(Press-News.org) Mill Valley, CA – September 5, 2024 – The SynGAP Research Fund 501(c)(3) is proud to announce its continued collaboration with the University of Pennsylvania’s (UPenn) Orphan Disease Center (ODC) through the Million Dollar Bike Ride (MDBR) Pilot Grant Program. ODC is accepting proposals for a grant award of $74,851 to further advance critical research in SYNGAP1-Related Disorders (SRD). Instructions for submitting a letter of interest are available here. Applications are due in two weeks by September 20, 2024.
Why We Participate in This Project
The SynGAP Research Fund (SRF) has been partnering with the MDBR at UPenn since 2019. This collaboration has been instrumental in advancing research for SRD. Since 2022, SRF Team has raised $111,778 and secured each year’s matching grant of $30,000, resulting in a total of $201,778 raised for SYNGAP1 research. This ongoing support has allowed us to make significant strides in understanding and developing potential treatments.
In 2022, the UPenn ODC awarded a follow-on grant to Dr. Elizabeth Heller, building on the initial funding provided by SRF. The 2022 grant, totaling $65,705 was composed of $35,705 from SRF’s fundraising efforts, matched by $30,000 from the ODC. Similarly, in 2023, a grant was awarded to Dr. Gemma Carvill, Northwestern University, for her groundbreaking work on missense and variants of uncertain significance (VUS), which builds on her research with EpiMVP. This grant amounted to $61,222, with $31,222 raised by SRF and an additional $30,000 provided by ODC.
Supporting SYNGAP1 Research: New Funding Opportunity Available
This year, we are thrilled to announce that $74,851 is available for researchers, comprising $44,851 from SRF fundraising and $30,000 from UPenn’s ODC MDBR program. We strongly encourage researchers to submit their proposals by September 20th, 2024, to continue the vital work of advancing research that supports therapeutic development for SRD.
Quotes from the SRF Team
Mike Graglia, the founder of SRF says, “This program is exceptional. The ODC deserves to be proud of it: facilitating fundraising, building community, and moving funding to science. I’m grateful to Aaron for bringing SRF into this effort and to Kali, Peter, Andra, Justin and all the families who give their time and energy to funding. Families building community and mobilizing resources is the only way we are going to see therapies in a timeframe that matters. Time is brain.”
Aaron Harding, SRF’s Team Captain and an avid cyclist, says about the MDBR, “In 2019, we started as a non-grant-matching team since I was riding anyway, but it was a great opportunity for SRF to become a part of something bigger and to promote the MDBR event.” Aaron added, “In 2021, Kali Worth’s incredible friends, led by Paula Lee, became the foundation of the SRF Cycling Team. We continue to grow the SRF Team each year; all thanks goes to the families.”
“The ODC MDBR SRF Funding allowed us to continue our research on SRD,” says SRF SAB member Elizabeth A Heller, PhD. “We apply CRISPR activation to the SYNGAP1 gene in rodent models of human patients. In this way, we restore the levels of SynGAP to rescue haploinsufficiency. Although CRISPR activation is a new technology, it is already finding its way into the clinic, underscoring the translational potential of our research.”
Andra Fox, mom of Reagan, said this about her first time participating: “What impacted us even more than the fundraising and the event itself was the experience of walking into a room of strangers and feeling the instant connection as parents of Syngapians. I felt it in the way they interacted with my daughter, the questions they asked, and in the stories and laughter we shared.” Andra, who rode with her husband, Isaiah, added, “I’m also grateful to the SynGAP Research Fund for their continued efforts and advocacy for all families affected by SRD.”
About SYNGAP1-Related Disorders (SRD)
SYNGAP1-Related Disorder (ICD-10 F78.A1; ICD-11 LD90.Y) is a rare genetic disorder caused by variants on the SYNGAP1 gene that reduce SynGAP protein levels. SRF has identified over 1,454 patients to date, and the number grows weekly. This protein acts as a regulator in the synapses (where neurons communicate with each other). When SynGAP protein levels are too low, we see an increase in excitability in the synapses making it difficult for neurons to communicate effectively. This leads to many neurological issues seen in SynGAP patients.
