People experiencing relatively mild cases of mental ill-health may be perceived differently by others depending on whether or not diagnostic labels are provided
The presence of labels may increase empathy and concern for affected individuals, but also pessimism about recovery
2024-08-28
(Press-News.org)
Diagnostic labels for people experiencing what some consider to be relatively milder forms of mental-ill health may affect how others perceive them for better and worse, according to a study published August 28, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS Mental Health by Nick Haslam from the University of Melbourne, Australia, and colleagues.
In recent years, there’s been a general shift to increased diagnoses of mental ill-health. Here, Haslam and colleagues investigate the implications of diagnosing individuals presenting with mild or marginal symptoms. In this research, symptoms were judged to be mild or marginal by members of the public who rated different examples ranging in severity from clearly below to clearly above the diagnostic threshold as determined by a scale in a prior study.
Haslam and colleagues provided research participants (who were U.S. adults recruited from an online platform) with short vignettes describing people presenting with mild or marginal symptoms of different mental illnesses. 261 participants in Study 1 were given three labeled (“This person has a diagnosis of ___”) or unlabeled vignettes describing people presenting with symptoms of major depressive disorder (MDD), bipolar disorder (BD), or generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). 684 participants in Study 2 were given one labeled or unlabeled vignette describing someone presenting with either post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), or binge-eating disorder (BED). Participants were asked about their empathy for the described individual, their support in offering accommodations (e.g. “This person’s employer should not hesitate to offer them extra time to complete work-related tasks”), their suitability for mental health treatment, the persistence of their difficulties (e.g. “This person is likely to fully recover from their problems.”), and their identity (e.g. “This person’s problems are an important part of who they are” (Study 2 only)).
In Study 1, labeled individuals tended to elicit more empathy and be seen as more suitable for treatment versus unlabeled individuals, but were also believed to have more persistent problems. Study 2 differed from Study 1 in that there was no significant difference between empathy for labeled versus unlabeled individuals, but it also found that labelled individuals were seen to have less capacity to overcome their problems. Participants’ ratings varied significantly depending on the described disorder, with MDD and PTSD eliciting especially high empathy and accommodation support.
The results suggest that expansive diagnostic concepts that include relatively mild symptoms may promote help-seeking, empathy, and support, but also undermine perceived agency and expectations that problems can be overcome. It’s critical to remember that the severity of symptoms of individuals with the conditions referred to in this study can change over time and “mild” is subjective. Additionally, the choice to obtain or choose a diagnostic label is a personal one and varies between individuals, conditions and communities.
The authors add: "Applying diagnostic labels to relatively mild forms of distress has mixed blessings. Our research shows that it can increase empathy and support for the person, but also make their problems seem out of their control and harder to overcome."
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS Mental Health: https://journals.plos.org/mentalhealth/article?id=10.1371/journal.pmen.0000096
Citation: Altmann B, Fleischer K, Tse J, Haslam N (2024) Effects of diagnostic labels on perceptions of marginal cases of mental ill-health. PLOS Ment Health 1(3): e0000096. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000096
Author Countries: Australia
Funding: This work was supported by Australian Research Council Discovery Project DP210103984 to NH. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-08-28
“Unhealthy commodities” such as tobacco, alcohol, ultra-processed foods, social media, and fossil fuels, as well as impacts of fossil fuel consumption such as climate change and air pollution are associated with depression, suicide, and self-harm, according to a study published August 28 by Kate Dun-Campbell from the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, and colleagues.
Globally, around one out of every eight people currently live with a mental health disorder. These disorders—including depression, suicide, anxiety, and other diseases and disorders—can have many underlying causes. ...
2024-08-28
Bacterial cells can “remember” brief, temporary changes to their bodies and immediate surroundings, a new Northwestern University and University of Texas-Southwestern study has found.
And, although these changes are not encoded in the cell’s genetics, the cell still passes memories of them to its offspring — for multiple generations.
Not only does this discovery challenge long-held assumptions of how the simplest organisms transmit and inherit physical traits, it also could be leveraged for new medical applications. For example, researchers could circumvent antibiotic resistance by subtly tweaking a pathogenic ...
