(Press-News.org) Gender nonconformity in 7-year-olds — as measured by levels of gender-conforming play — may be associated with autistic traits and behavioral difficulties in girls, and with peer relationship problems in boys, according to a new study published August 28, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Marlene Stratmann of Karlstad University, Sweden, and colleagues.
Gender nonconformity (GNC) refers to variations in gender expression from societal and cultural gender norms. In childhood, GNC can manifest itself in several ways, including play behavior, peer relationships, clothing, and body language. Childhood GNC does not directly indicate developing gender dysphoria (GD) later in life, although the phenomena are linked. Recently, studies have begun to establish a high co-occurrence of GNC, GD and autism spectrum disorder. However, most of this work has been carried out in clinical populations with existing diagnoses, which may lead to an overestimation of the associations between GNC and autistic traits and behavioral difficulties in a non-clinical population.
In the new study, researchers analyzed data on 718 children enrolled in the Swedish Environmental Longitudinal, Mother and Child, Asthma and Allergy (SELMA) study for which there were data on play behavior and behavioral outcomes. GNC play behavior was determined using the Preschool Activities Inventory, which includes 12 “feminine” and 12 “masculine” toys, play activities and child characteristics.
In both sexes, higher levels of gender nonconforming play was associated with increased behavioral difficulties. Higher masculine play behavior scores were associated with hyperactivity and inattention in both sexes. Higher feminine play scores in boys were associated with peer relationship problems, while higher masculine play scores in girls were associated with increased likelihood of autistic traits and behavioral difficulties.
The study involves a sample of children of only one age in a single country, and cannot be used to draw any conclusions as to causation. However, the authors conclude that gender nonconformity may be associated with behavioral challenges and difficulties in both sexes, even in children without any diagnoses.
The authors add: “The results showed that children who played more with toys traditionally considered for the opposite gender had more autistic traits and behavioral problems. At the same time it is very important to keep in mind that just because a girl decides to play rougher or a boy plays with dolls, it does not mean that there will be a link to behavioral difficulties or autistic traits in this child.”
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0308605
Citation: Özel F, Stratmann M, Papadopoulos FC, Rüegg J, Bornehag C-G (2024) Gender-specific play behavior in relation to autistic traits and behavioral difficulties at the age of seven in the SELMA study. PLoS ONE 19(8): e0308605. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0308605
Author Countries: Sweden, USA
Funding: This work received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under grant agreement no. 634880, EDC-MixRisk and the funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
Autistic traits, behavioral problems in 7-year-olds linked with gender nonconforming play
Study analyzed play behavior, behavioral outcomes, and autistic traits in more than 700 children in Sweden
2024-08-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Geographic differences in US homicide rates have decreased since the 1970s
2024-08-28
A new study finds that, counter to expectations, geographic disparities in rates of homicides in the US have decreased in recent decades. Richard Boylan of Rice University in Houston, Texas, US, presents these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on August 28, 2024.
Since the 1970s, gaps in economic and social wellbeing between Americans living in different regions have grown. Some researchers hypothesize that areas with reduced economic and social well-being would see higher rates of violent crime. For instance, impoverished areas with lower tax bases might receive less police protection, ...
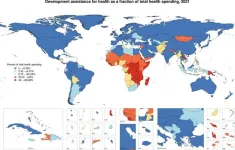
Lackluster prioritization of the health sector in government spending and dwindling donor contributions drive slow growth in health spending in Sub-Saharan Africa
2024-08-28
Slow growth in health sector spending is projected in Sub-Saharan Africa as reported in a study published in the open access journal, PLOS Global Public Health. The decline is expected to continue to 2050, according to Angela E Apeagyei and researchers at the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation, University of Washington, Seattle, and is driven by tepid growth in the share of government spending that is allocated to health and reductions in development assistance for health.
The research analyses data from databases covering development assistance for health, global health spending and gross domestic spending (GDP) per capita ...
People experiencing relatively mild cases of mental ill-health may be perceived differently by others depending on whether or not diagnostic labels are provided
2024-08-28
Diagnostic labels for people experiencing what some consider to be relatively milder forms of mental-ill health may affect how others perceive them for better and worse, according to a study published August 28, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS Mental Health by Nick Haslam from the University of Melbourne, Australia, and colleagues.
