Metasurfaces are two-dimensional counterparts of metamaterials, which are the artificial materials that possess unusual characteristics. With a variety of fascinatingly innovative and diverse uses, these specially-prepared surfaces with engineered patterns can modify the propagation of electromagnetic waves across the entire spectrum of wavelengths. Though the journey of metamaterials began with metal-dielectric systems, the metasurfaces have gone all-dielectric, and are crucial in applications relating to optoelectronic devices such as solar cells and light emitting diodes (LED) to improve their efficiency through a mere surface effect.
Student researchers led ...
2024-08-22
This year, New Zealand became among the first countries in the world to force their largest companies and financial institutions (about 200 in all) to disclose their climate-related risks and opportunities in their annual reports, and make regulatory filings.
Over the last month, these reports have been filed under the disclosure regime led by the Financial Markets Authority.
But do these kinds of initiatives improve environmental outcomes?
A new study, co-authored by Professor Charl de Villiers (University of Auckland, Business ...
2024-08-22
Solution-processed semiconductor nanocrystals are also called colloidal quantum dots (QDs). While the concept of size-dependent quantum effects had been long known to physicists, a sculpture of the theory into real nanodimensional objects remained impossible till the discovery of QDs. The size-dependent colors of QDs are essentially naked-eye, ambient-condition visualization of the quantum size effect. In recent years, researchers across the world have been searching for fascinating quantum effects or phenomena using the material platform of QDs, such as single-photon emission and quantum coherence manipulation.
Floquet states (i.e., ...
2024-08-22
Antarctica’s unique ecosystems could be threatened by the arrival of non-native marine species and marine pollution from Southern Hemisphere landmasses, new oceanographic modelling shows.
In a study published today in Global Change Biology, scientists from UNSW Sydney, ANU, University of Otago and the University of South Florida suggest that floating objects can reach Antarctic waters from more sources than previously thought.
“An increasing abundance of plastics and other human made debris in the oceans means there are potentially more opportunities ...
2024-08-22
A recent study has explored the legal and ethical challenges expected to arise in human brain organoid research.
Human brain organoids are three-dimensional neural tissues derived from stem cells that can mimic some aspects of the human brain. Their use holds incredible promise for medical advancements, but this also raises complex ethical and legal questions that need careful consideration.
Seeking to examine the various legal challenges that might arise in the context of human brain organoid research and its applications, the team of researchers, which included a legal scholar, identified and ...
2024-08-22
University of Queensland researchers have discovered a mechanism in DNA that regulates how disease-causing mutations are inherited.
Dr Anne Hahn and Associate Professor Steven Zuryn from UQ’s Queensland Brain Institute said the findings could provide a promising therapeutic avenue to stop the onset of heritable and age-related diseases.
“Mitochondrial DNA is essential for cell function,” Dr Hahn said.
“But as we age it mutates, contributing to diseases ...
2024-08-22
LA JOLLA, CA—In a struggle that probably sounds familiar to dieters everywhere, the less a Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) worm eats, the more slowly it loses fat. Now, scientists at Scripps Research have discovered why: a small molecule produced by the worms’ intestines during fasting travels to the brain to block a fat-burning signal during this time.
Although the exact molecule they identified in the worms has not yet been studied in humans, the new work helps scientists better ...
2024-08-22
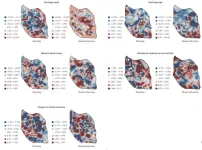
Modelling study using data on 854 European cities is the first to estimate current and future deaths from hot and cold temperatures at this level of regional detail for the entire continent.
Study suggests existing regional disparities in death risk from hot and cold temperatures among adults will widen in the future due to climate change and ageing populations.
A slight decline in cold-related deaths is projected by 2100, while deaths from heat will increase in all parts of Europe, most significantly in southern regions. Areas worst affected will include Spain, Italy, Greece and parts of France.
Currently, around eight times ...
2024-08-22
Suicide rates among doctors have declined over time, but are still significantly higher for female doctors compared with the general population, finds an analysis of evidence from 20 countries published by The BMJ today.
The researchers acknowledge that physician suicide risk varies across different countries and regions, but say the results highlight the ongoing need for continued research and prevention efforts, particularly among female physicians.
According to some estimates, one doctor dies by suicide every day in the US, and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Physicist Hollen honored as Moore Foundation Experimental Physics Investigator