(Press-News.org) PULLMAN, Wash. -- When young adults first go off to college, more communication with parents generally leads to better relationships, but parents should avoid always initiating it, according to a study led by Washington State University researchers.
In a paper published in the journal Emerging Adulthood, WSU Assistant Professor Jennifer Duckworth and co-authors found that phone, text, video or in-person communication made first-year students feel better about the relationship with their parents. Students also felt better about the relationship when parents offered support or advice, and when they discussed important topics, such as studying and friendships. However, researchers found negative associations when parents initiated nearly all of the communication.
“That could be indicative of over-involved parenting,” said Duckworth, a faculty member in WSU’s human development department. “It can be a fine line, but students with so-called ‘helicopter parents’ could have a more negative view of their relationship with those parents.”
The research shows that it’s beneficial for parents to regularly stay involved in students’ lives, provide support and discuss topics important to students without overwhelming them.
“Text messages are great for a quick check-in that can be very beneficial to the relationship quality,” Duckworth said. “If a student feels they have a good relationship, that’s indicative of well-being and positive behaviors like more studying and less alcohol and drug use.”
The study also shows that frequent communication improves the relationship between familial units.
“We looked at daily levels of parent/student communication, and days with communication were better for the relationship than days without any communication,” said Duckworth. “Similarly, days with more communication were better than days with less communication.”
The researchers were surprised by how consistent the findings were.
“On days when they communicated, and students were honest with their parents and parents offered support or advice, the students reported they felt more positive about their relationship the following day,” she said.
The study looked at the response results of 367 first-year WSU students who took a daily survey for seven consecutive days. The students were compensated up to $30 if they completed every survey, which was texted to their phones.
Breaking down the data, the authors found several differences. Female students reported more days of communication than males, with more time spent communicating. They discussed friendships and relationships more, but spent less time discussing time management than males.
Meanwhile, members of racially or ethnically minoritized groups reported fewer days communicating with their parents. While they spent less time communicating in general, students from minoritized groups spent more time talking on the telephone and video chatting with their parents than other groups. They also reported being less honest and spending less time talking about studying or grades, and drinking or substance use.
“We don’t know why this is the case,” Duckworth said. “It could reflect cultural or contextual differences, or differences in parenting styles. It’s definitely an area for future research.”
Duckworth wrote the paper with WSU colleagues Katherine Forsythe, Brittany Cooper and Laura Hill along with Matthew Bumpus, director of research and community impact at Innovia Foundation.
END
Communication helps parent relationships with new college students but has limits
More communication with parents generally leads to better relationships, but parents should avoid always initiating it
2024-09-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Natural selection may create inter-species exploitation
2024-09-03
A modeling study suggests that one-sided interspecies cooperation can spontaneously emerge and persist over time, despite only one species benefitting. Evolutionary game theory, and the prisoner’s dilemma in particular, are often used to model the evolution of cooperation within a single species. In the prisoner’s dilemma, both parties benefit by cooperating, but the greatest benefit is earned by a defector who plays with a cooperator. The temptation to cheat tends to push players towards defection, ...
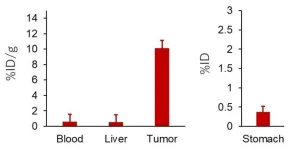
Targeted cancer therapies: Getting radioactive atoms to accumulate in tumors
2024-09-03
Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer among men worldwide, following lung cancer. In the United States alone, nearly 300,000 new cases are diagnosed annually. While reducing testosterone and other male hormones can be an effective treatment for prostate cancer, this approach becomes ineffective once the disease progresses to metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). At this stage, the cancer advances quickly and becomes resistant to conventional hormonal therapies and chemotherapy.
A clever strategy for fighting mCRPC is to exploit the ...
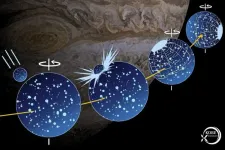
Gigantic asteroid impact shifted the axis of Solar System's biggest moon
2024-09-03
Around 4 billion years ago, an asteroid hit the Jupiter moon Ganymede. Now, a Kobe University researcher realized that the Solar System's biggest moon's axis has shifted as a result of the impact, which confirmed that the asteroid was around 20 times larger than the one that ended the age of the dinosaurs on Earth, and caused one of the biggest impacts with clear traces in the Solar System.
