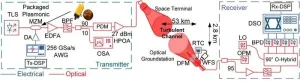
(Press-News.org) Researchers have achieved data rates as high as 424Gbit/s across a 53-km turbulent free-space optical link using plasmonic modulators— devices that uses special light waves called surface plasmon polaritons to control and change optical signals. The new research lays the groundwork for high-speed optical communication links that transmit data over open air or space.
Free-space-optical communication networks could aid space exploration because they can provide high-speed, high-capacity data transmission with lower latency and less interference than traditional radio frequency communication systems. This could lead to more efficient data transfer, better connectivity and enhanced capabilities for space missions.
Laurenz Kulmer from the Leuthold group of ETH Zurich will present this research at Frontiers in Optics + Laser Science (FiO LS), which will be held 23 – 26 September 2024 at the Colorado Convention Center in Denver.
“High-speed free-space transmission is an option to connect the world, or it may serve as a backup if underwater cables break,” said Kulmer. “Nevertheless, it is also a step towards a new cheap high-speed internet that may connect all locations across the world. This way it may contribute towards a stable, high-speed internet for millions of people who are currently unconnected.”
Plasmonic modulators are ideal for space communication links because they are compact while also operating at high speeds over a wide temperature range with low energy consumption.
In free-space optical outdoor experiments, the researchers achieved information rates of up to 424 Gbit/s below a 25% SD FEC threshold — the point at which a system can still fix errors in transmitted data despite interference or noise. Experiments using a plasmonic IQ modulator in a standard fiber system achieved an even higher throughput of up to 774 Gbit/s/pol while staying below a 25% SD FEC threshold.
Based on these results, the researchers say that combining plasmonic modulators with coherent free-space optical communication could help increase overall throughput, with speeds potentially reaching 1.4 Tbit/s. The findings also show that it is favorable to operate free-space optical links at the highest speeds, rather than using higher order modulation formats and low speeds. With additional improvements in device design and photonic integration, the researchers say it should be feasible to reach polarization multiplexing data rates above 1 Tbit/s for each polarization channel.
“In a next step we are going to test the long-term reliability of our devices,” said Kulmer. “High-speed performance has been shown, but we have to make sure they can operate for years to come in the harshest of environments, space.”
About Frontiers in Optics + Laser Science
Frontiers in Optics, the annual meeting for Optica is presented with Laser Science, the annual meeting of the American Physical Society, Division of Laser Science. The two meetings unite communities from both societies for comprehensive and current research in a diverse collection of optics and photonics topics and across the disciplines of physics, biology and chemistry. The 2024 FiO LS Conference will feature hundreds of live contributed and invited talks. More information at https://www.frontiersinoptics.com.
About Optica
Optica, Advancing Optics and Photonics Worldwide, is the society dedicated to promoting the generation, application, archiving and dissemination of knowledge in the field. Founded in 1916, it is the leading organization for scientists, engineers, business professionals, students and others interested in the science of light. Optica's renowned publications, meetings, online resources and in-person activities fuel discoveries, shape real-life applications and accelerate scientific, technical and educational achievement. Discover more at: Optica.org
END
Plasmonic modulators could enable high-capacity space communication
High-speed free-space data transmission could improve connectivity for space missions
2024-09-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UPenn’s Orphan Disease Center to amplify SYNGAP1 research: SynGAP Research Fund’s Million Dollar Bike Ride team raises $74,851 for one-year grant
2024-09-06
Mill Valley, CA – September 5, 2024 – The SynGAP Research Fund 501(c)(3) is proud to announce its continued collaboration with the University of Pennsylvania’s (UPenn) Orphan Disease Center (ODC) through the Million Dollar Bike Ride (MDBR) Pilot Grant Program. ODC is accepting proposals for a grant award of $74,851 to further advance critical research in SYNGAP1-Related Disorders (SRD). Instructions for submitting a letter of interest are available here. Applications are due in two weeks by September 20, 2024.
Why We Participate in This Project
The SynGAP Research ...
Crystallized alternative DNA structure sheds light on insulin and diabetes
2024-09-06
The first crystal structure of an alternative DNA shape from the insulin gene has been revealed by a UCL-led research team.
DNA is widely accepted to be formed of two strands that wind around one another, known as a double helix, but it is possible for DNA to change shape and structure. The new study, published in Nature Communications, reveals the detail in the structure of a type of DNA called i-motif by crystallising it for the first time.
Co-lead author Dr Zoë Waller (UCL School of Pharmacy) ...
Protecting just 0.7% of world’s land could help save a third of most unique and endangered species
2024-09-06
Conservation efforts directed towards just 0.7% of the world’s land mass could help protect one third of the world’s threatened and unique tetrapod (four-limbed vertebrate) species, new research by Imperial College London, On the Edge, and ZSL has shown.
