(Press-News.org) London, United Kingdom – 29 August 2024: According to research presented today at ESC Congress 2024,1 patients with stable coronary artery disease who quit smoking at any timepoint after their diagnosis reduced their risk of a major event by almost 50%. In contrast, there was minimal impact on cardiovascular risk in patients who reduced their smoking habits.
The international CLARIFY registry (prospeCtive observational LongitudinAl RegIstry oF patients with stable coronary arterY disease) assessed the impact of smoking status on cardiovascular events in patients with coronary artery disease. The registry included 32,378 patients with the condition. The occurrence of a major adverse cardiovascular event (MACE), defined as cardiovascular death or myocardial infarction during the 5-year follow-up period, was analysed.
Patients were included in the study at an average of 6.5 years after their coronary artery disease diagnosis: at inclusion, 13,366 patients (41.3%) had never smoked, 14,973 (46.2%) were former smokers and 4,039 (12.5%) were current smokers. Among the former smokers who smoked at the time of coronary artery disease diagnosis, 72.8% discontinued smoking within the following year, while only 27.2% quit in subsequent years. “Interestingly, the first year after diagnosis was the crucial window for quitting. At the time of diagnosis, we should emphasise the importance of quitting and support patients in this challenge,” said study author, Dr. Jules Mesnier of Hospital Bichat-Claude Bernard, Paris, France.
Patients who quit smoking after coronary artery disease diagnosis significantly improved their cardiovascular outcomes regardless of when they quit, with a 44% reduction in the risk of MACE (adjusted hazard ratio [HR] 0.56; 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.42–0.76; p<0.001). Among smokers who reduced the amount smoked, the risk of MACE was not significantly altered compared with smokers who did not change their smoking habits (adjusted HR 0.96; 95% CI 0.74–1.26; p=0.78). The risk of MACE after a coronary artery disease diagnosis increased by 8% for each additional year of active smoking (adjusted HR 1.08; 95% CI 1.04–1.12 per year). Although smokers who quit smoking achieved a rapid significant reduction in risk of MACE compared to smokers, they never achieved the cardiovascular risk level of patients who never smoked, even after years of smoking cessation.
Dr. Mesnier concluded: “I like to tell my patients that it is never too soon or too late to stop smoking, though the sooner a patient stops, the better to lower cardiovascular risk. And it is not enough to reduce smoking. Short, clear messages are needed for smokers at every medical intervention highlighting the need to quit. Telling patients they can cut their risk of a subsequent major event or death by half – as we have shown here – is a powerful message.” Measures to promote smoking cessation include brief advice, counselling and behavioural interventions, as well as pharmacological therapy.2
ENDS
Notes to editors
Funding: None.
Disclosures: None.
References and notes
1The abstract “Trajectories in smoking habits and outcomes in patients with stable coronary artery disease” will be presented at the session ‘Epidemiology and risk factors in cardiovascular disease’, which takes place on Friday 30 August 2024 at 11:35 BST at Station 3.
2Visseren FLJ, Mach F, Smulders YM, et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice. Eur Heart J. 2021;42:3227–3337.
ESC Press Office
Tel: +33 6 61 40 18 84
Email: press@escardio.org
The hashtag for ESC Congress 2024 is #ESCCongress
Follow us on X @ESCardioNews
Journalists are invited to become accredited and register here.
Check out the ESC Media and Embargo Policy.
About ESC Congress 2024
It is the world’s largest gathering of cardiovascular professionals, disseminating ground-breaking science both onsite in London and online – from 30 August to 2 September. Explore the scientific programme. More information is available from the ESC Press Office at press@escardio.org.
About the European Society of Cardiology
The ESC brings together healthcare professionals from more than 150 countries, working to advance cardiovascular medicine and help people to live longer, healthier lives.
END
Quitting smoking nearly halves heart attack risk, cutting down does little
2024-08-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Children contribute to group projects when there are clear and common goals
2024-08-29
Children can work together to reach a target that benefits a whole group even if it is at a personal cost to themselves, a new study has shown.
Researchers invited groups of six to 10-year-olds to take part in a game where they were each given containers of water and could decide how much of it to offer into a common pool.
If the group contributed a certain amount of water it resulted in benefits for the whole group, but children also obtained benefits for any water they kept.
At the same time, the ...
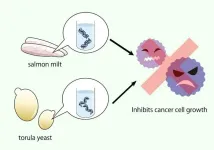
Dine on DNA: Compounds from nucleic acids in food show anticancer effects
2024-08-29
When people eat, they ingest the nucleic acids that reside in all living things. The compounds in these acids could inhibit the growth of cancer cells, according to findings published in PLOS ONE by Osaka Metropolitan University Associate Professor Akiko Kojima-Yuasa of the Graduate School of Human Life and Ecology and colleagues.
Consuming nucleic acids found in food has been shown to boost the immune system and prevent some diseases. The nucleotides and nucleosides that result from digesting the acids are largely responsible for these beneficial effects.
Professor ...
