(Press-News.org)
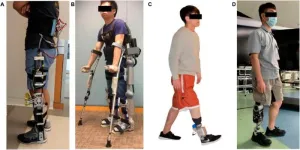
A research paper by scientists at Hainan University proposed FSS-eq2Seq as a 2-stage strategy for gait synergy modeling in lower limb assistive devices to achieve synergic and user-adaptive trajectories that improve human-machine interactions.
The new research paper, published on Jul. 03 in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems, indicatedSeq2Seq outperforms LSTM, RNN, and GRU in both interlimb and intralimb synergy modeling. Further, FS significantly improves Seq2Seq’s modeling performance.
The concept of gait synergy provides novel human-machine interfaces and has been applied to the control of lower limb assistive devices, such as powered prostheses and exoskeletons. Specifically, based on gait synergy, the assistive device can generate/predict the appropriate reference trajectories precisely for the affected or missing parts from the motions of sound parts of the patients. Optimal modeling for gait synergy methods that involves optimal combinations of features (inputs) is required to achieve synergic trajectories that improve human-machine interaction. However, previous studies lack thorough discussions on the optimal methods for synergy modeling. In addition, feature selection (FS) which is crucial for reducing data dimensionality and improving modeling quality has often been neglected in previous studies. “Control of active assistive devices is a critical and challenging issue when designing and generating user-, temporal-, and phase-adaptive and synergistic reference trajectories for various patients.” explained study author Fengyan Liang, a professor at Hainan University. Here, the author comprehensively investigated modeling methods and FS using 4 up-to-date neural networks: sequence-to-sequence (Seq2Seq), long short-term memory (LSTM), recurrent neural network (RNN), and gated recurrent unit (GRU). We also conducted complete FS using 3 commonly used methods: random forest, information gain, and Pearson correlation. “Our findings reveal that Seq2Seq (mean absolute error: 0.404° and 0.596°, respectively) outperforms LSTM, RNN, and GRU for both interlimb and intralimb synergy modeling. Furthermore, FS is proven to significantly improve Seq2Seq’s modeling performance (P < 0.05). FS-Seq2Seq even outperforms methods used in existing studies.” said study authors.
The present study aimed to identify the optimal modeling method and feature combinations for modeling interlimb and intralimb synergies to generate desirable trajectories for the control of lower limb assistive devices. "Consequently, a 2-stage strategy, FS-Seq2Seq, is proposed for gait synergy modeling in trajectory generation on assistive devices," said Fengyan Liang. Previous synergy modeling studies have not comprehensively compared the modeling methods and neglected the FS processes. This study emphasizes the promise of synergy-based trajectory prediction for assistive devices and provides insights into achieving optimal modeling with optimal feature combinations, resulting in synergic and user-adaptive trajectories that improve human-machine interactions.
The work demonstrates the FS-Seq2Seq as a 2-stage strategy offers advantages over other approaches in terms of performance and accuracy for modeling interlimb and intralimb synergies. This study emphasizes the promise of synergy-based trajectory prediction for assistive devices to achieve synergic and user-adaptive trajectories that improve human-machine interactions. Our results further emphasize the importance of conducting systematic FS before synergy modeling in future studies. Future research efforts should hence continue to explore and refine these techniques to further improve assistive device control.
Authors of the paper include Fengyan Liang, Lifen Mo, Yiou Sun, Cheng Guo, Fei Gao, Wei-Hsin Liao, Junyi Cao, Binbin Li, Zhenhua Song, Dong Wang, Ming Yin
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 32360196, and 32160204), the Key R&D Project of Hainan Province (grant nos. ZDYF2022- SHFZ302 and ZDYF2022SHFZ275), the Major Science and Technology Projects of Hainan Province (grant no. ZDKJ- 2021032), Hainan Province Clinical Medical Center (no. 0202067), Science, Technology, and Innovation Commission of Shenzhen Municipality (STIC; project no. SGDX20220530111005036), Basic and Applied Basic Research Fund of Guangdong Province: Regional Joint Fund Project Youth Fund (project no. 2021A- 1515110356), Shenzhen Science and Technology Plan Project (project no. JCYJ20220818101407016), and by the Project of Sanya Yazhou Bay Science and Technology City (no. SCKJJYRC-2023-27).
The paper, “Interlimb and Intralimb Synergy Modeling for Lower Limb Assistive Devices: Modeling Methods and Feature Selection” was published in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems on Jul 03, 2024, at DOI: 10.34133/cbsystems.0122.
