Unraveling the role of CDCA7 in maintenance of DNA methylation
2024-08-26
(Press-News.org)
DNA methylation, a process by which methyl groups are added to DNA molecules, is essential for the maintenance of DNA and the overall health of an organism. Disruptions in the standard DNA methylation patterns can lead to immunodeficiency and diseases such as cancer. Helicase lymphoid-specific (HELLS) is an enzyme that facilitates DNA methylation by remodeling the nucleosome - the tightly packed structure of DNA wound around histone proteins. The absence of HELLS or its activator, cell division cycle associated 7 (CDCA7) is known to be a factor that leads to the disruption of DNA methylation. Mutations in the genes that code for HELLS and CDCA7 cause rare disorder immunodeficiency, centromeric instability, and facial anomalies (ICF) syndrome.
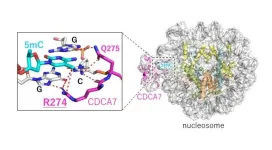
Understanding why CDCA7-HELLS is crucial for maintaining DNA methylation is vital for gaining insights into the mechanism of disorders such as ICF syndrome. In a recent study published in Science Advances on August 23 2024, researchers have found that CDCA7 can recognize hemimethylation of DNA—a state where one strand of the DNA’s double helix is methylated but not the other—and recruit HELLS to complete methylation of the DNA. The researchers found that the hemimethylation-sensing zinc finger (HMZF) of CDCA7, which has been conserved throughout evolution, is key to its ability to perform maintenance DNA methylation. “We found that the CDCA7 gene, known as the causative gene of ICF syndrome, promotes DNA methylation by controlling the ubiquitination of histone H3 through specific binding to hemimethylated DNA on nucleosomes,” explains Associate Professor Atsuya Nishiyama from the Division of Cancer Cell Biology, The Institute of Medical Science, The University of Tokyo, one of the lead researchers of the study.
Dr. Nishiyama, together with Professor Hironori Funabiki and Dr. Isabel Wassing at The Rockefeller University, Professor Kyohei Arita from Yokohama City University and Professor Makoto Nakanishi from The University of Tokyo, examined the structure of the complex formed by CDCA7 and the nucleosome using single particle cryo-electron microscopy. They found that CDCA7, unlike other DNA methylation activators, uniquely identifies hemimethylated DNA in the outward-facing major groove of the nucleosome core particle (NCP). This discovery explains why mutations in CDCA7 associated with ICF syndrome led to a defective DNA maintenance methylation mechanism.
“Our findings suggest that CDCA7 and HELLS promote DNA methylation in a mechanism distinct from de novo DNA methylation, which is now consolidated by our demonstration that the CDCA7 HMZF domain specifically recognizes hemimethylated CpG, the substrate of the maintenance DNA methyltransferase DNMT1. ICF disease-associated mutations in the CDCA7 gene abolish its hemimethylated DNA binding, supporting the functional importance of hemimethylation detection by the CDCA7 gene,” Dr. Nishiyama notes.
These pioneering findings not only advance potential therapies for ICF syndrome but also open new frontiers in cancer prevention and anti-aging. Disruptions in DNA methylation is linked to cancer, while inefficient methylation is a hallmark of cellular aging. “Our study lays the groundwork for the development of new DNA methylation inhibitors and therapeutic drugs for ICF syndrome. Therapies that artificially regulate CDCA7-dependent DNA methylation may also prevent cancer and aging and help extend healthy lifespan,” Dr. Nishiyama concludes.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-08-26
RESTON, Va. — Two recent amphibian-focused studies shed light on the ecological importance of red-backed salamanders, while confirming that proactive measures would prevent costly impacts from a wildlife disease spreading across Europe that has not yet reached North America.
Scientists knew that red-backed salamanders were abundant in eastern North America, but a recent study found their densities and biomass across the region were much higher than expected. The study authors estimated an average of ...
2024-08-26
The fight against cancer is an arms race, and one of the most effective weapons in clinicians’ arsenals is immunotherapy. Immune checkpoint therapy has become the standard for treating several types of cancer. However, the Nobel Prize-winning strategy is ineffective for most pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) patients.
