(Press-News.org) SAN FRANCISCO — The University of South Carolina and the Public Library of Science (PLOS) today announced a three-year Open Access agreement that allows researchers to publish in PLOS journals[1] without incurring article processing charges (APC). This partnership brings together two organizations that believe researchers should be able to access content freely and make their work available publicly, regardless of their access to funds.
“The evidence is undeniable — open research enables the convergence of disciplines that drives scientific innovations,” said Amie Freeman, University Libraries Assistant Head of Acquisitions and Scholarly Communication. “This agreement with PLOS gives our researchers more avenues to provide their work to the public, and, in doing so, increases readership and opportunities for societal impact.”
Researchers from the University of South Carolina will have unlimited opportunity to publish over three years and will not be charged any APCs. This agreement furthers PLOS’ mission of making open access publishing available to all while ensuring that its journals include research from authors representing a diverse array of disciplines, career stages and geographies.
“The agreement with the University of South Carolina is yet another step in our goal of empowering authors who want to publish their research openly,” said Roheena Anand, Executive Director of Global Publishing Development & Sales at PLOS. “This agreement demonstrates our effort to build a truly ‘open to read, open to publish’ environment for authors as well as our commitment to our library partners.”
#####
About the Public Library of Science
PLOS is a nonprofit, open access publisher empowering researchers to accelerate progress in science and medicine by leading a transformation in research communication. Since our founding in 2001, PLOS journals have helped break boundaries in research communication to provide more opportunities, choice, and context for researchers and readers. For more information, visit http://www.plos.org.
About the University of South Carolina
The University of South Carolina is a globally recognized, high-impact research university committed to a superior student experience and to innovation in learning, research and community engagement. Founded in 1801, the university is a top-tier Carnegie Foundation research institution offering the No. 1 first-year student experience among public universities and more than 300 academic degree programs. More than 50,000 students are enrolled at one of 20 locations throughout the state, including the research campus in Columbia. With 60 nationally ranked academic programs — including top-ranked programs in international business, the nation's best honors college and distinguished programs in engineering, law, medicine, public health and the arts — the university is helping to build healthier, more educated communities in South Carolina and around the world.
CONTACTS:
David Knutson
Sr. Communications Manager, PLOS
651-260-8288
dknutson@plos.org
Amie Freeman
Assistant Head of Acquisitions and Scholarly Communication, University of South Carolina
803-777-8280
dillarda@mailbox.sc.edu
[1] PLOS ONE, PLOS Digital Health, PLOS Computational Biology, PLOS Pathogens, PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases, PLOS Genetics and PLOS Complex Systems.
END
PLOS and the University of South Carolina announce APC-free Open Access publishing agreement
2024-08-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Why children can’t pay attention to the task at hand
2024-08-26
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Scientists have learned that children find it hard to focus on a task, and often take in information that won’t help them complete their assignment. But the question is, why?
In a new study, researchers found that this “distributed attention” wasn’t because children’s brains weren’t mature enough to understand the task or pay attention, and it wasn’t because they were easily distracted and lacked the control to focus.
It now appears that kids distribute their attention broadly either out of simple curiosity or because their working memory isn’t developed enough to complete a task without “over ...
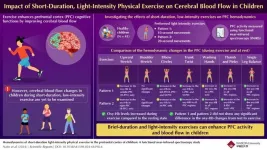
Short-duration, light-intensity exercises improve cerebral blood flow in children
2024-08-26
Cognitive functions, also known as intellectual functions, encompass thinking, understanding, memory, language, computation, and judgment, and are performed in the cerebrum. The prefrontal cortex (PFC), located in the frontal lobe of the cerebral cortex, handles these functions. Studies have shown that exercise improves cognitive function through mechanisms such as enhanced cerebral blood flow, structural changes in the brain, and promotion of neurogenesis. However, 81% of children globally do not engage in enough physical activity, leading to high levels of sedentary behavior and insufficient exercise. This lack of physical ...
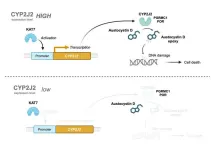
Exploring the role of cytochrome oxygenases in augmenting austocystin D-mediated cytotoxicity
2024-08-26
Austocystin D, a natural compound produced by fungi, has been recognized for its cytotoxic effects and anticancer activity in various cell types. It exhibits potent activity even in cells that express proteins associated with multidrug resistance, attracting significant global research interest. Austocystin D promotes cell death by damaging their DNA, a process which might be dependent on cytochrome P450 (CYP) oxygenase enzymes. Notably, austocystin D has shown significant activity against cancer cells with increased CYP expression. However, the specific role and function of the CYP2J2 enzyme in the cytotoxicity of austocystin D remain ...
