(Press-News.org) “We are extremely happy about the freshly granted ERC project for Hannah Schneider. Thereby, the European Research Agency distinguished a highly talented young researcher, who develops new ideas and approaches to explore anatomical roots traits that are highly relevant for stress tolerance and resource efficiency of crops”, says Prof. Dr. Nicolaus von Wirén, Managing Director at IPK. “The new ERC project of the scientist from Minnesota, whom we allured to IPK just last October, follows the two previous ERC-Starting Grant holders Martin Mascher and Stefan Heckmann and will bring great international visibility to root research at IPK.”
“The ERC Starting grant is a huge recognition for our work. I am very excited to continue our research on root development and am looking forward to continue collaboration with colleagues at the IPK”, says Prof. Dr. Hannah Schneider, head of IPK’s research group “Genetics and Physiology of Root Development”. The FATE project, for which she wants to dedicate the funding, is primarily concerned with the root cortex, which plays a key role in the growth and function of the plant. The project aims to engineer crop roots to better forage soil and capture resources. “This will have significant benefits for global agriculture, as nutrient limitations are a major challenge for crop growth and will become even more critical with climate change”, emphasises Prof. Dr. Hannah Schneider.
She was also recently awarded 1 million euros from the Leibniz Professorship Program. This second 5-year project investigates the physiological function and genetic control of a root anatomical trait in barley in the context of multiple environmental stresses including drought and soil compaction. This project will work to develop anatomical traits to be used in breeding programs to improve stress tolerance in barley and other crops.
The ERC, set up by the European Union in 2007, is the premier European funding organisation for excellent frontier research. The funding - totalling nearly €780 million - supports cutting-edge research in a wide range of fields, from life sciences and physics to social sciences and humanities. It will help young researchers at the beginning of their careers to launch their own projects, form their teams and pursue their most promising ideas. Most recently, the IPK scientists Dr. Stefan Heckmann and Dr. Martin Mascher received a Starting Grant in 2020.
“The European Commission is proud to support the curiosity and passion of our early-career talent under our Horizon Europe programme. The new ERC Starting Grants winners aim to deepen our understanding of the world. Their creativity is vital to finding solutions to some of the most pressing societal challenges”, says EU Research Commissioner, Iliana Ivanova. “In this call, I am happy to see one of the highest shares of female grantees to date, a trend that I hope will continue. Congratulations to all!”
The successful candidates proposed to host their projects at universities and research centres in 24 EU Member States and associated countries, including Germany (98 grants), the Netherlands (51), the UK (50) and France (49). This competition attracted 3,474 proposals, which were evaluated by peer review panels of internationally renowned researchers. Overall, 14.2% of the proposals were selected for funding. 44% of these Starting Grants were awarded to female researchers.
END
ERC Starting Grant for IPK root researcher Prof. Dr. Hannah Schneider
2024-09-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
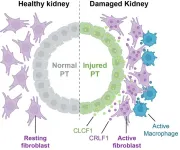
New study shows cells get involved in unhealthy relationships after acute kidney injury (AKI) in mice
2024-09-05
A study published in Nature Communications provides new insight into how damaged cells interact within disease-promoting microenvironments following acute kidney injury, or AKI. With limited treatment options, AKI frequently progresses to chronic kidney disease (CKD), which affects more than 1 in 7 U.S. adults—an estimated 37 million people.
The new findings may contribute to future efforts to prevent CKD, which can lead to kidney failure.
The study brought together scientists from Andy McMahon’s lab at USC and Long Cai’s lab at Caltech, with support from a USC Broad Innovation Award that funded the cross-institutional research collaboration.
In ...
Will humans accept robots that can lie? Scientists find it depends on the lie
2024-09-05
Honesty is the best policy… most of the time. Social norms help humans understand when we need to tell the truth and when we shouldn’t, to spare someone’s feelings or avoid harm. But how do these norms apply to robots, which are increasingly working with humans? To understand whether humans can accept robots telling lies, scientists asked almost 500 participants to rate and justify different types of robot deception.
“I wanted to explore an understudied facet of robot ethics, to contribute to our understanding of mistrust ...
