(Press-News.org) SAN ANTONIO — August 26, 2024 — Southwest Research Institute will highlight its capacity to advance military medicine and human performance at the Military Health System Research Symposium, August 26-29, in Kissimmee, Florida.
“Southwest Research Institute has a long history of working with several DOD agencies,” said Senior Research Engineer Kreg Zimmern of SwRI’s Chemistry and Chemical Engineering Division. “SwRI offers multidisciplinary expertise, allowing us to manage government contracts and provide a one-stop shop for research and development.”
Zimmern will showcase the SwRI-developed Advanced Military Measure of Olfaction (AMMO) kit, which can be deployed anywhere from sports competitions to battlefields. The low-cost smell test uses the ability to identify an array of scents to screen for traumatic brain injuries.
Other chemistry-focused innovations include SwRI’s Defense Threat Reduction Agency research to develop antidotes for nerve agents used in chemical warfare.
“SwRI also has played a pivotal role in developing synthetic oxygen carriers, blood substitutes and whole blood analogs for both commercial and government clients,” said SwRI Research Engineer Nick McMahon of SwRI’s Pharmaceutical and Bioengineering Department.
SwRI’s exhibit will also demonstrate the Engine for Automatic Biomechanical Evaluation (ENABLE™), a tool that the U.S. Air Force recently used to identify trainees at risk for noncombat injuries. Each year, millions of military personnel suffer musculoskeletal injuries, including from routine overuse. Such injuries cost the U.S. government billions of dollars in direct and indirect costs.
“SwRI supports the military health system using a wide variety of biomechanical tools and approaches with the goal of understanding injury,” said Lead Engineer Travis Eliason, a key member of SwRI’s Human Performance Initiative. The multidisciplinary research team leverages biomechanical engineering and computer science to develop solutions for military, medical and sports clients.
“Combining high-fidelity modeling of the human body with novel markerless biomechanics technology, we take a holistic view of the individual to predict injury and help develop countermeasures,” said Eliason.
Visit booth No. 312 at MHSRS to learn how SwRI has invested in chemistry, computer science and engineering to help the U.S. Department of Defense support warfighters with military medicine, training and combat solutions.
For more information visit https://www.swri.org/industries/biochemistry-bioengineering or https://www.swri.org/industry/biomechanics-human-performance.
END
SwRI showcases latest warfighter research at military health research symposium
Institute features innovative medical devices, blood substitutes, markerless motion capture
2024-08-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientific consensus can strengthen pro-climate attitudes in society
2024-08-26
Climate scientists have long agreed that humans are largely responsible for climate change. A new study, co-led by Bojana Većkalov from the University of Amsterdam and Sandra Geiger from the University of Vienna, finds that communicating the scientific consensus about climate change can clear up misperceptions and strengthen beliefs about the existence and the causes of climate change. The team surveyed over 10,000 people from 27 countries on 6 continents. The study has just been published in the renowned journal Nature Human Behaviour.
Scientific consensus identifying humans as primarily responsible ...
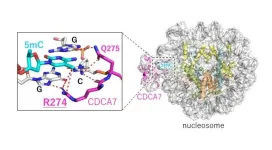
Unraveling the role of CDCA7 in maintenance of DNA methylation
2024-08-26
DNA methylation, a process by which methyl groups are added to DNA molecules, is essential for the maintenance of DNA and the overall health of an organism. Disruptions in the standard DNA methylation patterns can lead to immunodeficiency and diseases such as cancer. Helicase lymphoid-specific (HELLS) is an enzyme that facilitates DNA methylation by remodeling the nucleosome - the tightly packed structure of DNA wound around histone proteins. The absence of HELLS or its activator, cell division cycle associated 7 (CDCA7) is known to be a factor that leads to the disruption of DNA methylation. Mutations in the genes that code for HELLS and CDCA7 cause rare disorder immunodeficiency, ...
Study finds salamanders are surprisingly abundant in northeastern forests
2024-08-26
RESTON, Va. — Two recent amphibian-focused studies shed light on the ecological importance of red-backed salamanders, while confirming that proactive measures would prevent costly impacts from a wildlife disease spreading across Europe that has not yet reached North America.
Scientists knew that red-backed salamanders were abundant in eastern North America, but a recent study found their densities and biomass across the region were much higher than expected. The study authors estimated an average of ...
Old chemo drug, new pancreatic cancer therapy?
2024-08-26
The fight against cancer is an arms race, and one of the most effective weapons in clinicians’ arsenals is immunotherapy. Immune checkpoint therapy has become the standard for treating several types of cancer. However, the Nobel Prize-winning strategy is ineffective for most pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) patients.
