(Press-News.org) LOUISVILLE, Ky. – The University of Louisville’s groundbreaking Green Heart Louisville Project has found that people living in neighborhoods where the number of trees and shrubs was more than doubled showed lower levels of a blood marker of inflammation than those living outside the planted areas. General inflammation is an important risk indicator for heart disease and other chronic diseases.
The Christina Lee Brown Envirome Institute launched the first-of-its-kind project in 2018 in partnership with The Nature Conservancy, Washington University in St. Louis, Hyphae Design Laboratory and others to study whether and how living among more densely greened surroundings contributes to better heart health. The design of the study closely mirrors clinical trials which test whether medical treatments are effective. The team applied the treatment – the addition of large trees and shrubs – to some participants’ neighborhoods but not to others. They then compared residents’ health data to see how the addition of the trees affected their health.
“The Green Heart Louisville Project is an excellent example of how our university’s innovative and collaborative researchers are working to improve lives in our community and far beyond,” UofL President Kim Schatzel said. “Trees are beautiful, but these results show that the trees around us are also beneficial to individual and community health. Through this and many other projects, the Envirome Institute is improving health at the community level, not just for individuals, but for everyone living in a neighborhood.”
To understand the state of community’s health at the start of the study, researchers took blood, urine, hair and nail samples and documented health data from 745 people living in a four-square-mile area of south Louisville. The researchers also took detailed measurements of tree coverage and levels of air pollution in the area.
Following this baseline data collection, the Envirome Institute worked with The Nature Conservancy and a host of local partners and contractors to plant more than 8,000 large trees and shrubs in designated neighborhoods within the project area. Those living in the greened area were considered the treated population and the results obtained from this population were compared with residents of adjacent neighborhoods, where the project team did not plant any trees.
After the plantings, the research team reassessed residents’ health. They found that those living in the greened area had 13-20% lower levels of a biomarker of general inflammation, a measure called high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) than those living in the areas that did not receive any new trees or shrubs. Higher levels of hsCRP are strongly associated with a risk of cardiovascular disease and are an even stronger indicator of heart attack than cholesterol levels. Higher CRP levels also indicate a higher risk of diabetes and certain cancers.
A reduction of hsCRP by this percentage corresponds to nearly 10-15% reduction in the risk of heart attacks, cancer or dying from any disease.
“These results from the Green Heart Louisville Project indicate that trees contribute more to our lives than beauty and shade. They can improve the health of the people living around them,” said Aruni Bhatnagar, director of the Envirome Institute and UofL professor of medicine. “Although several previous studies have found an association between living in areas of high surrounding greenness and health, this is the first study to show that a deliberate increase in greenness in the neighborhood can improve health. With these results and additional studies that we hope to report soon, we are closer to understanding the impact of local tree cover on residents’ health. This finding will bolster the push to increase urban greenspaces.”
As more is known about the health impacts of increased tree cover, increased greening in cities may emerge as a key method to improve public health.
“Most of us intuitively understand that nature is good for our health. But scientific research testing, verifying and evaluating this connection is rare,” said Katharine Hayhoe, chief scientist of The Nature Conservancy. “These recent findings from the Green Heart Project build the scientific case for the powerful connections between the health of our planet and the health of all of us.”
Earlier in August, the Green Heart Louisville Project was awarded an additional $4.6 million in funding from the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences to support continued research over the next five years.
These findings were presented by Daniel Riggs, UofL assistant professor of environmental medicine, at the 36th Annual Conference of the International Society for Environmental Epidemiology in Santiago, Chile on Aug. 26.
END
UofL Green Heart Louisville Project study shows reduced inflammation in residents after adding trees to their neighborhoods
Inflammation is associated with increased risk of heart disease and cancer
2024-08-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
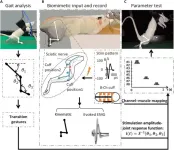
Biomimetic peripheral nerve stimulation promotes the rat hindlimb motion modulation in stepping: An experimental analysis
2024-08-27
A research paper by scientists at Beijing Institute of Technology presented a sciatic nerve stimulation method that will aid in lower extremity standing and stepping.
The new research paper, published on Jul. 04 in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems, used the electrical nerve stimulation method and achieved muscle control via different sciatic nerve branches to facilitate the regulation of lower limb movements during stepping and standing.
Peripheral nerve stimulation is an effective neuromodulation method in patients with lower extremity movement disorders caused by stroke, spinal cord injury, or other diseases. ...
The brain’s balancing system
2024-08-27
A finding by a McGill-led team of neuroscientists could open doors to new treatments for a range of psychiatric and neurological disorders attributed to dysfunctions in specific dopamine pathways.
