(Press-News.org)
A study led by the UAB Institut de Neurociències and published in the journal Nature Communications demonstrates in animal models how daily administration of cannabidiol (CBD), a substance obtained from the cannabis plant, extends lifespan and improves symptoms associated with Leigh syndrome. This severe mitochondrial disease affecting children is characterised by a progressive decline in cognitive and motor functions and premature death. The research group also demonstrated in both mice and fibroblasts from children with the disease that CBD improves cellular function.
Leigh syndrome is a rare mitochondrial disease particularly affecting the organs and tissues that require most energy: the muscles and nervous system. It is characterized by progressive neuromuscular decline and premature death, and there are currently no approved treatments. That is why it is urgent to find a solution for patients suffering from this disease.
Drs. Emma Puighermanal and Albert Quintana, researchers from the Laboratory of Mitochondrial Neuropathology of the Institut de Neurociències at the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (INc-UAB), have spent years studying the disease. They seek to understand the processes causing dysfunction of mitochondria, organelles in charge of providing energy to cells, and to find therapies capable of reverting this.
In a study published in Nature Communications, researchers have now demonstrated that daily administration of CBD is a promising treatment option. Through its multiple action it provides antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anticonvulsant effects, which improve the symptomatology and help recover cell functions in patients. The study was conducted with two different Leigh syndrome mouse models, as well as with fibroblast cells from patients.
The results revealed that CBD acts at many levels within the cell, including activating a protein inside the cell nucleus known as PPARγ. This protein regulates the expression of many genes involved in the immune response, oxidation and mitochondrial function, and has been seen to be altered by the disease. Moreover, CBD increases the expression of the metallothionein protein, which enhances its antioxidant response.
In the animal models, cannabidiol administration improved neuropathology in the affected brain regions, breathing abnormalities and social deficits, and also delayed motor decline and neurodegenerative signs. In addition, mice receiving treatment lived significantly longer than those with no treatment. In the fibroblast cells from patients, CBD improved their antioxidant processes.
"The benefits we observed, together with CBD’s safe and well-tolerated profile, show it to be a truly promising treatment for patients with Leigh syndrome", explains Dr. Albert Quintana, researcher at the INc-UAB and lecturer in the Department of Cellular Biology, Physiology and Immunology at the UAB.
One year ago, the researchers obtained an orphan drug designation for CBD by the European Medicines Agency, which entails many benefits such as a reduction in the costs of developing the drug. “CBD has already been approved by the US regulatory agency FDA for the treatment of other rare paediatric diseases. We hope all of this will help in the translation of our results to clinical practices”, concludes Dr. Emma Puighermanal, researcher at the INc-UAB and lead author of the article.
The research, conceived and coordinated by the INc-UAB, also included the collaboration of the Institute for Neuroscience of Alicante (UMH-CSIC), the Institute of Neurosciences of the University of Barcelona (UBneuro), the Neurocentre Magendie of France, and the company Minoryx Therapeutics.
END
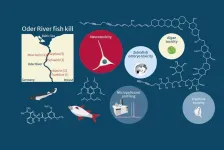
Summer 2022’s environmental disaster led to the death of up to 60 per cent of fish biomass and up to 85 per cent of mussel and snail biomass in the River Oder. In August 2022, the UFZ set up an interdisciplinary ad hoc working group together with researchers from the Leibniz Institute of Freshwater Ecology and Inland Fisheries (IGB), the University of Veterinary Medicine, Vienna (Vetmeduni) and the University of Birmingham. They took water samples at five locations along the Oder, extracted poisoned ...
“This editorial explores its impact on expanding datasets, improving image quality, and enabling predictive oncology.”
BUFFALO, NY- September 6, 2024 – A new editorial was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on September 4, 2024, entitled, “Generative AI in oncological imaging: Revolutionizing cancer detection and diagnosis.”
Generative AI is revolutionizing oncological imaging, enhancing cancer detection and diagnosis. This editorial explores its impact on expanding ...