Symptoms of SYNGAP1 include primarily neurological issues, including autism spectrum disorder, intellectual disability, epilepsy, hypotonia (low muscle tone), gross and fine motor delays, and visual abnormalities such as strabismus (crossed eyes) as well as gastrointestinal challenges and disordered sleep.
About the SynGAP Research Fund (SRF)
The mission of the SynGAP Research Fund (SRF) is to improve the quality of life for SYNGAP1 patients through the research and development of treatments, therapies, and support systems.
SRF was founded in the US in 2018 as a 501(c)(3) US public charity, and families created sister organizations for SRF in the UK in 2020, in Europe (Netherlands) in 2022, and in Latin America (Colombia) in 2023.
Completely family-led, SRF is the largest non-government funder of SynGAP research having committed over $6 million in grants. The founders cover operational costs, ensuring donations fund science & patient-related programs. SRF’s grant program awards one or two-year grants to investigators, physician residents, and clinicians interested in studying SYNGAP1. SRF grants are intended to help researchers explore novel ideas and answer open questions related to the clinical aspects of and therapies for SRD.
For more on SRF, visit curesyngap1.org or follow @cureSYNGAP1 on LinkedIn, YouTube, Instagram, Facebook, TikTok, or X.
SRF is a member of FasterCures, COMBINEDBrain, Global Genes Foundation Alliance, Everylife Foundation Community Congress, Epilepsies Action Network, Personalized Medicine Coalition, Rare Epilepsy Network, Epilepsy Leadership Council, Alliance for Genetic Etiologies in Neurodevelopmental Disorders and Autism (AGENDA), California Action Link for Rare Diseases, American Brain Coalition, Genetic Alliance UK, Rare Disease UK, Syndromes Without a Name (SWAN UK), Jumpstart Program, Patient Worthy, Autism Brain Net, Innovation and Value Initiative, Rare Disease Diversity Coalition, Cambridge Rare Disease Network, Breaking Down Barriers, Rare-X, Mencap, IndoUSRare, and The World Orphan Drug Congress.
END
UPenn’s Orphan Disease Center to amplify SYNGAP1 research: SynGAP Research Fund’s Million Dollar Bike Ride team raises $74,851 for one-year grant
Apply for SYNGAP1 funding of ~$75K by September 20, 2024
2024-09-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Crystallized alternative DNA structure sheds light on insulin and diabetes
2024-09-06
The first crystal structure of an alternative DNA shape from the insulin gene has been revealed by a UCL-led research team.
DNA is widely accepted to be formed of two strands that wind around one another, known as a double helix, but it is possible for DNA to change shape and structure. The new study, published in Nature Communications, reveals the detail in the structure of a type of DNA called i-motif by crystallising it for the first time.
Co-lead author Dr Zoë Waller (UCL School of Pharmacy) ...
Protecting just 0.7% of world’s land could help save a third of most unique and endangered species
2024-09-06
Conservation efforts directed towards just 0.7% of the world’s land mass could help protect one third of the world’s threatened and unique tetrapod (four-limbed vertebrate) species, new research by Imperial College London, On the Edge, and ZSL has shown.
The study, led by researchers at Imperial College London and published this week in Nature Communications, finds that large gains in conservation are possible by focusing on areas home to exceptional biodiversity and species with high levels of evolutionary distinctiveness and global ...
TGF-beta and RAS signaling are both required for lung cancer metastasis, study finds
2024-09-06
When it comes to cancer metastasis, it takes two to tango. That was one of the key findings of a new study led by researchers at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK): The TGF-beta and RAS signaling pathways work together to spur the spread of cancer in lung adenocarcinoma, a leading cause of cancer deaths around the world.
Take away one of those two signals, and lung cancer will not be able to spread (metastasize) to new parts of the body, their findings in animal models suggest.
The research, published September 6 in Cell, points to new opportunities to potentially prevent metastasis, thanks to an updated understanding of the underlying processes.
“About ...
5 lessons to level up conservation successfully
2024-09-06
Conservation needs to scale successfully to protect nature. A new paper takes lessons from around the world to show how that might be done.
To reverse biodiversity loss and meet ambitious global targets, conservation programmes designed to preserve everything from forests to fish need to work ‘at scale’.
