Discovery of a rare genotype causing primary ovarian insufficiency
2024-08-27
(Press-News.org) Scientists at deCODE genetics and collaborators, have identified a sequence variant in the CCDC201 gene that when inherited from both parents homozygous causes menopause on average nine years earlier.
deCODE genetics, a subsidiary of Amgen, and collaborators from Iceland, Denmark, the UK, and Norway published a study in Nature Genetics today revealing a rare genotype with a significant impact on women's health.
Age at menopause significantly affects fertility and disease risk. This research focused on recessive models, or on individuals with two copies of a sequence variant called homozygotes, which are less commonly studied then the additive model, which mainly relies on individuals carrying one copy of a sequence variant, especially when this one is rare. By analyzing data from over 174,000 women across Iceland, Denmark, the UK, and Norway, the researchers discovered a stop gain variant leading to a change from and Arginine at position 162 to Termination in the CCDC201 gene, that dramatically impacts AOM.
The CCDC201 gene, only identified in humans as a protein coding gene in 2022 and has since then been shown to be highly expressed in egg cells, and this study demonstrates that its complete loss-of-function significantly impacts female reproductive health.
Women carrying two copies of this variant, referred to as homozygotes, experience menopause an average of nine years earlier than non-carriers.. This homozygous genotype is found in roughly 1 in 10,000 women of Northern European descent, leads to primary ovarian insufficiency, defined as age at menopause before the age of 40, in nearly half of carriers. Consequently, women with this genotype have fewer children and have children very rarely after the age of 30.
This discovery highlights the importance of considering various genetic models in understanding diseases such as primary ovarian insufficiency.
The study underscores the potential benefits of genetic counseling for women with this specific genotype. Early diagnosis allows for informed reproductive choices and management of symptoms associated with early menopause.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-08-27
London, United Kingdom – 27 Aug 2024: New research presented at the ESC Congress 2024 in London, UK (30 August – 2 September) shows that women in the menopause transition period show changes in their blood cholesterol profiles which could have an adverse impact on their cardiovascular health.
“There is an increase in ‘bad’ low-density type lipoprotein (LDL) particles and a decrease in ‘good’ high-density lipoprotein particles (HDL) that takes place during and after the menopause transition,” says study author Dr Stephanie Moreno, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX, USA. “Taken ...
2024-08-27
Millions of women who work in the fisheries industry are being left behind as technologies develop to counter the effects of climate change and economic pressures.
New research led by the University of East Anglia (UEA) looks specifically at post-harvest fisheries and aquaculture, where women constitute 50 per cent of the total workforce. Despite their significant contributions women often remain invisible, are unpaid or underpaid, their work seen as an extension of household work.
The findings, ‘A systematic review of the impact of post-harvest aquatic food ...
2024-08-27
The James Webb Space Telescope has spotted six likely rogue worlds—objects with planetlike masses but untethered from any star’s gravity—including the lightest ever identified with a dusty disk around it.
The elusive objects offer new evidence that the same cosmic processes that give birth to stars may also play a common role in making objects only slightly bigger than Jupiter.
“We are probing the very limits of the star forming process,” said lead author Adam Langeveld, an astrophysicist at Johns Hopkins University. “If you have an object that looks like a young Jupiter, is it possible that ...
2024-08-27
A two-faced star, a star as massive as the Sun but as compact as the Moon, and star ‘corpses’ that engulf entire planets and disrupt planetary orbits. Ilaria Caiazzo, an astrophysicist who has made stunning discoveries, joins the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) as a new assistant professor. Her path led her from philosophy to studying stellar evolution and death while managing her broad interests including movie production.
Ilaria Caiazzo has always had a broad spectrum of interests. Her path to astrophysics started in philosophy and ...
2024-08-27
Dungeons and Dragons is a hugely popular roleplaying game enjoyed by millions of people all over the world, both in person and online, every day.
However, new research has found it could be particularly beneficial for people with autism, giving them a safe space to engage in social interactions away from some of the challenges they face in their daily lives.
The study, published in the journal Autism, was led by researchers from the University of Plymouth’s School of Psychology along with colleagues at Edge ...
2024-08-27
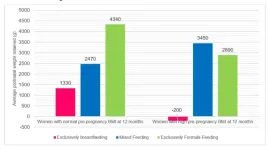
27 August 2024, Singapore – A KK Women’s and Children’s Hospital (KKH) study[1] on breastfeeding practices revealed that among the women who exclusively breastfed, those with high body mass index[2] (BMI) before pregnancy lost more weight than women with a healthy BMI pre-pregnancy.
Women with high BMI who exclusively breastfed, in addition to losing their pregnancy weight, lost an extra 200 grammes on average, 12 months after childbirth. Women with normal BMI who exclusively breastfed lost weight ...
2024-08-27
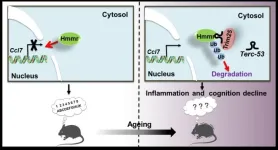
The authors investigate the physiological functions of Terc-53 by creating transgenic mice that overexpress this noncoding RNA. They observe that Terc-53 overexpression affects normal aging in mammals, contributing to cognitive decline and shortened lifespan. Mechanistically, they find that Terc-53 binds to and promotes the degradation of Hmmr, leading to enhanced inflammation in tissues and accelerated aging. They also note that Hmmr levels decrease with age in certain brain regions, similar to Terc-53's pattern, and that restoring Hmmr levels can improve cognitive abilities ...
2024-08-27
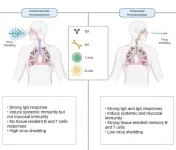
A next-generation COVID-19 mucosal vaccine is set to be a gamechanger not only when delivering the vaccine itself, but also for people who are needle-phobic.
New Griffith University research, published in Nature Communications, has been testing the efficacy of delivering a COVID-19 vaccine via the nasal passages.
Professor Suresh Mahalingam from Griffith’s Institute for Biomedicine and Glycomics has been working on this research for the past four years.
“This is a live attenuated intranasal vaccine, called CDO-7N-1, designed ...
2024-08-27
A research group led by Nagoya University has developed an innovative approach to creating anti-counterfeiting labels for high-value goods. Their findings, published in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, enhance the security of the currently used cholesteric liquid crystals (CLCs) by adding fluorescent dyes to produce florescent CLCs (FCLCs).
Using this unique technology, the group created unique labels with almost impossible-to-counterfeit security features. These advanced labels are designed to protect valuable items, important documents, and sensitive products ...
2024-08-27
The Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology funded two research projects in 2024 as part of its research seed grant program. The program supports interdisciplinary research projects and is now in its second year.
This year, two research projects beginning in May 2024 received $75,000 per year for up to two years.
Research projects seeded by the Beckman Institute anticipate growth and typically lead to external funding proposals after the two-year seeding term.
Exploring how ASD-related genes influence brain networks that guide behavior
The CDC estimates that “1 in 36 children has been identified with autism spectrum disorder,” or ASD.
ASDs ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Discovery of a rare genotype causing primary ovarian insufficiency