(Press-News.org) If you upset one bee, what determines whether the entire hive decides to avenge her grievance? A $1.2 million grant will support UC Riverside scientists in answering questions like these about how honeybees communicate.
Every third bite of food you eat has been pollinated by a bee. They are central to worldwide food production, but there have been an alarming number of die-offs recorded since 2006. One solution to this issue is the use of special survivor bees that are more resistant to pests and diseases that are killing managed honeybees.
Commonly found in Southern California, the survivor bees appear to be tolerant of deadly mites as well as extreme heat and drought. Genetically, they are the most diverse honeybees in the world, with a mix of African and European genes. However, they tend to behave with more defensiveness than the European-origin honeybees currently used for agriculture.
Defensive behaviors can include bumping beekeeper veils, chasing, or stinging entities perceived as threats. To breed these behaviors out of the bees, scientists need to know what triggers them.
“If we understand what stresses out the survivor bees, that can inform different beekeeping strategies, as well as a breeding program to help unravel the defensiveness,” said UCR entomologist Barbara Baer-Imhoof, who is co-leading this program alongside UCR colleagues, entomologist Boris Baer and insect neuroscientist Ysabel Giraldo.
Baer and Baer-Imhoof run CIBER, the Center for Integrative Bee Research at UCR, where they study stressors responsible for the decline in bee health, and work on solutions to those problems, including new tools for monitoring the health of bees in managed hives.
For this grant, the researchers will determine how environmental threats are perceived and processed by individual bees, and then eventually how they are communicated to other members of the hive. This communication chain is a fundamental but still unsolved challenge in science.
Another aspect to this grant from the W.M. Keck Foundation is learning whether scientists ought to reconsider how they view bee societies. In addition to inter-bee communication, the project will ascertain how honeybees transmit information to subsequent generations of progeny, beyond the lifespan of any one generation.
Because hives can retain information, the researchers argue there should be a paradigm shift in the way bees are studied. “The fact that they are able to do this can be considered a cultural achievement,” said Baer.
Like human societies, there is a lot of variation amongst individual members.
“Some bees have different personalities. They’re not like little robots that give the same predictable response to every smell or situation. Why? That’s part of what we want to know,” Baer said.
As the bees employ a combination of vibrations, chemicals, smells, sounds, and movements to communicate, Giraldo’s laboratory will use genetic tools to learn about the brain cells controlling these interactions.
“The tools we have are powerful enough to allow us to understand the responses of individual brain regions in real time, and give us a high-resolution picture of what’s happening, Giraldo said.
The bee has only a million brain cells, which is not much compared to mice, which have an average of 70 million neurons. However, bees can solve math equations and dance for one another.
“They can do complicated things,” Baer said. “They must be extremely efficient on an individual level to use the available brain power for complex tasks like these.”
Based in Los Angeles, the W. M. Keck Foundation was established in 1954 by the late W. M. Keck, founder of the Superior Oil Company. The foundation’s grant-making is focused primarily on pioneering efforts in the areas of medical research and science and engineering. The foundation also supports undergraduate education and maintains a Southern California Grant Program that provides support for the Los Angeles community, with a special emphasis on children and youth. For more information, visit www.wmkeck.org
“On behalf of the UCR community, I extend our sincere thanks to the W.M. Keck Foundation,” said Chancellor Kim Wilcox. “Funding from the foundation will support innovative projects that aim to develop new strategies for understanding and protecting bees. These efforts are crucial as pollinators play a key role in the health of ecosystems and the production of food worldwide.”
Listen to Boris Baer and Barbara Baer-Imhoof discuss killer bees' role in shaping the agriculture of the future, here.
END
A $1.2 million Rosetta stone for honeybees
W.M. Keck grant helps scientists decipher bee language
2024-09-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
ERC Starting Grant for IPK root researcher Prof. Dr. Hannah Schneider
2024-09-05
“We are extremely happy about the freshly granted ERC project for Hannah Schneider. Thereby, the European Research Agency distinguished a highly talented young researcher, who develops new ideas and approaches to explore anatomical roots traits that are highly relevant for stress tolerance and resource efficiency of crops”, says Prof. Dr. Nicolaus von Wirén, Managing Director at IPK. “The new ERC project of the scientist from Minnesota, whom we allured to IPK just last October, follows the two previous ERC-Starting Grant holders Martin Mascher and Stefan Heckmann and will bring great international visibility to root research at IPK.”
“The ...
New study shows cells get involved in unhealthy relationships after acute kidney injury (AKI) in mice
2024-09-05
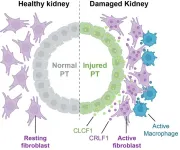
A study published in Nature Communications provides new insight into how damaged cells interact within disease-promoting microenvironments following acute kidney injury, or AKI. With limited treatment options, AKI frequently progresses to chronic kidney disease (CKD), which affects more than 1 in 7 U.S. adults—an estimated 37 million people.