For those struggling with a psychiatric disorder such as schizophrenia, addiction or ADHD, or with neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease or Alzheimer’s, there might be good news ahead. The neuroscientists have discovered that a small group of dopamine neurons in the striatum play a crucial role in balancing several essential brain functions, including those related to reward, cognition and movement.
Dopamine ...
Bubbling, frothing and sloshing: Long-hypothesized plasma instabilities finally observed
2024-08-27
Whether between galaxies or within doughnut-shaped fusion devices known as tokamaks, the electrically charged fourth state of matter known as plasma regularly encounters powerful magnetic fields, changing shape and sloshing in space. Now, a new measurement technique using protons, subatomic particles that form the nuclei of atoms, has captured details of this sloshing for the first time, potentially providing insight into the formation of enormous plasma jets that stretch between the stars.
Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) created ...
Brain research: Study shows what your favourite film genres reveal about your brain
2024-08-27
Crime films, action films, comedies, or documentaries? A person's favourite film genre reveals a lot about how their brain works. This is the finding of a new study led by the Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) that compared data on film preferences with recordings of the brain activity of around 260 people. Fans of action films and comedies reacted very strongly to negative emotional stimuli, while participants who favoured documentaries or crime films and thrillers had a significantly weaker reaction. The results were published in the journal "Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience".
Films are ...
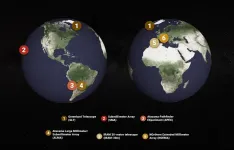
Event horizon telescope makes highest-resolution black hole detections from Earth
2024-08-27
The Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) Collaboration has conducted test observations achieving the highest resolution ever obtained from the surface of the Earth, by detecting light from the centers of distant galaxies at a frequency of around 345 GHz.
When combined with existing images of supermassive black holes at the hearts of M87 and Sgr A at the lower frequency of 230 GHz, these new results will not only make black hole photographs 50% crisper but also produce multi-color views of the region immediately outside the boundary of these cosmic beasts.
The new detections, led by scientists from the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian (CfA) that ...
EHT scientists make highest-resolution observations yet from the surface of Earth
2024-08-27
The Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) Collaboration has conducted test observations, using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) and other facilities, that achieved the highest resolution ever obtained from the surface of Earth [1]. They managed this feat by detecting light from distant galaxies at a frequency of around 345 GHz, equivalent to a wavelength of 0.87 mm. The Collaboration estimates that in future they will be able to make black hole images that are 50% more detailed than was possible before, bringing the region immediately outside the boundary of nearby supermassive black holes into sharper focus. They will also ...
A human-centered AI tool to improve sepsis management
2024-08-27
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A proposed artificial intelligence tool to support clinician decision-making about hospital patients at risk for sepsis has an unusual feature: accounting for its lack of certainty and suggesting what demographic data, vital signs and lab test results it needs to improve its predictive performance.
The system, called SepsisLab, was developed based on feedback from doctors and nurses who treat patients in the emergency departments and ICUs where sepsis, the body’s overwhelming response to an infection, is most ...
MIT Press’s Direct to Open (D2O) seeks funding to continue expanding access to leading scholarship in 2025
2024-08-27
At the MIT Press, we believe that everyone deserves access to scholarship. Our dedication to this mission remains strong as we head into the fourth funding cycle for Direct to Open (D2O), our model for open access monographs. Libraries and consortia can commit to support the program through November 30, 2024.
“Direct to Open is a game changer,” said Amy Brand, Director and Publisher at the MIT Press. “We know that open scholarship benefits authors, readers, and the academy at large. This is why we ...
Obesity and susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2
2024-08-27
A study finds an increased risk of developing a productive SARS-CoV-2 infection in obese people. Obesity is known to predict worse outcomes and higher mortality for those with COVID-19. Masanori Aikawa and colleagues sought to determine if obesity also affected the likelihood of getting ill in the first place. To investigate, the authors analyzed electronic medical records for 687,813 patients from the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, including 72,613 individuals with suspected SARS-CoV-2 exposure, 18,447 of whom tested positive. The authors limited their data to a timeframe before vaccination became widespread in Massachusetts, to avoid the possible confounding ...
Darwin’s longstanding interest in biological rhythms
2024-08-27
A close reading of Darwin’s work suggests a deep interest in cyclical events. Rhythmic phenomena in nature—today the subjects of the field of chronobiology—have been studied since at least the 18th century. In a perspective, Tiago Gomes de Andrade and Andrew D. Beale examined the writings and work of Charles Darwin to explore and share the eminent naturalist’s deep fascination with biological rhythms. Darwin’s work on the “sleep movements” in plants, published in 1880 with his son Francis is well known. This work examined the daily cycle of opening and closing of leaves. But as far ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
[Press-News.org] UofL Green Heart Louisville Project study shows reduced inflammation in residents after adding trees to their neighborhoodsInflammation is associated with increased risk of heart disease and cancer