2024-08-28
If you’ve seen those viral social media videos of dogs using soundboard buttons to “talk,” you’re not alone. These buttons have taken the pet world by storm, leading to impressive and sometimes seemingly miraculous feats shared across platforms like TikTok and Instagram. But are these dogs truly communicating, or are they just responding to cues from their owners?
Now, a new study published in PLOS ONE – by researchers from the University of California San Diego and other institutions – ...
2024-08-28
Researchers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst and UMass Chan Medical School have demonstrated in mice a new method to combat pancreatic cancer. The study, published in Science Translational Medicine, outlines the synergistic effects of a novel nanoparticle drug-delivery system to activate an immune pathway in combination with tumor-targeting agents.
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is the most common form of pancreatic cancer. With a dismal,13% five-year survival rate, it is the third leading cause of cancer deaths.
One major ...
2024-08-28
An archaeogenetic study sheds new light on the isolated medieval community Las Gobas in northern Spain. Besides isolation and endogamy, the researchers have also identified the variola virus which can offer a new explanation on how smallpox entered Iberia.
Researchers from Sweden and Spain have conducted a comprehensive archaeogenetic study on a community that lived on the border between the northern Christian kingdoms and Al-Andalus during the early Medieval period. This dynamic era, especially ...
2024-08-28
A new discovery by researchers at the RIKEN Center for Biosystems Dynamics (BDR) in Japan upends decades of assumptions regarding DNA replication. Led by Ichiro Hiratani and colleagues, the experiments published August 28 in Nature show that DNA replication in early embryos is different from what past research has taught, and includes a period of instability that is prone to chromosomal copying errors. As failed pregnancies and developmental disorders are often related to chromosomal abnormalities the findings could impact the field of reproductive medicine, perhaps leading to improved methods of in vitro fertilization (IVF).
During embryogenesis, ...
2024-08-28
NEW YORK, NY (Aug. 28, 2024)--An analysis of more than 1.6 million brain cells from older adults has captured the cellular changes that occur in the early stages of Alzheimer’s disease, potentially revealing new routes for preventing the most common cause of dementia in older individuals.
The study also identified a second community of cells that drives the older brain down a different path that does not lead to Alzheimer’s disease.
“Our study highlights that Alzheimer’s is a disease of many cells and their interactions, not just a single type of dysfunctional ...
2024-08-28
When it comes to survival, plants have a huge disadvantage compared to many other living organisms: they cannot simply change their location if predators or pathogens attack them or the environmental conditions change to their disadvantage.
For this reason, plants have developed different strategies with which they react to such attacks. Such reactions are usually triggered by certain signals from the environment. As has long been known, the intracellular calcium concentration plays an important role in the processing of these signals.
However, in addition to changes in the cytoplasmic calcium level, changes in the cell's ...
2024-08-28
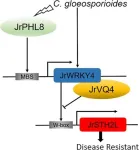
A pivotal study has pinpointed a gene module crucial for enhancing walnut trees' resistance to anthracnose, a widespread fungal disease threatening the walnut industry. The research reveals how the JrPHL8-JrWRKY4-JrSTH2L module regulates disease defense, opening up new opportunities for breeding resistant walnut varieties and promoting sustainable cultivation practices.
Anthracnose, caused by Colletotrichum gloeosporioides, poses a significant threat to walnut production, causing severe losses ...
2024-08-28
Roadway-related incidents are a leading cause of flood fatalities nationwide, but limited flood-reporting tools make it difficult to evaluate road conditions in real time.
Existing tools — traffic cameras, water-level sensors and even social media data — can provide observations of flooding, but they are often not primarily designed for sensing flood conditions on roads and do not work in conjunction. A network of sensors could improve situational flood level awareness; however, they are expensive to operate at scale.
Engineers at Rice University have developed a possible solution to this problem: an automated data ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] People experiencing relatively mild cases of mental ill-health may be perceived differently by others depending on whether or not diagnostic labels are provided
The presence of labels may increase empathy and concern for affected individuals, but also pessimism about recovery