END
Fossils are used to reconstruct evolutionary history, but not all animals and plants become fossils and many fossils are destroyed before we can find them (e.g., the rocks that contain the fossils are destroyed by erosion). As a result, the fossil record has gaps and is incomplete, and we’re missing data that we need to reconstruct evolutionary history. Now, a team of sedimentologists and stratigraphers from the Netherlands and the UK examined how this incompleteness influences the reconstruction of evolutionary history. To their surprise, they found that the incompleteness itself is actually not such a big issue. “It’s ...
About The Study: This study found that heat-related mortality rates in the U.S. increased between 1999 and 2023, especially during the last 7 years. Although a study using data through 2018 found a downward trend in heat-related mortality in the U.S., this study is the first to our knowledge to demonstrate a reversal of this trend from 2016 to 2023. These results align with site-specific data analyzed in a global study that suggest increases in heat-related mortality. As temperatures continue to rise because of climate change, the recent increasing trend is likely to continue. Local authorities in high-risk areas should consider investing in the expansion of access to hydration centers ...
MADISON – Transgender students are more likely to seek support from school staff and less likely to seek support from their parents when compared to their cisgender peers, according to a new study from researchers at the University of Wisconsin–Madison and New York University.
The study, published in JAMA Pediatrics, found among students who felt depressed or anxious, transgender students were 74% less likely than their cisgender peers to seek help from parents than from adults in schools. It also found transgender students were 25% less likely than cisgender students to seek support from ...
About The Study: In this longitudinal cohort study of economically and racially diverse U.S. youth, there was evidence of differential susceptibility and resilience for mental health problems during the pandemic that was associated with prepandemic mental health and sociodemographic characteristics. These differences are critical to understand for recovery and may yield novel insights into causes of youth mental health problems.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Courtney ...
About The Study: In this cross-sectional cohort study of 170 former football players and 54 unexposed controls, larger perivascular space (PVS) volume was associated with greater exposure to repetitive head impacts (RHI). Additionally, PVS volume was associated with worse performance on cognitive tests. These findings suggest that PVS volume may contribute to the association between exposure to RHI, cognitive impairment, and the development of RHI-associated neurodegeneration.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding ...
COLLEGE PARK, Md. – Who hasn’t sat in a medical office, listening to computer keys clacking while their provider rapidly types up notes, wondering what they are spending so much time writing about? For doctors, who have always written clinical care notes but increasingly must spend time cataloging billing details, this additional documentation is a major source of job dissatisfaction and burnout. A new study out today by University of Maryland’s School of Public Health illuminates a solution that can meaningfully reduce the amount of time doctors spend writing notes, without losing vital information.
“Providers are already stretched thin and under intense pressure to ...
NEW YORK, NY (AUGUST 26, 2024) — A team of scientists from The New York Stem Cell Foundation (NYSCF) Research Institute and Case Western Reserve University has created the largest reported collection of stem cell models from multiple sclerosis (MS) patients and used them to identify unique ways in which glia – integral support cells in the brain – contribute to the disease.
The study, published today in Cell Stem Cell, is the first to report that glial cells from MS patients have intrinsic hallmarks of disease, independent of immune system influences, which points to the power of stem cells for revealing new disease biology and to the need for ...
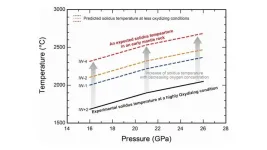
It is widely accepted that the early Earth largely consisted of molten magma, forming a global ocean of magma. This extreme state of Earth was likely caused by the intense heat generated from accretionary impacts, meaning the collision of smaller celestial bodies with Earth. Understanding the formation of this magma ocean is crucial for comprehending Earth’s formation. A major problem with current magma ocean formation models is the lack of consensus on the melting temperatures of deep mantle rocks. Models explaining Earth’s core formation use a specific ...
When astronomers got their first glimpses of galaxies in the early universe from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, they were expecting to find galactic pipsqueaks, but instead they found what appeared to be a bevy of Olympic bodybuilders. Some galaxies appeared to have grown so massive, so quickly, that simulations could not account for them. Some researchers suggested this meant that something might be wrong with the theory that explains what the universe is made of and how it has evolved since the big bang, known as the standard model of cosmology.
According to a new study in The Astrophysical Journal led by University of Texas at Austin graduate student ...
SAN ANTONIO — August 26, 2024 — Southwest Research Institute will highlight its capacity to advance military medicine and human performance at the Military Health System Research Symposium, August 26-29, in Kissimmee, Florida.
“Southwest Research Institute has a long history of working with several DOD agencies,” said Senior Research Engineer Kreg Zimmern of SwRI’s Chemistry and Chemical Engineering Division. “SwRI offers multidisciplinary expertise, allowing us to manage government contracts ...