(Press-News.org) Inflammation of the abdominal cavity in human fetuses resulting from a perforation of their intestine is likely to be caused by proteins contained in the fetal stool. This is the result of a Kobe University study that establishes a new mouse model allowing research and drug development for a condition that is otherwise difficult to approach.
The fetus’s stool, called the “meconium,” is sterile but nevertheless causes inflammation of the abdominal cavity when it leaks out of the intestine after a perforation. Called “meconium peritonitis,” this is a life-threatening condition for the baby with a mortality rate of 10%-15% in humans, and neither a cause nor a treatment have been established.
The Kobe University pediatrician FUJIOKA Kazumichi and his team therefore decided to replicate the condition in mice. Since the intestinal development of mice and humans is different, the intestine of a newborn mouse pup is equivalent to that of a human fetus after the 12th week of pregnancy, but even so, the mouse pup is too small and fragile to induce the condition through an operation. The research team therefore created a slurry of meconium, which they took from human newborns, and injected it into the abdominal cavity of the pups. They then characterized the resulting condition and compared the pups’ mortality rates in response to different treatments.
Their results, published in the journal Pediatric Research, show that mortality was not influenced by antibiotic treatment, ruling out a bacterial cause. However, when they heat-treated the meconium slurry before injection, which disrupts the natural shapes of proteins, they found a significant reduction in mortality. This indicates that proteins contained in the meconium are responsible for the inflammation and in particular the researchers assume digestive enzymes that are abundant in the meconium to be the culprits.
The Kobe University development has more general implications, too. In a different set of experiments, Fujioka and his team characterized the condition of the mice pups after the meconium slurry administration by analyzing the mice’s biochemical and gene expression profiles. Comparing that to the results of a previously established mouse model, where the pups were injected an extract of intestinal contents of adult mice, they could show that their model results in different symptoms. Believing that their model is thus likely to be specific to meconium-caused inflammation, the researchers argue that it is an apt platform to conduct more research on the condition.
Fujioka and his team hope that their work will enable the search for an effective treatment of the condition, which occurs in about one out of every 35,000 live births. They conclude their paper saying, “As our mouse model is simple and highly reproducible, it can be used in research to elucidate the pathophysiology of meconium peritonitis.”
This research was funded by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (grants 18K15710 and 20K08229), the Morinaga Hoshi-kai Foundation, the Kawano Masanori Memorial Public Interest Incorporated Foundation for the Promotion of Pediatrics and the Japan Foundation for Pediatric Research.
Kobe University is a national university with roots dating back to the Kobe Commercial School founded in 1902. It is now one of Japan’s leading comprehensive research universities with nearly 16,000 students and nearly 1,700 faculty in 10 faculties and schools and 15 graduate schools. Combining the social and natural sciences to cultivate leaders with an interdisciplinary perspective, Kobe University creates knowledge and fosters innovation to address society’s challenges.
END
Mouse study: Proteins do the damage in fetal abdominal inflammation
2024-08-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Let me take a look: AI could boost diagnostic imaging results
2024-08-22
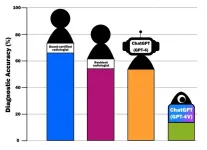
In radiology, diagnostic imaging requires specialized knowledge to interpret the findings associated with a wide variety of diseases. Fortunately, in recent years, generative AI models, such as Chat Generative Pre-trained Transformer (ChatGPT), have shown potential as diagnostic tools in the medical field, but their accuracy must be evaluated for optimal use in the future.
Therefore, Dr. Daisuke Horiuchi and Associate Professor Daiju Ueda of Osaka Metropolitan University’s Graduate School of Medicine led a research team that compared the diagnostic accuracy of ChatGPT and radiologists. They used 106 musculoskeletal radiology cases with patient medical history, images, ...
Prof Carl Kocher explores how you can stretch your mind to grasp quantum entanglement
2024-08-22
My new article, ‘Quantum Entanglement of Optical Photons: The First Experiment, 1964-67’, is intended to convey the spirit of a small research project that reaches into uncharted territory. The article breaks with tradition, as it offers a first-person account of the strategy and challenges for the experiment, as well as an interpretation of the final result and its significance. In this guest editorial, I will introduce the subject and also attempt to illuminate the question ‘What is a paradox?’
Let’s begin with the gyroscope that I bought when I was eight, from a store ...