The study, led by researchers at Imperial College London and published this week in Nature Communications, finds that large gains in conservation are possible by focusing on areas home to exceptional biodiversity and species with high levels of evolutionary distinctiveness and global ...
TGF-beta and RAS signaling are both required for lung cancer metastasis, study finds
2024-09-06
When it comes to cancer metastasis, it takes two to tango. That was one of the key findings of a new study led by researchers at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK): The TGF-beta and RAS signaling pathways work together to spur the spread of cancer in lung adenocarcinoma, a leading cause of cancer deaths around the world.
Take away one of those two signals, and lung cancer will not be able to spread (metastasize) to new parts of the body, their findings in animal models suggest.
The research, published September 6 in Cell, points to new opportunities to potentially prevent metastasis, thanks to an updated understanding of the underlying processes.
“About ...
5 lessons to level up conservation successfully
2024-09-06
Conservation needs to scale successfully to protect nature. A new paper takes lessons from around the world to show how that might be done.
To reverse biodiversity loss and meet ambitious global targets, conservation programmes designed to preserve everything from forests to fish need to work ‘at scale’.
Scaling can mean three things. Scaling ‘out’ means expanding a programme to new people and places, while scaling ‘up’ means bringing in higher-level institutions, such as governments introducing policies or incentives that make it easier for individuals and private companies to engage.
Scaling ‘deep’ means changing hearts and minds – ...
Researchers advance new class of quantum critical metal that could advance electronic devices
2024-09-06
A new study led by Rice University’s Qimiao Si has unveiled a new class of quantum critical metal, shedding light on the intricate interactions of electrons within quantum materials. Published in Physical Review Letters on Sept. 6, the research explores the effects of Kondo coupling and chiral spin liquids within specific lattice structures.
“The insights gained from this discovery could lead to the development of electronic devices with extreme sensitivity, driven by the unique properties of quantum-critical ...
DOE, ORNL announce opportunity to define the future of high-performance computing
2024-09-06
The U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Office of Science (SC) today announced a new research and development opportunity led by Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) to advance technologies and drive new capabilities for future supercomputers. This industry research program worth $23 million, called New Frontiers, will initiate partnerships with multiple companies to accelerate the R&D of critical technologies with renewed emphasis on energy efficiency for the next generation of post-exascale computing in the 2029 ...
Cannabidiol demonstrated to alleviate symptoms of Leigh syndrome
2024-09-06
A study led by the UAB Institut de Neurociències and published in the journal Nature Communications demonstrates in animal models how daily administration of cannabidiol (CBD), a substance obtained from the cannabis plant, extends lifespan and improves symptoms associated with Leigh syndrome. This severe mitochondrial disease affecting children is characterised by a progressive decline in cognitive and motor functions and premature death. The research group also demonstrated in both mice and fibroblasts from children with ...
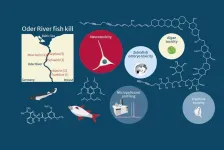
A chemical cocktail of micropollutants amplified the effect of algal toxins causing mass fish mortality on the River Oder in 2022
2024-09-06
Summer 2022’s environmental disaster led to the death of up to 60 per cent of fish biomass and up to 85 per cent of mussel and snail biomass in the River Oder. In August 2022, the UFZ set up an interdisciplinary ad hoc working group together with researchers from the Leibniz Institute of Freshwater Ecology and Inland Fisheries (IGB), the University of Veterinary Medicine, Vienna (Vetmeduni) and the University of Birmingham. They took water samples at five locations along the Oder, extracted poisoned ...
Generative AI in cancer imaging: revolutionizing detection & diagnosis
2024-09-06
“This editorial explores its impact on expanding datasets, improving image quality, and enabling predictive oncology.”
BUFFALO, NY- September 6, 2024 – A new editorial was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on September 4, 2024, entitled, “Generative AI in oncological imaging: Revolutionizing cancer detection and diagnosis.”
Generative AI is revolutionizing oncological imaging, enhancing cancer detection and diagnosis. This editorial explores its impact on expanding ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
USF study: Gag grouper are overfished in the Gulf; this new tool could help
New study from Jeonbuk National University finds current climate pledges may miss Paris targets
Theoretical principles of band structure manipulation in strongly correlated insulators with spin and charge perturbations
A CNIC study shows that the heart can be protected during chemotherapy without reducing antitumor efficacy
Mayo Clinic study finds single dose of non-prescribed Adderall raises blood pressure and heart rate in healthy young adults
Engineered immune cells show promise against brain metastases in preclinical study
Improved EV battery technology will outmatch degradation from climate change
AI cancer tools risk “shortcut learning” rather than detecting true biology
Painless skin patch offers new way to monitor immune health
Children with poor oral health more often develop cardiovascular disease as adults
GLP-1 drugs associated with reduced need for emergency care for migraine
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
[Press-News.org] Plasmonic modulators could enable high-capacity space communicationHigh-speed free-space data transmission could improve connectivity for space missions