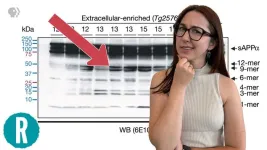
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, Aug. 26, 2024 — In June 2024, a landmark Alzheimer's research paper was retracted due to fraud allegations. Did we waste billions of dollars and thousands of hours of scientists’ time? Maybe not. There are now two potentially helpful drugs on the market targeting the subject of the paper: amyloid beta. This video breaks down the amyloid-beta hypothesis, the fraud itself and where we go from here.
Reactions is a video series produced by the American Chemical Society and PBS Digital Studios. Subscribe to Reactions and follow us on X, formerly Twitter @ACSReactions.
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world’s scientific knowledge. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Follow us: Twitter | Facebook | Instagram
END
How a retracted paper affected the course of Alzheimer’s research (video)
2024-08-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Genotype Matters: Tailored screening for germline CHEK2 variants
2024-08-26
“In our study, we postulated that these differences were driven by three common low-risk (LR) missense variants: p.I157T, p.S428F, and p.T476M, all of which have a BC odds ratio of <1.4.”
BUFFALO, NY- August 26, 2024 – A new editorial was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on July 10, 2024, entitled, “Genotype matters: Personalized screening recommendations for germline CHEK2 variants.”
Recognized as a moderate-risk gene, CHEK2—responsible for encoding the CHK2 protein, ...
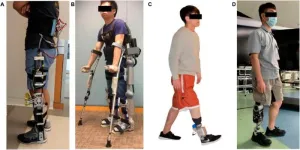
Interlimb and intralimb synergy modeling for lower limb assistive devices: Modeling methods and feature selection
2024-08-26
A research paper by scientists at Hainan University proposed FSS-eq2Seq as a 2-stage strategy for gait synergy modeling in lower limb assistive devices to achieve synergic and user-adaptive trajectories that improve human-machine interactions.
The new research paper, published on Jul. 03 in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems, indicatedSeq2Seq outperforms LSTM, RNN, and GRU in both interlimb and intralimb synergy modeling. Further, FS significantly improves Seq2Seq’s modeling performance.
The concept of gait synergy provides novel human-machine interfaces and has been applied ...
Darwin’s fear was unjustified: Writing evolutionary history by bridging the gaps
2024-08-26
Fossils are used to reconstruct evolutionary history, but not all animals and plants become fossils and many fossils are destroyed before we can find them (e.g., the rocks that contain the fossils are destroyed by erosion). As a result, the fossil record has gaps and is incomplete, and we’re missing data that we need to reconstruct evolutionary history. Now, a team of sedimentologists and stratigraphers from the Netherlands and the UK examined how this incompleteness influences the reconstruction of evolutionary history. To their surprise, they found that the incompleteness itself is actually not such a big issue. “It’s ...
Trends of heat-related deaths in the US, 1999-2023
2024-08-26
About The Study: This study found that heat-related mortality rates in the U.S. increased between 1999 and 2023, especially during the last 7 years. Although a study using data through 2018 found a downward trend in heat-related mortality in the U.S., this study is the first to our knowledge to demonstrate a reversal of this trend from 2016 to 2023. These results align with site-specific data analyzed in a global study that suggest increases in heat-related mortality. As temperatures continue to rise because of climate change, the recent increasing trend is likely to continue. Local authorities in high-risk areas should consider investing in the expansion of access to hydration centers ...
Transgender students more likely than cisgender peers to seek support from school staff, UW–Madison and NYU study finds
2024-08-26
MADISON – Transgender students are more likely to seek support from school staff and less likely to seek support from their parents when compared to their cisgender peers, according to a new study from researchers at the University of Wisconsin–Madison and New York University.
The study, published in JAMA Pediatrics, found among students who felt depressed or anxious, transgender students were 74% less likely than their cisgender peers to seek help from parents than from adults in schools. It also found transgender students were 25% less likely than cisgender students to seek support from ...
Longitudinal changes in youth mental health from before to during the COVID-19 pandemic
2024-08-26
About The Study: In this longitudinal cohort study of economically and racially diverse U.S. youth, there was evidence of differential susceptibility and resilience for mental health problems during the pandemic that was associated with prepandemic mental health and sociodemographic characteristics. These differences are critical to understand for recovery and may yield novel insights into causes of youth mental health problems.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Courtney ...
Repetitive head impacts and perivascular space volume in former football players
2024-08-26
About The Study: In this cross-sectional cohort study of 170 former football players and 54 unexposed controls, larger perivascular space (PVS) volume was associated with greater exposure to repetitive head impacts (RHI). Additionally, PVS volume was associated with worse performance on cognitive tests. These findings suggest that PVS volume may contribute to the association between exposure to RHI, cognitive impairment, and the development of RHI-associated neurodegeneration.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding ...
Sharing expands caring – UMD study finds solution to a major source of doctor burnout
2024-08-26
COLLEGE PARK, Md. – Who hasn’t sat in a medical office, listening to computer keys clacking while their provider rapidly types up notes, wondering what they are spending so much time writing about? For doctors, who have always written clinical care notes but increasingly must spend time cataloging billing details, this additional documentation is a major source of job dissatisfaction and burnout. A new study out today by University of Maryland’s School of Public Health illuminates a solution that can meaningfully reduce the amount of time doctors spend writing notes, without losing vital information.
“Providers are already stretched thin and under intense pressure to ...
Human stem cell models point to glia as key players in multiple sclerosis
2024-08-26
NEW YORK, NY (AUGUST 26, 2024) — A team of scientists from The New York Stem Cell Foundation (NYSCF) Research Institute and Case Western Reserve University has created the largest reported collection of stem cell models from multiple sclerosis (MS) patients and used them to identify unique ways in which glia – integral support cells in the brain – contribute to the disease.
The study, published today in Cell Stem Cell, is the first to report that glial cells from MS patients have intrinsic hallmarks of disease, independent of immune system influences, which points to the power of stem cells for revealing new disease biology and to the need for ...
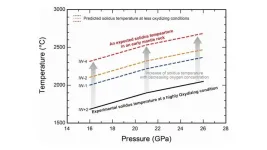
Uncovering the role of oxygen concentration in the formation of early earth magma ocean
2024-08-26
It is widely accepted that the early Earth largely consisted of molten magma, forming a global ocean of magma. This extreme state of Earth was likely caused by the intense heat generated from accretionary impacts, meaning the collision of smaller celestial bodies with Earth. Understanding the formation of this magma ocean is crucial for comprehending Earth’s formation. A major problem with current magma ocean formation models is the lack of consensus on the melting temperatures of deep mantle rocks. Models explaining Earth’s core formation use a specific ...