The new findings may contribute to future efforts to prevent CKD, which can lead to kidney failure.
The study brought together scientists from Andy McMahon’s lab at USC and Long Cai’s lab at Caltech, with support from a USC Broad Innovation Award that funded the cross-institutional research collaboration.
In ...
Will humans accept robots that can lie? Scientists find it depends on the lie
2024-09-05
Honesty is the best policy… most of the time. Social norms help humans understand when we need to tell the truth and when we shouldn’t, to spare someone’s feelings or avoid harm. But how do these norms apply to robots, which are increasingly working with humans? To understand whether humans can accept robots telling lies, scientists asked almost 500 participants to rate and justify different types of robot deception.
“I wanted to explore an understudied facet of robot ethics, to contribute to our understanding of mistrust ...
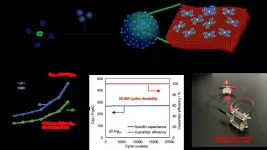
Achieving a supercapacitor through the 'molecular coating' approach
2024-09-05
Researchers at Tohoku University have successfully increased the capacity, lifetime durability, and cost-effectiveness of a capacitor in their pursuit of a more power-efficient future. A capacitor is a device used as part of a circuit that can store and release energy, just like a battery. What makes a capacitor different from a battery is that it takes much less time to charge. For example, your cellphone battery will power your phone instantly, but charging that battery back up to 100% when it dies is far from instantaneous.
While this makes capacitors sound like the superior choice, they have some big drawbacks that need to be overcome. Firstly, their capacity is much smaller ...
Novel biomarker could lead to early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease, pilot study suggests
2024-09-05
New research has discovered a unique and promising avenue for diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease (AD) earlier – by analysing AD biomarkers in blood – so that the impacts of dementia can be reduced.
AD is the most common form of dementia, estimated to contribute to 60-70 per cent of cases, or more than 33 million cases worldwide, according to the World Health Organisation. Currently incurable, AD is usually diagnosed when a person is having significant difficulties with memory and thinking that impact their daily life.
University of Melbourne researcher Dr Brandon Mahan leads a group of analytical geochemists from the Faculty ...
WEHI bioinformatician wins prestigious Eureka prize
2024-09-05
WEHI’s Bioinformatics division head, Professor Gordon Smyth, has won the 2024 Eureka Prize for Excellence in Research Software.
The award recognises Prof Smyth’s lead role in developing and designing the limma software package, which helps researchers detect changes in gene activity.
limma has helped researchers around the world detect changes in gene activity – a crucial element to finding new treatments for a range of diseases, like cancer – and has been used or cited in more than 70,000 published papers worldwide.
The Australian Museum Eureka Prizes are ...
The dictionary of termites has been rewritten
2024-09-05
Termites have a bad reputation. Most think of them as pests, a status that isn’t helped by their recent reclassification into the cockroach family.
But not only do the termites that cause serious problems for humans only make up 3.5% of all termite species, termites also serve as crucial ecosystem engineers, maintaining the infrastructure of various environments. Like earthworms, they circulate nutrients by decomposing plant materials, and they play the important role of bioturbators: much like plowing a field, termites aerate the soil, expose underground nutrients, and let water infiltrate deeper layers of soil – ...
CABBI team designs efficient bioenergy crops that need less water to grow
2024-09-05
Drought stress has long been a limiting factor for crop production around the world, a challenge exacerbated by climate change.
For more than a century, scientists have targeted a key plant trait known as water use efficiency (WUE) to help crops grow with less water and avoid suffering from drought stress. Greater WUE can help plants avoid drought stress — but for most crops it’s also associated with lower productivity when water is plentiful.
In a pair of new studies published in the Journal of Experimental Botany, ...
Texas A&M researchers discover that sustained neck exertions change the spine and muscles, causing pain
2024-09-05
Learning new languages, sending emails, attending a virtual class, or speaking to loved ones halfway around the world are just some of the tasks accomplished by touching a button on a smartphone. Unfortunately, the ease and convenience of modern devices have also come with a painful crick in the neck. The sedentary nature of work and prolonged use of hand-held devices and computers have contributed to a sharp increase in neck pain.
While fatigue in neck muscles has long been suspected of causing pain, the actual mechanical changes in the spine and muscles that precede weakness remain an outstanding question.
Now, using high-precision X-ray ...
Air pollution linked to higher risk of infertility in men
2024-09-05
Long term exposure to fine particulate matter (PM2.5) air pollution is linked to a higher risk of infertility in men, whereas road traffic noise is linked to a higher risk of infertility in women over 35, finds a Danish study published by The BMJ today.
If these findings are confirmed in future studies, they could help guide strategies to regulate noise and air pollution to protect the general population from these exposures, say the researchers.
Infertility is a major global health problem affecting one in seven couples trying to conceive.
Several ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
[Press-News.org] A $1.2 million Rosetta stone for honeybeesW.M. Keck grant helps scientists decipher bee language