Ganymede is the largest moon in the Solar System, bigger even than the planet Mercury, and is also interesting for the liquid water oceans beneath its icy surface. Like the Earth’s moon, it is tidally locked, meaning that it always shows the ...
Finger wrap uses sweat to provide health monitoring at your fingertips—literally
2024-09-03
A sweat-powered wearable has the potential to make continuous, personalized health monitoring as effortless as wearing a Band-Aid. Engineers at the University of California San Diego have developed an electronic finger wrap that monitors vital chemical levels—such as glucose, vitamins, and even drugs—present in the same fingertip sweat from which it derives its energy.
The advance was published Sept. 3 in Nature Electronics by the research group of Joseph Wang, a professor in the Aiiso Yufeng Li Family Department of Chemical and Nano Engineering ...
Large sharks may be hunting each other – and scientists know because of a swallowed tracking tag
2024-09-03
Who killed the pregnant porbeagle?
In a marine science version of the game Cluedo, researchers from the US have now accused a larger shark, with its deciduous triangular teeth, in the open sea southwest of Bermuda. This scientific whodunnit is published in Frontiers in Marine Science.
“This is the first documented predation event of a porbeagle shark anywhere in the world,” said lead author Dr Brooke Anderson, a former graduate student at Arizona State University.
“In one event, the population not only lost a reproductive female that could contribute to population growth, but it also lost all her developing ...
Can’t stop belching? Dietary habits or disease could be the reason
2024-09-03
Belching is a common bodily function, but when it escalates to a level that interferes with daily life, it is defined as belching disorders. International surveys have reported that approximately 1% of adults have belching disorders, but the percentage in Japan and the factors involved often elude medical professionals.
To examine the relationship between the rate of belching disorders, comorbidities, and lifestyles in Japan, a research team led by Professor Yasuhiro Fujiwara of Osaka Metropolitan University’s Graduate School of Medicine ...
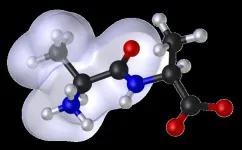
Exploring peptide clumping for improved drug and material solutions
2024-09-03
Scientists from China have investigated how short peptide chains aggregate together in order to deepen our understanding of the process, which is crucial for drug stability and material development. Their study, published in JACS Au, provides valuable insights into how short proteins called peptides interact, fold, and function. These findings have significant implications for medicine, material science, and biotechnology.
Peptides are short chains of amino acids that play essential roles in the body by building structures, speeding up chemical reactions, and supporting our immune system. The specific function of a protein is determined by how its amino acids interact with each other and ...
Young adults let down by ‘postcode lottery’ for ADHD treatment - national survey
2024-09-03
A national survey conducted as part of University of Exeter research has found huge variation in treatment for ADHD, highlighting the struggle many young adults face once they turn 18.
Researchers have warned that the current system is failing many young adults as they transition from children’s to adult’s services - suddenly finding themselves unable to access treatment because services do not link up effectively.
More than 750 people from across the country – including commissioners, healthcare professionals working ...
False-positive mammography result may discourage women from subsequent screening
2024-09-02
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 2 September 2024
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
1. ...
False-positive mammograms discourage some women from future screenings
2024-09-02
Early detection of breast cancer through mammography screening continues to save lives. However, abnormal findings on mammograms can lead to women being recalled for additional imaging and biopsies, many of which turn out to be “false positives,” meaning they do not result in a cancer diagnosis. False positives can also have financial implications for patients and cause significant emotional anxiety.
A major, new study led by the UC Davis Comprehensive Cancer Center has found that women who received a false-positive result that required additional imaging or biopsy were less likely to return ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
[Press-News.org] Communication helps parent relationships with new college students but has limitsMore communication with parents generally leads to better relationships, but parents should avoid always initiating it