“Immune checkpoint therapy is only an option in rare cases of PDAC,” Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Professor Douglas Fearon says. “It’s only effective for patients with a specific subtype of PDAC—that’s less than 5% of all cases.”
Until recently, it was thought that PDAC didn’t ...
2024-08-26
A new study uses co-creation with reference communities to develop an app for sign language machine translation (SLMT). The research team designed a theatrical performance in sign language, seen through the eyes of artificial intelligence (AI), as one of the methodologies. “Historically, deaf people have been excluded from the development of automatic translation technologies,” says Shaun O’Boyle, Research Fellow in the School of Inclusive and Special Education (Dublin City University DCU). “This has often caused backlash and resistance from deaf communities, as the projects were designed and ...
2024-08-26
SAN FRANCISCO — The University of South Carolina and the Public Library of Science (PLOS) today announced a three-year Open Access agreement that allows researchers to publish in PLOS journals[1] without incurring article processing charges (APC). This partnership brings together two organizations that believe researchers should be able to access content freely and make their work available publicly, regardless of their access to funds.
“The evidence is undeniable — open research enables the convergence of ...
2024-08-26
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Scientists have learned that children find it hard to focus on a task, and often take in information that won’t help them complete their assignment. But the question is, why?
In a new study, researchers found that this “distributed attention” wasn’t because children’s brains weren’t mature enough to understand the task or pay attention, and it wasn’t because they were easily distracted and lacked the control to focus.
It now appears that kids distribute their attention broadly either out of simple curiosity or because their working memory isn’t developed enough to complete a task without “over ...
2024-08-26
Cognitive functions, also known as intellectual functions, encompass thinking, understanding, memory, language, computation, and judgment, and are performed in the cerebrum. The prefrontal cortex (PFC), located in the frontal lobe of the cerebral cortex, handles these functions. Studies have shown that exercise improves cognitive function through mechanisms such as enhanced cerebral blood flow, structural changes in the brain, and promotion of neurogenesis. However, 81% of children globally do not engage in enough physical activity, leading to high levels of sedentary behavior and insufficient exercise. This lack of physical ...
2024-08-26
Austocystin D, a natural compound produced by fungi, has been recognized for its cytotoxic effects and anticancer activity in various cell types. It exhibits potent activity even in cells that express proteins associated with multidrug resistance, attracting significant global research interest. Austocystin D promotes cell death by damaging their DNA, a process which might be dependent on cytochrome P450 (CYP) oxygenase enzymes. Notably, austocystin D has shown significant activity against cancer cells with increased CYP expression. However, the specific role and function of the CYP2J2 enzyme in the cytotoxicity of austocystin D remain ...
2024-08-26
Research Highlights:
People diagnosed with unruptured cerebral aneurysms (weakened areas in brain blood vessels) who are being monitored without treatment have a higher risk of developing mental illness compared to those who have not been diagnosed with a cerebral aneurysm. The largest impact was among adults younger than age 40.
The study conducted in South Korea found that the psychological burden caused by the diagnosis of an unruptured aneurysm may contribute to the development of mental health conditions, such as anxiety, stress, depression, eating ...
2024-08-26
A new Nature Human Behaviour study, jointly led by Dr Margherita Malanchini at Queen Mary University of London and Dr Andrea Allegrini at University College London, has revealed that non-cognitive skills, such as motivation and self-regulation, are as important as intelligence in determining academic success. These skills become increasingly influential throughout a child's education, with genetic factors playing a significant role. The research, conducted in collaboration with an international team of experts, suggests that fostering non-cognitive skills alongside cognitive abilities could significantly improve educational ...
2024-08-26
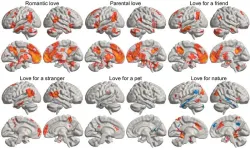
We use the word ‘love’ in a bewildering range of contexts — from sexual adoration to parental love or the love of nature. Now, more comprehensive imaging of the brain may shed light on why we use the same word for such a diverse collection of human experiences.
‘You see your newborn child for the first time. The baby is soft, healthy and hearty — your life’s greatest wonder. You feel love for the little one.’
The above statement was one of many simple scenarios presented to fifty-five parents, self-described as being in a loving relationship. Researchers from Aalto University utilised ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Unraveling the role of CDCA7 in maintenance of DNA methylation