“Immune checkpoint therapy is only an option in rare cases of PDAC,” Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Professor Douglas Fearon says. “It’s only effective for patients with a specific subtype of PDAC—that’s less than 5% of all cases.”
Until recently, it was thought that PDAC didn’t ...
Shakespeare in sign language, seen through AI
2024-08-26
A new study uses co-creation with reference communities to develop an app for sign language machine translation (SLMT). The research team designed a theatrical performance in sign language, seen through the eyes of artificial intelligence (AI), as one of the methodologies. “Historically, deaf people have been excluded from the development of automatic translation technologies,” says Shaun O’Boyle, Research Fellow in the School of Inclusive and Special Education (Dublin City University DCU). “This has often caused backlash and resistance from deaf communities, as the projects were designed and ...
PLOS and the University of South Carolina announce APC-free Open Access publishing agreement
2024-08-26
SAN FRANCISCO — The University of South Carolina and the Public Library of Science (PLOS) today announced a three-year Open Access agreement that allows researchers to publish in PLOS journals[1] without incurring article processing charges (APC). This partnership brings together two organizations that believe researchers should be able to access content freely and make their work available publicly, regardless of their access to funds.
“The evidence is undeniable — open research enables the convergence of ...
Why children can’t pay attention to the task at hand
2024-08-26
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Scientists have learned that children find it hard to focus on a task, and often take in information that won’t help them complete their assignment. But the question is, why?
In a new study, researchers found that this “distributed attention” wasn’t because children’s brains weren’t mature enough to understand the task or pay attention, and it wasn’t because they were easily distracted and lacked the control to focus.
It now appears that kids distribute their attention broadly either out of simple curiosity or because their working memory isn’t developed enough to complete a task without “over ...
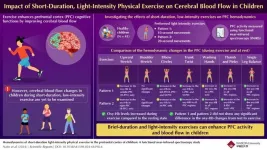
Short-duration, light-intensity exercises improve cerebral blood flow in children
2024-08-26
Cognitive functions, also known as intellectual functions, encompass thinking, understanding, memory, language, computation, and judgment, and are performed in the cerebrum. The prefrontal cortex (PFC), located in the frontal lobe of the cerebral cortex, handles these functions. Studies have shown that exercise improves cognitive function through mechanisms such as enhanced cerebral blood flow, structural changes in the brain, and promotion of neurogenesis. However, 81% of children globally do not engage in enough physical activity, leading to high levels of sedentary behavior and insufficient exercise. This lack of physical ...
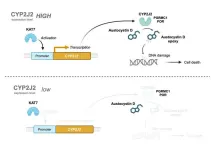
Exploring the role of cytochrome oxygenases in augmenting austocystin D-mediated cytotoxicity
2024-08-26
Austocystin D, a natural compound produced by fungi, has been recognized for its cytotoxic effects and anticancer activity in various cell types. It exhibits potent activity even in cells that express proteins associated with multidrug resistance, attracting significant global research interest. Austocystin D promotes cell death by damaging their DNA, a process which might be dependent on cytochrome P450 (CYP) oxygenase enzymes. Notably, austocystin D has shown significant activity against cancer cells with increased CYP expression. However, the specific role and function of the CYP2J2 enzyme in the cytotoxicity of austocystin D remain ...
Knowing you have a brain aneurysm may raise anxiety risk, other mental health conditions
2024-08-26
Research Highlights:
People diagnosed with unruptured cerebral aneurysms (weakened areas in brain blood vessels) who are being monitored without treatment have a higher risk of developing mental illness compared to those who have not been diagnosed with a cerebral aneurysm. The largest impact was among adults younger than age 40.
The study conducted in South Korea found that the psychological burden caused by the diagnosis of an unruptured aneurysm may contribute to the development of mental health conditions, such as anxiety, stress, depression, eating ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
Modernization can increase differences between cultures
Cannabis intoxication disrupts many types of memory
Heat does not reduce prosociality
Advancing brain–computer interfaces for rehabilitation and assistive technologies
Detecting Alzheimer's with DNA aptamers—new tool for an easy blood test
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal study develops radiomics model to predict secondary decompressive craniectomy
New molecular switch that boosts tooth regeneration discovered
Jeonbuk National University researchers track mineral growth on bioorganic coatings in real time at nanoscale
Convergence in the Canopy: Why the Gracixalus weii treefrog sounds like a songbird
Subway systems are uncomfortably hot — and worsening
Granular activated carbon-sorbed PFAS can be used to extract lithium from brine
How AI is integrated into clinical workflow lowers medical liability perception
New biotech company to accelerate treatments for heart disease
One gene makes the difference: research team achieves breakthrough in breeding winter-hardy faba beans
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
[Press-News.org] SwRI showcases latest warfighter research at military health research symposiumInstitute features innovative medical devices, blood substitutes, markerless motion capture