(Press-News.org) Darwin was puzzled by cooperation in nature—it ran directly against natural selection and the notion of survival of the fittest. But over the past decades, evolutionary mathematicians have used game theory to better understand why mutual cooperation persists when evolution should favour self-serving cheaters.
At a basic level, cooperation flourishes when the costs to cooperation are low or the benefits large. When cooperation becomes too costly, it disappears—at least in the realm of pure mathematics. Symbiotic relationships between species—like those between pollinators and plants–are more complex, but follow similar patterns.
But new modelling published today in PNAS Nexus adds a wrinkle to that theory, indicating that cooperative behaviour between species may break down in situations where, theoretically at least, it should flourish.
“As we began to improve the conditions for cooperation in our model, the frequency of mutually beneficial behaviour in both species increases, as expected,” says Dr. Christoph Hauert, a mathematician at the University of British Columbia who studies evolutionary dynamics.
“But as the frequency of cooperation in our simulation gets higher—closer to 50 per cent—suddenly there's a split. More cooperators pool in one species and fewer in the other—and this asymmetry continues to get stronger as the conditions for cooperation get more benign.”
While this ‘symmetry breaking of cooperation’ between two populations has been modelled by mathematicians before, this is the first model that enables individuals in each group to interact and join forces in a more natural way.
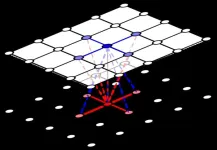
Dr. Hauert and colleague Dr. György Szabó from the Hungarian Research Network used computational spatial models to arrange individuals from the two species on separate lattices facing one another. This enables cooperators to form clusters and reduce their exposure to (and exploitation by) cheaters by more frequently interacting with other cooperators.
“Because we chose symmetric interactions, the level of cooperation is the same in both populations,” says Dr. Hauert. “Clusters can still form and protect cooperators but now they need to be synchronized across lattices because that’s where the interactions occur.”
"The odd symmetry breaking in cooperation shows parallels to phase transitions in magnetic materials and highlights the success of approaches developed in statistical and solid state physics,” says Dr. Szabó.
"At the same time the model sheds light on spikes in dramatic changes in behaviour that can significantly affect the interactions in complex living systems."
The research was supported by the National Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada.
Mutualisms: cooperation between species
A model developed by evolutionary mathematicians in Canada and Europe shows that as cooperation becomes easier, it can unexpectedly break down. Watch a simulation of spatial interactions of cooperators and defectors for each species under different scenarios.
END
Mathematicians model a puzzling breakdown in cooperative behaviour
2024-09-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Kessler Foundation scientists publish protocol for combining aerobic exercise and cognitive rehabilitation in multiple sclerosis
2024-09-03
East Hanover, NJ – September 3, 2024 – Researchers at Kessler Foundation have published a new clinical protocol examining the combination of aerobic exercise and cognitive rehabilitation to improve learning and memory in individuals with multiple sclerosis (MS) who have mobility disability. The article, “Rationale and methodology for examining the combination of aerobic exercise and cognitive rehabilitation on new learning and memory in persons with multiple sclerosis and mobility disability: Protocol for a randomized controlled trial,” was published online and will appear in print in Contemporary Clinical Trials, ...
New hope for progressive supranuclear palsy with innovative trial
2024-09-03
$75 million NIH grant could lead to the first effective drugs for a condition with few treatment options
A clinical trial that will test three drugs concurrently, and could include more, represents new hope for patients with progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP), an incurable neurodegenerative disorder that usually kills within seven years after symptoms start.
Researchers hope the trial, which will be led by UC San Francisco and conducted at up to 50 sites nationwide, will lead to the development of new therapies. There are currently no drugs to stall the disease’s deadly progression.
The ...
Mass General Brigham Gene and Cell Therapy Institute launches RNA Therapeutics Core
2024-09-03
The Mass General Brigham Gene and Cell Therapy Institute (GCTI) today announced it has launched the RNA Therapeutics Core, a first-of-its-kind, state-of-the-art facility and resource to advance the use of RNA technologies within and beyond the Mass General Brigham research ecosystem. This new Core is dedicated to accelerating the exploration of novel therapeutic targets to effectively translate RNA-based medicines into clinical practice by leveraging advanced RNA vectors and delivery systems.