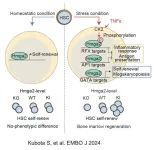
Unveiling the secret of blood regeneration: New insights into stress responses in hematopoietic stem cells (HSC)
2024-08-22
Kumamoto University researchers have made a groundbreaking discovery that sheds light on how the HMGA2 gene—an essential transcriptional activator involved in chromatin modification—regulates stress responses in hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), thereby enhancing blood cell production recovery.
Exposure to infections or treatments such as chemotherapy often leads to a rapid decline in blood cells, including red blood cells and platelets. HSCs, which reside in the bone marrow that can develop into various types of blood cells, are crucial for recovering from these stress-induced blood disorders. Under stressd ...
MCG physicians working to help prevent vision loss associated with space travel
2024-08-22
Physicians at the Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University are working with Polaris Dawn, the first of the Polaris Program’s three human spaceflight missions, to better understand the eye changes many astronauts experience during spaceflight that can leave them with a wide range of symptoms once they return to Earth — from a new need for glasses to significant loss of vision. The Polaris Program is a first-of-its-kind effort to rapidly advance human spaceflight capabilities while continuing to raise funds and awareness for important causes on Earth.
More than 70% of astronauts experience a phenomenon ...
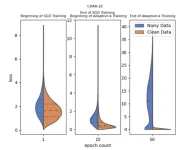
Adaptive-k: A simple and effective method for robust training in label noisy datasets
2024-08-22
Training deep learning models on large datasets is essential for their success; however, these datasets often contain label noise, which can significantly decrease the classification performance on test datasets. To address this issue, a research team consisting of Enes Dedeoglu, H. Toprak Kesgin, and Prof. Dr. M. Fatih Amasyali from Yildiz Technical University developed a groundbreaking method called Adaptive-k, which improves the optimization process and yields better results in the presence of label noise. Their research was published on 15 August 2024 in ...
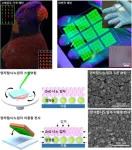
Developing innovative new display technologies! Create ultrahigh-definition screens efficiently!
2024-08-22
□ A team led by Professor Ji-woong Yang of DGIST’s (President Kun-woo Lee) Department of Energy Science and Engineering, in collaboration with Professor Moon-kee Choi of UNIST's Department of New Materials and Dr. Taeg-hwan Hyun of the IBS Nanoparticle Research Center, has developed a double-layer dry transfer printing technology that simultaneously transfers light-emitting and electron-transferring layers onto a substrate. This technology is expected to provide a more life-like view in augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), greatly enhancing the immersive experience.
□ ...
Physicist Hollen honored as Moore Foundation Experimental Physics Investigator
2024-08-22
Shawna Hollen, associate professor of physics, has been named to The Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation’s 2024 cohort of Experimental Physics Investigators. The prestigious honor, which is accompanied by $1.25 million in funding over the next five years, will advance understanding of the link between charge density waves and quantum dots, two physical phenomena that could lead to improvements in quantum computing.
“The ideas that I put forward [in my proposal] haven’t been demonstrated. It’s not something that anyone else ...
How do the characteristics of historic urban landscapes influence public sentiments, and what implications do these findings have for urban planning and development strategies?
2024-08-22
In 2011, UNESCO issued The UNESCO Recommendation on the Historic Urban Landscape (“The Recommendation” hereafter), introducing the concept of “historic urban landscape” (HUL). HUL is defined as “the urban context and its geographical setting taking into consideration the historical layering of cultural and natural values and attributes”. It is noteworthy that ancient towns or historic cities, as an important subclass of HUL, have garnered increasing attention. In recent years, public perception and emotional experience of physical environments have become ...
Low-cost flexible metasurfaces to increase the efficiency of optoelectronic devices
2024-08-22
Metasurfaces are two-dimensional counterparts of metamaterials, which are the artificial materials that possess unusual characteristics. With a variety of fascinatingly innovative and diverse uses, these specially-prepared surfaces with engineered patterns can modify the propagation of electromagnetic waves across the entire spectrum of wavelengths. Though the journey of metamaterials began with metal-dielectric systems, the metasurfaces have gone all-dielectric, and are crucial in applications relating to optoelectronic devices such as solar cells and light emitting diodes (LED) to improve their efficiency through a mere surface effect.
Student researchers led ...
When climate reporting fails to create impact
2024-08-22
This year, New Zealand became among the first countries in the world to force their largest companies and financial institutions (about 200 in all) to disclose their climate-related risks and opportunities in their annual reports, and make regulatory filings.
Over the last month, these reports have been filed under the disclosure regime led by the Financial Markets Authority.
But do these kinds of initiatives improve environmental outcomes?
A new study, co-authored by Professor Charl de Villiers (University of Auckland, Business ...