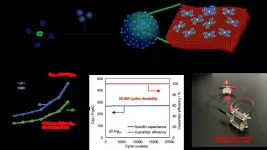
Achieving a supercapacitor through the 'molecular coating' approach
2024-09-05
Researchers at Tohoku University have successfully increased the capacity, lifetime durability, and cost-effectiveness of a capacitor in their pursuit of a more power-efficient future. A capacitor is a device used as part of a circuit that can store and release energy, just like a battery. What makes a capacitor different from a battery is that it takes much less time to charge. For example, your cellphone battery will power your phone instantly, but charging that battery back up to 100% when it dies is far from instantaneous.
While this makes capacitors sound like the superior choice, they have some big drawbacks that need to be overcome. Firstly, their capacity is much smaller ...
Novel biomarker could lead to early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease, pilot study suggests
2024-09-05
New research has discovered a unique and promising avenue for diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease (AD) earlier – by analysing AD biomarkers in blood – so that the impacts of dementia can be reduced.
AD is the most common form of dementia, estimated to contribute to 60-70 per cent of cases, or more than 33 million cases worldwide, according to the World Health Organisation. Currently incurable, AD is usually diagnosed when a person is having significant difficulties with memory and thinking that impact their daily life.
University of Melbourne researcher Dr Brandon Mahan leads a group of analytical geochemists from the Faculty ...
WEHI bioinformatician wins prestigious Eureka prize
2024-09-05
WEHI’s Bioinformatics division head, Professor Gordon Smyth, has won the 2024 Eureka Prize for Excellence in Research Software.
The award recognises Prof Smyth’s lead role in developing and designing the limma software package, which helps researchers detect changes in gene activity.
limma has helped researchers around the world detect changes in gene activity – a crucial element to finding new treatments for a range of diseases, like cancer – and has been used or cited in more than 70,000 published papers worldwide.
The Australian Museum Eureka Prizes are ...
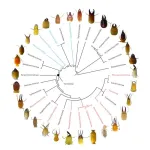
The dictionary of termites has been rewritten
2024-09-05
Termites have a bad reputation. Most think of them as pests, a status that isn’t helped by their recent reclassification into the cockroach family.
But not only do the termites that cause serious problems for humans only make up 3.5% of all termite species, termites also serve as crucial ecosystem engineers, maintaining the infrastructure of various environments. Like earthworms, they circulate nutrients by decomposing plant materials, and they play the important role of bioturbators: much like plowing a field, termites aerate the soil, expose underground nutrients, and let water infiltrate deeper layers of soil – ...
CABBI team designs efficient bioenergy crops that need less water to grow
2024-09-05
Drought stress has long been a limiting factor for crop production around the world, a challenge exacerbated by climate change.
For more than a century, scientists have targeted a key plant trait known as water use efficiency (WUE) to help crops grow with less water and avoid suffering from drought stress. Greater WUE can help plants avoid drought stress — but for most crops it’s also associated with lower productivity when water is plentiful.
In a pair of new studies published in the Journal of Experimental Botany, ...
Texas A&M researchers discover that sustained neck exertions change the spine and muscles, causing pain
2024-09-05
Learning new languages, sending emails, attending a virtual class, or speaking to loved ones halfway around the world are just some of the tasks accomplished by touching a button on a smartphone. Unfortunately, the ease and convenience of modern devices have also come with a painful crick in the neck. The sedentary nature of work and prolonged use of hand-held devices and computers have contributed to a sharp increase in neck pain.
While fatigue in neck muscles has long been suspected of causing pain, the actual mechanical changes in the spine and muscles that precede weakness remain an outstanding question.
Now, using high-precision X-ray ...
Air pollution linked to higher risk of infertility in men
2024-09-05
Long term exposure to fine particulate matter (PM2.5) air pollution is linked to a higher risk of infertility in men, whereas road traffic noise is linked to a higher risk of infertility in women over 35, finds a Danish study published by The BMJ today.
If these findings are confirmed in future studies, they could help guide strategies to regulate noise and air pollution to protect the general population from these exposures, say the researchers.
Infertility is a major global health problem affecting one in seven couples trying to conceive.
Several ...
Prostate cancer rates across Europe since 1980 “indicative of overdiagnosis” say experts
2024-09-05
Rates of prostate cancer across Europe since 1980 are “indicative of overdiagnosis”, say researchers in a study published by The BMJ today.
Overdiagnosis refers to the detection of harmless cancers that are unlikely to cause symptoms or death during a patient’s lifetime, which can lead to unnecessary treatment, negative impacts on quality of life, and wasted healthcare resources.
The findings show rapid increases in the number of new cases (incidence) in parallel with uptake of so far predominantly opportunistic ...