MCG scientists working to understand why men with prostate cancer are at higher risk of Alzheimer’s
2024-08-29
AUGUSTA, Ga. (Aug. 29, 2024) – Researchers at the Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University are searching for a better way to understand why many men with prostate cancer end up with Alzheimer’s disease, and whether it’s the standard hormone therapy treatment or an overactive immune response that actually contributes to the problem.
The hormone therapy, androgen deprivation therapy, known as ADT, treats the cancer by reducing testosterone, which the cancer needs to grow. But androgen is a key regulator of amyloid metabolism and when it’s removed from the equation, more amyloid is left to form the plaques that are a hallmark of Alzheimer’s.
“We ...
Ancient sea cow attacked by a crocodile and sharks sheds new light on prehistoric food chains
2024-08-29
A new study describing how a prehistoric sea cow was preyed upon by not one, but two different carnivores – a crocodilian and a shark – is revealing clues into both the predation patterns of ancient creatures and the wider food chain millions of years ago.
Published in the peer-reviewed Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology, the findings mark one of the few examples of a creature being preyed upon by different animals during the Early to Middle Miocene epoch (23 million to 11.6 million years ago).
Predation marks in the skull indicate that the dugongine sea cow, ...
Georgia Tech neuroscientists explore the intersection of music and memory
2024-08-29
By Jerry Grillo
The soundtrack of this story begins with a vaguely recognizable and pleasant groove. But if I stop writing and just listen for a second, the music reveals itself completely. In Freddie Hubbard’s comfortable, lilting trumpet solo over Herbie Hancock’s melodic, repetitive piano vamping, I recognize “Cantaloupe Island.” Then, with my fingers again poised at the keyboard, Freddie and Herbie fade into the background, followed by other instrumental music: captivating — but not distracting — sonic nutrition, feeding my concentration and productivity.
Somewhere, I think, Yiren Ren is studying, focused on her ...
Waging war on ‘superbugs’ in aged care
2024-08-29
There’s an urgent need for more careful antibiotic management to protect older people living in residential aged care from the dangerous spread of antibiotic resistant bacteria or ‘superbugs’, researchers from Flinders University and SAHMRI warn.
A new study published in the well-respected Journal of Infection, explores the link between the widespread use of antibiotics in residential aged care and the resulting antibiotic resistant bacteria in the gut that can be passed on to other residents.
“Commonly ...
Increasing risk of synthetic opioid drug overdoses in Australia
2024-08-29
A recent study has uncovered alarming insights into the dangers posed by fentanyl-contaminated drug supplies in Australia, including a heightened risk of lethal overdose.
The study, titled ‘The gear could be cut with fentanyl which is starting to happen more in Australia’: Exploring Overdose Survivors’ Perspectives on Toxic Supply and Safe Consumption, aimed to explore the role of synthetic opioids in overdoses among Queenslanders.
Led by Griffith University’s Dr Timothy Piatkowski, Emma Kill and Steph Reeve in partnership with the Queensland ...
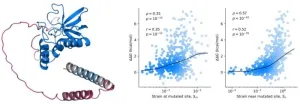
Protein mutant stability can be inferred from AI-predicted structures
2024-08-29
Researchers at the Center for Algorithmic and Robotized Synthesis within the Institute for Basic Science have taken a significant step forward in understanding the stability of proteins by leveraging the power of AI. The research team used AlphaFold2 to explore how mutations affect protein stability—a crucial factor in ensuring proteins function correctly and do not cause diseases like Alzheimer's.
DeepMind’s AlphaFold algorithm, which can accurately predict a protein’s structure from ...
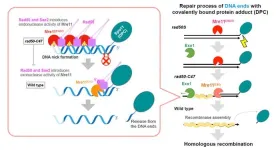
Shedding light on the mechanism of yeast DNA repair
2024-08-29
DNA damage is a cellular phenomenon that introduces structural abnormalities in double-stranded DNA. External factors, such as radiation or chemical agents, as well as internal factors, such as blocked DNA replication, can generate double-strand breaks (DSBs) in DNA. To counteract DNA damage, cells engage in DNA repair to preserve genetic integrity and ensure cell survival as failure to repair DSBs has serious health complications like increased risk of cancer.
DSBs are repaired by two mechanisms called non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) and homologous recombination (HR). NHEJ is the predominant DNA repair mechanism in human somatic cells and is ...
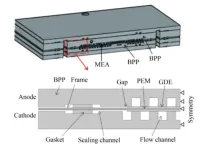
Improvement of durability of membrane electrode assembly by frame sealing structure in temperature shock
2024-08-29
Fuel cells offer a promising solution for clean energy with advantages over traditional electric power systems, including extended driving range and higher energy density. Despite these benefits, the high costs and durability concerns associated with fuel cell stacks have limited their commercialization. The durability of membrane electrode assemblies (MEAs), a key component of proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs), is particularly affected by the frame sealing structure, which is often overlooked in research.
The study, conducted by Tiankuo Chu ...