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 11 A.M. ET FRIDAY, SEPTEMBER 6. 2024
Individuals involved in the criminal legal system have a high rate of opioid use disorder (OUD) and a high risk of overdose death compared to the general population, yet the most effective treatments—medications for opioid use disorder (MOUD)—are underutilized in criminal legal settings where treatment is mandated as part of a person’s probation or parole. Medications are often not provided due to stigma or lack of adequate funding for evidence-based care. According to a study ...
Age-related changes in the fibroblasts, cells that create the skin’s structure, contribute to the development of aggressive, treatment-resistant melanoma in males, according to research in mice by the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center.
The study was published online Sept. 6 in Cell.
The risk of developing melanoma, a potentially deadly skin cancer, increases with age. Men are more at risk than women, and tend to develop more aggressive, hard-to-treat melanomas, particularly at advanced ages, says Ashani Weeraratna, Ph.D., the Bloomberg ...
About The Study: This population-based cross-sectional study of U.S. cancer incidence trends found that rates of diagnosis improved in 2021 but continued to be lower than expected, adding to the existing deficit of diagnosed cases from 2020. Particular attention should be directed at strategies to immediately increase cancer screenings to make up lost ground.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Krystle A. Lang Kuhs, PhD, MPH, email krystle.kuhs@uky.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.32288)
Editor’s Note: Please see ...
Scientists from Swansea University have developed a new tool to help identify optimal photovoltaic (PV) materials capable of maximising crop growth while generating solar power.
In a recent study published in Solar RRL, academics from the University’s Department of Physics have been exploring the effect of semi-transparent PV materials placed over crops – an exemplary application of agrivoltaics (solar panels combined with agricultural settings).
As part of this work, the team has developed an innovative freeware tool that predicts the light transmission, absorption, and power generation of different PV materials nearly anywhere on the globe using ...
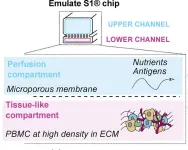
Researchers at the Institut Pasteur in France have developed artificial “lymphoid organ-chips” that recreate much of the human immune system’s response to booster vaccines. The technology, described in an article to be published September 6 in the Journal of Experimental Medicine (JEM), could potentially be used to evaluate the likely effectiveness of new protein and mRNA-based booster vaccines for COVID-19 and other infectious diseases.
The rapid mutation and evolution of SARS-CoV-2 and other viruses ...
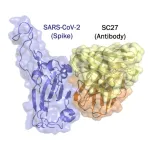
SAN ANTONIO -- A monoclonal antibody appears effective at neutralizing the numerous variants of SARS-CoV-2, as well as related viruses in animals that could pose a threat if they were to begin spreading in people. The antibody, called SC27, was recently described in Cell Reports Medicine.
The finding opens the possibility of broader, more effective treatments to work against current and future COVID variants.
Monoclonal antibody SC27 was identified, developed and provisionally patented by a team of researchers led ...
Every cell in our body contains the same DNA, yet liver cells are different from brain cells, and skin cells differ from muscle cells. What determines these differences? It all comes down to gene regulation; essentially how and when genes are turned on and off to meet the cell’s demands. But gene regulation is quite complex, especially because it is itself regulated by other parts of DNA.
Gene regulators: Enhancers, transcription factors
There are two important components that control gene regulation: the first are enhancers, which are short bits of DNA that increase the likelihood that a ...
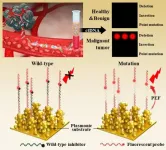
Dr. Min-young Lee and Dr. Sung-gyu Park of the Advanced Bio and Healthcare Materials Research Division at KIMS have developed a technology that can detect cancer mutant genes in blood with the world's highest sensitivity of 0.000000001% based on plasmonic nanomaterials for optical signal amplification. The team tested blood samples from lung cancer patients (stages 1-4) and healthy individuals for EGFR mutations and achieved a diagnostic accuracy of 96%.
Previously utilized genetic analysis technologies had low analytical sensitivity to detect mutated genes compared to normal genes, making it difficult to accurately diagnose early-stage cancer patients. ...