Until now, a Core of this kind has not existed within an academic setting. With this launch, the RNA Therapeutics Core enables ...
Dangerous airborne fungus boosted by California droughts
2024-09-03
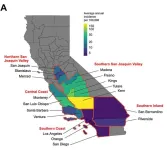
Valley fever is an emerging fungal disease in the western United States that most often causes flu-like symptoms, but can also cause dangerous or even deadly complications. By analyzing data on reported cases of Valley fever in California, which have increased dramatically over the last two decades, researchers from University of California San Diego and University of California, Berkeley, have identified seasonal patterns that could help individuals and public health officials better prepare for future surges in Valley fever cases. The findings also have important implications for how the changing climate can exacerbate the threat of infectious diseases. The findings are published in The ...
$1.8 million NIH grant to FAU engineering fuels quest to decode human evolution
2024-09-03
Natural selection is an important evolutionary force that enables humans to adapt to new environments and fight disease-causing pathogens. However, the unique footprints of natural selection in our genome can be buried beneath those left by other evolutionary forces. Thus, by leveraging information about multiple evolutionary forces, researchers can identify signatures of natural selection in the human genome, and ultimately determine its role in human adaptation and disease.
Low-cost DNA sequencing has ...
Communication helps parent relationships with new college students but has limits
2024-09-03
PULLMAN, Wash. -- When young adults first go off to college, more communication with parents generally leads to better relationships, but parents should avoid always initiating it, according to a study led by Washington State University researchers.
In a paper published in the journal Emerging Adulthood, WSU Assistant Professor Jennifer Duckworth and co-authors found that phone, text, video or in-person communication made first-year students feel better about the relationship with their parents. Students also felt better about the relationship when parents offered support or advice, and when they discussed important topics, such as studying and friendships. However, researchers found ...
Natural selection may create inter-species exploitation
2024-09-03
A modeling study suggests that one-sided interspecies cooperation can spontaneously emerge and persist over time, despite only one species benefitting. Evolutionary game theory, and the prisoner’s dilemma in particular, are often used to model the evolution of cooperation within a single species. In the prisoner’s dilemma, both parties benefit by cooperating, but the greatest benefit is earned by a defector who plays with a cooperator. The temptation to cheat tends to push players towards defection, ...
Targeted cancer therapies: Getting radioactive atoms to accumulate in tumors
2024-09-03
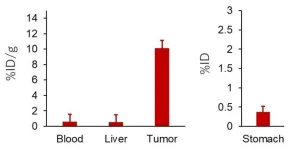
Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer among men worldwide, following lung cancer. In the United States alone, nearly 300,000 new cases are diagnosed annually. While reducing testosterone and other male hormones can be an effective treatment for prostate cancer, this approach becomes ineffective once the disease progresses to metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). At this stage, the cancer advances quickly and becomes resistant to conventional hormonal therapies and chemotherapy.
A clever strategy for fighting mCRPC is to exploit the ...
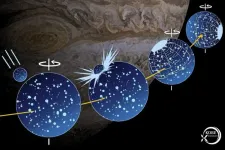
Gigantic asteroid impact shifted the axis of Solar System's biggest moon
2024-09-03
Around 4 billion years ago, an asteroid hit the Jupiter moon Ganymede. Now, a Kobe University researcher realized that the Solar System's biggest moon's axis has shifted as a result of the impact, which confirmed that the asteroid was around 20 times larger than the one that ended the age of the dinosaurs on Earth, and caused one of the biggest impacts with clear traces in the Solar System.
Ganymede is the largest moon in the Solar System, bigger even than the planet Mercury, and is also interesting for the liquid water oceans beneath its icy surface. Like the Earth’s moon, it is tidally locked, meaning that it always shows the ...
Finger wrap uses sweat to provide health monitoring at your fingertips—literally
2024-09-03
A sweat-powered wearable has the potential to make continuous, personalized health monitoring as effortless as wearing a Band-Aid. Engineers at the University of California San Diego have developed an electronic finger wrap that monitors vital chemical levels—such as glucose, vitamins, and even drugs—present in the same fingertip sweat from which it derives its energy.
The advance was published Sept. 3 in Nature Electronics by the research group of Joseph Wang, a professor in the Aiiso Yufeng Li Family Department of Chemical and Nano Engineering ...