Knowing you have a brain aneurysm may raise anxiety risk, other mental health conditions
2024-08-26
Research Highlights:
People diagnosed with unruptured cerebral aneurysms (weakened areas in brain blood vessels) who are being monitored without treatment have a higher risk of developing mental illness compared to those who have not been diagnosed with a cerebral aneurysm. The largest impact was among adults younger than age 40.
The study conducted in South Korea found that the psychological burden caused by the diagnosis of an unruptured aneurysm may contribute to the development of mental health conditions, such as anxiety, stress, depression, eating ...
Non-cognitive skills: the hidden key to academic success
2024-08-26
A new Nature Human Behaviour study, jointly led by Dr Margherita Malanchini at Queen Mary University of London and Dr Andrea Allegrini at University College London, has revealed that non-cognitive skills, such as motivation and self-regulation, are as important as intelligence in determining academic success. These skills become increasingly influential throughout a child's education, with genetic factors playing a significant role. The research, conducted in collaboration with an international team of experts, suggests that fostering non-cognitive skills alongside cognitive abilities could significantly improve educational ...
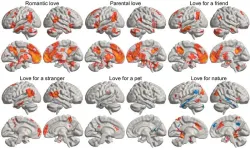
Finding love: Study reveals where love lives in the brain
2024-08-26
We use the word ‘love’ in a bewildering range of contexts — from sexual adoration to parental love or the love of nature. Now, more comprehensive imaging of the brain may shed light on why we use the same word for such a diverse collection of human experiences.
‘You see your newborn child for the first time. The baby is soft, healthy and hearty — your life’s greatest wonder. You feel love for the little one.’
The above statement was one of many simple scenarios presented to fifty-five parents, self-described as being in a loving relationship. Researchers from Aalto University utilised ...
Researchers develop high-entropy non-covalent cyclic peptide glass
2024-08-26
Researchers from the Institute of Process Engineering (IPE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have developed a sustainable, biodegradable, biorecyclable material: high-entropy non-covalent cyclic peptide (HECP) glass. This innovative glass features enhanced crystallization-resistance, improved mechanical properties, and increased enzyme tolerance, laying the foundation for its application in pharmaceutical formulations and smart functional materials. This study was published in Nature Nanotechnology on ...
Mapping the sex life of Malaria parasites at single cell resolution, reveals the genetics underlying Malaria transmission
2024-08-26
Malaria is caused by a eukaryotic microbe of the Plasmodium genus, and is responsible for more deaths than all other parasitic diseases combined. In order to transmit from the human host to the mosquito vector, the parasite has to differentiate to its sexual stage, referred to as the gametocyte stage. Unlike primary sex determination in mammals, which occurs at the chromosome level, it is not known what causes this unicellular parasite to form males and females. New research at Stockholm University has implemented high-resolution genomic tools to map the global repertoire of genes ...
Communicating consensus strengthens beliefs about climate change
2024-08-26
Climate scientists have long agreed that humans are largely responsible for climate change. However, people often do not realize how many scientists share this view. A new 27-country study published in the journal Nature Human Behaviour finds that communicating the consensus among scientists can clear up misperceptions and strengthen beliefs about climate change.
The study is co-led by Bojana Većkalov at the University of Amsterdam and Sandra Geiger of the University of Vienna. Kai Ruggeri, professor of health policy and management at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health, is the corresponding author.
Scientific consensus identifying humans as primarily ...
Almost half of FDA-approved AI medical devices are not trained on real patient data
2024-08-26
Artificial intelligence (AI) has practically limitless applications in healthcare, ranging from auto-drafting patient messages in MyChart to optimizing organ transplantation and improving tumor removal accuracy. Despite their potential benefit to doctors and patients alike, these tools have been met with skepticism because of patient privacy concerns, the possibility of bias, and device accuracy.
In response to the rapidly evolving use and approval of AI medical devices in healthcare, a multi-institutional team of researchers at the UNC School of Medicine, Duke University, Ally Bank, Oxford University, Colombia University, and University of Miami have been on a mission to build ...