(Press-News.org) About The Study: Patients with post–COVID-19 mRNA vaccination myocarditis, contrary to those with post–COVID-19 myocarditis, show a lower frequency of cardiovascular complications than those with conventional myocarditis at 18 months. However, affected patients, mainly healthy young men, may require medical management up to several months after hospital discharge.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Laura Semenzato, MSc (laura.semenzato@assurance-maladie.fr) and Mahmoud Zureik, MD, PhD (Mahmoud.ZUREIK@ansm.sante.fr).
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.16380)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Media advisory: This study is being presented at the 2024 International Society for Pharmacoepidemiology Annual Meeting.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/10.1001/jama.2024.16380?guestAccessKey=07ee8e37-54d7-4436-8659-20e806e46c32&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=082624
END
Long-term prognosis of patients with myocarditis attributed to COVID-19 mRNA vaccination, SARS-CoV-2 infection, or conventional etiologies
JAMA
2024-08-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
LZ experiment sets new record in search for dark matter
2024-08-26
Figuring out the nature of dark matter, the invisible substance that makes up most of the mass in our universe, is one of the greatest puzzles in physics. New results from the world’s most sensitive dark matter detector, LUX-ZEPLIN (LZ), have narrowed down possibilities for one of the leading dark matter candidates: weakly interacting massive particles, or WIMPs.
LZ, led by the Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab), hunts for dark matter from a cavern nearly one mile underground at the Sanford Underground Research Facility in South Dakota. The experiment’s new results explore weaker dark matter interactions ...
Astrophysicists use AI to precisely calculate universe’s ‘settings’
2024-08-26
The standard model of the universe relies on just six numbers. Using a new approach powered by artificial intelligence, researchers at the Flatiron Institute and their colleagues extracted information hidden in the distribution of galaxies to estimate the values of five of these so-called cosmological parameters with incredible precision.
The results were a significant improvement over the values produced by previous methods. Compared to conventional techniques using the same galaxy data, the approach yielded less than half ...
SETI Institute starts first low frequency search for alien technology in distant galaxies
2024-08-26
August 26, 2024, Mountain View, CA -- The SETI Institute, the Berkeley SETI Research Center and the International Centre for Radio Astronomy Research announced a groundbreaking study using the Murchison Widefield Array (MWA) in Western Australia. Led by Dr. Chenoa Tremblay of the SETI Institute and Prof. Steven Tingay of Curtin University, this research is the first to search for signs of alien technology in galaxies beyond our own, focusing on low radio frequencies (100 MHz). This innovative study used the MWA’s large field of view (FOV), allowing the team to cover about 2,800 galaxies in one observation, of which 1300 we know the distance to. Usually, the search for extraterrestrial ...
Bicycle rolling-stop laws don’t lead to unsafe behavior by riders or motorists, research shows
2024-08-26
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Laws that let bicyclists treat stop signs as yield signs lead neither riders nor motorists to act unsafely, according to a groundbreaking Oregon State University study.
The project by OSU College of Engineering researchers featured a novel experimental technique – linking separate bicycle and motor vehicle simulators – and the findings are important as more and more states consider bicycle rolling-stop legislation, said David Hurwitz, the study’s leader.
“It required fully connecting two independent simulators, running subjects in pairs simultaneously and having each subject interacting with an avatar of the other in a shared virtual ...
How a retracted paper affected the course of Alzheimer’s research (video)
2024-08-26
WASHINGTON, Aug. 26, 2024 — In June 2024, a landmark Alzheimer's research paper was retracted due to fraud allegations. Did we waste billions of dollars and thousands of hours of scientists’ time? Maybe not. There are now two potentially helpful drugs on the market targeting the subject of the paper: amyloid beta. This video breaks down the amyloid-beta hypothesis, the fraud itself and where we go from here.
Reactions is a video series produced by the American Chemical Society and PBS Digital Studios. Subscribe to Reactions and follow us on X, formerly Twitter @ACSReactions.
The American Chemical ...
Genotype Matters: Tailored screening for germline CHEK2 variants
2024-08-26
“In our study, we postulated that these differences were driven by three common low-risk (LR) missense variants: p.I157T, p.S428F, and p.T476M, all of which have a BC odds ratio of <1.4.”
BUFFALO, NY- August 26, 2024 – A new editorial was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on July 10, 2024, entitled, “Genotype matters: Personalized screening recommendations for germline CHEK2 variants.”
Recognized as a moderate-risk gene, CHEK2—responsible for encoding the CHK2 protein, ...
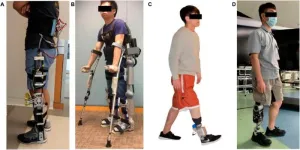
Interlimb and intralimb synergy modeling for lower limb assistive devices: Modeling methods and feature selection
2024-08-26
A research paper by scientists at Hainan University proposed FSS-eq2Seq as a 2-stage strategy for gait synergy modeling in lower limb assistive devices to achieve synergic and user-adaptive trajectories that improve human-machine interactions.
The new research paper, published on Jul. 03 in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems, indicatedSeq2Seq outperforms LSTM, RNN, and GRU in both interlimb and intralimb synergy modeling. Further, FS significantly improves Seq2Seq’s modeling performance.
The concept of gait synergy provides novel human-machine interfaces and has been applied ...
Darwin’s fear was unjustified: Writing evolutionary history by bridging the gaps
2024-08-26
Fossils are used to reconstruct evolutionary history, but not all animals and plants become fossils and many fossils are destroyed before we can find them (e.g., the rocks that contain the fossils are destroyed by erosion). As a result, the fossil record has gaps and is incomplete, and we’re missing data that we need to reconstruct evolutionary history. Now, a team of sedimentologists and stratigraphers from the Netherlands and the UK examined how this incompleteness influences the reconstruction of evolutionary history. To their surprise, they found that the incompleteness itself is actually not such a big issue. “It’s ...
Trends of heat-related deaths in the US, 1999-2023
2024-08-26
About The Study: This study found that heat-related mortality rates in the U.S. increased between 1999 and 2023, especially during the last 7 years. Although a study using data through 2018 found a downward trend in heat-related mortality in the U.S., this study is the first to our knowledge to demonstrate a reversal of this trend from 2016 to 2023. These results align with site-specific data analyzed in a global study that suggest increases in heat-related mortality. As temperatures continue to rise because of climate change, the recent increasing trend is likely to continue. Local authorities in high-risk areas should consider investing in the expansion of access to hydration centers ...
Transgender students more likely than cisgender peers to seek support from school staff, UW–Madison and NYU study finds
2024-08-26
MADISON – Transgender students are more likely to seek support from school staff and less likely to seek support from their parents when compared to their cisgender peers, according to a new study from researchers at the University of Wisconsin–Madison and New York University.
The study, published in JAMA Pediatrics, found among students who felt depressed or anxious, transgender students were 74% less likely than their cisgender peers to seek help from parents than from adults in schools. It also found transgender students were 25% less likely than cisgender students to seek support from ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Long-term prognosis of patients with myocarditis attributed to COVID-19 mRNA vaccination, SARS-CoV-2 infection, or conventional etiologiesJAMA