In recent years, there’s been a general shift to increased diagnoses of mental ill-health. Here, Haslam and colleagues investigate the implications of diagnosing individuals presenting with ...
Unhealthy commodities—like alcohol and social media—are connected with poor mental health
2024-08-28
“Unhealthy commodities” such as tobacco, alcohol, ultra-processed foods, social media, and fossil fuels, as well as impacts of fossil fuel consumption such as climate change and air pollution are associated with depression, suicide, and self-harm, according to a study published August 28 by Kate Dun-Campbell from the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, and colleagues.
Globally, around one out of every eight people currently live with a mental health disorder. These disorders—including depression, suicide, anxiety, and other diseases and disorders—can have many underlying causes. ...
Bacterial cells transmit memories to offspring
2024-08-28
Bacterial cells can “remember” brief, temporary changes to their bodies and immediate surroundings, a new Northwestern University and University of Texas-Southwestern study has found.
And, although these changes are not encoded in the cell’s genetics, the cell still passes memories of them to its offspring — for multiple generations.
Not only does this discovery challenge long-held assumptions of how the simplest organisms transmit and inherit physical traits, it also could be leveraged for new medical applications. For example, researchers could circumvent antibiotic resistance by subtly tweaking a pathogenic ...
Dogs understand words from soundboard buttons, study reveals
2024-08-28
If you’ve seen those viral social media videos of dogs using soundboard buttons to “talk,” you’re not alone. These buttons have taken the pet world by storm, leading to impressive and sometimes seemingly miraculous feats shared across platforms like TikTok and Instagram. But are these dogs truly communicating, or are they just responding to cues from their owners?
Now, a new study published in PLOS ONE – by researchers from the University of California San Diego and other institutions – ...
New pancreatic cancer treatment proves effective in shrinking, clearing tumors
2024-08-28
Researchers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst and UMass Chan Medical School have demonstrated in mice a new method to combat pancreatic cancer. The study, published in Science Translational Medicine, outlines the synergistic effects of a novel nanoparticle drug-delivery system to activate an immune pathway in combination with tumor-targeting agents.
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is the most common form of pancreatic cancer. With a dismal,13% five-year survival rate, it is the third leading cause of cancer deaths.
One major ...
Study reveals isolation, endogamy and pathogens in early medieval Spanish community
2024-08-28
An archaeogenetic study sheds new light on the isolated medieval community Las Gobas in northern Spain. Besides isolation and endogamy, the researchers have also identified the variola virus which can offer a new explanation on how smallpox entered Iberia.
Researchers from Sweden and Spain have conducted a comprehensive archaeogenetic study on a community that lived on the border between the northern Christian kingdoms and Al-Andalus during the early Medieval period. This dynamic era, especially ...
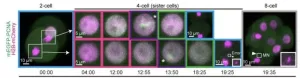
Chromosome copying errors pinpointed in embryo development
2024-08-28
A new discovery by researchers at the RIKEN Center for Biosystems Dynamics (BDR) in Japan upends decades of assumptions regarding DNA replication. Led by Ichiro Hiratani and colleagues, the experiments published August 28 in Nature show that DNA replication in early embryos is different from what past research has taught, and includes a period of instability that is prone to chromosomal copying errors. As failed pregnancies and developmental disorders are often related to chromosomal abnormalities the findings could impact the field of reproductive medicine, perhaps leading to improved methods of in vitro fertilization (IVF).
During embryogenesis, ...
A cellular community in the brain drives Alzheimer’s disease
2024-08-28
NEW YORK, NY (Aug. 28, 2024)--An analysis of more than 1.6 million brain cells from older adults has captured the cellular changes that occur in the early stages of Alzheimer’s disease, potentially revealing new routes for preventing the most common cause of dementia in older individuals.
The study also identified a second community of cells that drives the older brain down a different path that does not lead to Alzheimer’s disease.
“Our study highlights that Alzheimer’s is a disease of many cells and their interactions, not just a single type of dysfunctional ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Roadmap for Europe’s biodiversity monitoring system
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
[Press-News.org] Autistic traits, behavioral problems in 7-year-olds linked with gender nonconforming playStudy analyzed play behavior, behavioral outcomes, and autistic traits in more than 700 children in Sweden