Scaling can mean three things. Scaling ‘out’ means expanding a programme to new people and places, while scaling ‘up’ means bringing in higher-level institutions, such as governments introducing policies or incentives that make it easier for individuals and private companies to engage.
Scaling ‘deep’ means changing hearts and minds – ...
Researchers advance new class of quantum critical metal that could advance electronic devices
2024-09-06
A new study led by Rice University’s Qimiao Si has unveiled a new class of quantum critical metal, shedding light on the intricate interactions of electrons within quantum materials. Published in Physical Review Letters on Sept. 6, the research explores the effects of Kondo coupling and chiral spin liquids within specific lattice structures.
“The insights gained from this discovery could lead to the development of electronic devices with extreme sensitivity, driven by the unique properties of quantum-critical ...
DOE, ORNL announce opportunity to define the future of high-performance computing
2024-09-06
The U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Office of Science (SC) today announced a new research and development opportunity led by Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) to advance technologies and drive new capabilities for future supercomputers. This industry research program worth $23 million, called New Frontiers, will initiate partnerships with multiple companies to accelerate the R&D of critical technologies with renewed emphasis on energy efficiency for the next generation of post-exascale computing in the 2029 ...
Cannabidiol demonstrated to alleviate symptoms of Leigh syndrome
2024-09-06
A study led by the UAB Institut de Neurociències and published in the journal Nature Communications demonstrates in animal models how daily administration of cannabidiol (CBD), a substance obtained from the cannabis plant, extends lifespan and improves symptoms associated with Leigh syndrome. This severe mitochondrial disease affecting children is characterised by a progressive decline in cognitive and motor functions and premature death. The research group also demonstrated in both mice and fibroblasts from children with ...
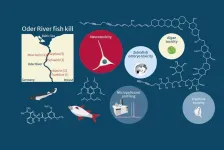
A chemical cocktail of micropollutants amplified the effect of algal toxins causing mass fish mortality on the River Oder in 2022
2024-09-06
Summer 2022’s environmental disaster led to the death of up to 60 per cent of fish biomass and up to 85 per cent of mussel and snail biomass in the River Oder. In August 2022, the UFZ set up an interdisciplinary ad hoc working group together with researchers from the Leibniz Institute of Freshwater Ecology and Inland Fisheries (IGB), the University of Veterinary Medicine, Vienna (Vetmeduni) and the University of Birmingham. They took water samples at five locations along the Oder, extracted poisoned ...
Generative AI in cancer imaging: revolutionizing detection & diagnosis
2024-09-06
“This editorial explores its impact on expanding datasets, improving image quality, and enabling predictive oncology.”
BUFFALO, NY- September 6, 2024 – A new editorial was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on September 4, 2024, entitled, “Generative AI in oncological imaging: Revolutionizing cancer detection and diagnosis.”
Generative AI is revolutionizing oncological imaging, enhancing cancer detection and diagnosis. This editorial explores its impact on expanding ...
Disparity in access to medications for opioid use disorder persist in criminal legal settings
2024-09-06
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 11 A.M. ET FRIDAY, SEPTEMBER 6. 2024
Individuals involved in the criminal legal system have a high rate of opioid use disorder (OUD) and a high risk of overdose death compared to the general population, yet the most effective treatments—medications for opioid use disorder (MOUD)—are underutilized in criminal legal settings where treatment is mandated as part of a person’s probation or parole. Medications are often not provided due to stigma or lack of adequate funding for evidence-based care. According to a study ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
Digital microsteps as scalable adjuncts for adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
Researchers develop a biomimetic platform to enhance CAR T cell therapy against leukemia
Heart and metabolic risk factors more strongly linked to liver fibrosis in women than men, study finds
Governing with AI: a new AI implementation blueprint for policymakers
Recent pandemic viruses jumped to humans without prior adaptation, UC San Diego study finds
Exercise triggers memory-related brain 'ripples' in humans, researchers report
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
[Press-News.org] UPenn’s Orphan Disease Center to amplify SYNGAP1 research: SynGAP Research Fund’s Million Dollar Bike Ride team raises $74,851 for one-year grantApply for SYNGAP1 funding of ~$75K by September 20, 2024