(Press-News.org) Older women struggling with urinary incontinence can benefit from regular, low-impact exercise, with yoga as well as stretching and strengthening showing benefits in a new study published Aug. 27 in Annals of Internal Medicine.
The research, led by scientists at Stanford Medicine and the University of California, San Francisco, is part of a larger effort to identify low-risk, low-cost ways to treat one of the most common health problems women face as they age.
After 12 weeks of a low-impact yoga program, study participants had about 65% fewer episodes of incontinence. Women in a control group doing stretching and strengthening exercises experienced a similar benefit over the same time period. The benefits are on par with the effects of medications used to address incontinence, the researchers said.
“Our study was testing the kind of yoga that just about anyone can do, with modifications for different physical abilities,” said the study’s senior author, Leslee Subak, MD, chair of obstetrics and gynecology at Stanford Medicine. “What I love about it is that it’s safe, inexpensive, doesn’t require a doctor and accessible wherever you live.” Because the trial was conducted partly during the COVID-19 pandemic, many participants received their yoga or exercise instruction via online meetings, exercising in their own homes, she noted.
The study’s lead author is Alison Huang, MD, professor of medicine, urology, and epidemiology and biostatistics at UCSF.
Urinary incontinence, which affects more than half of middle-aged women and up to 80% of 80-year-olds, can lead to a variety of other problems, from social isolation to bone fractures caused by falls. But there is help.
“Part of the problem is that incontinence is stigmatized; we don’t talk about it,” said Subak, the Katharine Dexter McCormick and Stanley McCormick Memorial Professor III. “Or we hear folklore about this being normal when you get older. In fact, it’s very common but it’s not inevitable, and we have very effective ways of treating it.”
Addressing a common problem
Incontinence deserves good treatment because of the many ways it interferes with people’s lives.
“It takes away independence,” Subak said. “My patients will say, ‘I can’t stay with my kids or grandkids because I’m afraid I’ll wet the bed, and I can’t talk about it; it’s too embarrassing.’”
Patients may avoid activities that could boost their well-being, such as exercising and seeing friends. They are more likely to be admitted to a nursing home and to suffer certain serious medical problems such as hip fractures.
“Incontinence and overactive bladder are among the biggest risk factors for falls and fractures among older women,” Subak said. “You’re rushing to the bathroom at night — with the lights off — tripping and falling, and breaking a hip.”
Some factors that contribute to risk for incontinence can’t be changed, such as aging or having had children. But others are modifiable.
“A lot of my research has focused on weight loss and physical activity, which in fact are effective treatments,” Subak said. She became interested in studying yoga as a treatment after some of her patients told her it helped them.
Being active helps
The study compared two 12-week exercise programs: 121 participants were randomly assigned to yoga, and 119 to a physical conditioning control group. The participants were women with urinary incontinence that caused symptoms at least once a day. They were 45 to 90 years old, with a mean age of 62.
In the yoga program, participants learned 16 hatha yoga poses intended to strengthen the pelvic floor, via two 90-minute sessions per week. The pelvic floor consists of the muscles that form the base of the pelvis and hold its organs — including the bladder and urethra — in place. Participants were also asked to practice yoga for at least one hour per week outside of class and to maintain a practice log.
Participants in the control group spent an equal amount of time in exercise classes, but their classes focused on nonspecific stretching and strengthening exercises that did not engage the pelvic floor. They were also asked to practice for an additional hour per week and keep a practice log.
The study began with in-person classes, then transitioned to a videoconference format when the COVID-19 pandemic lockdowns began.
Participants recorded when they leaked urine and classified whether each episode was urgency incontinence, when an overactive bladder causes a person to feel the need to urinate more often than usual, or stress incontinence, in response to pressure in the abdomen, such as from coughing or sneezing. They also answered standard questionnaires about their bladder function.
At the beginning of the study, the participants had an average of 3.4 episodes of urinary incontinence per day, including 1.9 urgency-type episodes and 1.4 stress-type episodes.
By the end of the 12-week programs, participants in the yoga group were experiencing 2.3 fewer episodes of incontinence per day, on average. Those in the physical conditioning group were experiencing 1.9 fewer episodes per day.
The two treatments are about equally effective, with both approaches reducing episodes of incontinence by around 60%, and the benefits from both treatments are meaningful, Subak said. Patients who would like to try these approaches can search for low-impact Iyengar yoga or low-impact exercise classes in their communities or online, she said, adding that instructors should be able to adapt the activity to participants’ physical limitations.
“I’m impressed that exercise did so well and impressed that yoga did so well,” Subak said. “One of the take-home messages from this study is ‘Be active!’”
Other nonsurgical treatments for incontinence, including medications, typically result in a 30% to 70% improvement in symptoms, she noted.
If a patient asked whether yoga could help with incontinence, “I would say that I think it’s a great idea to try it if you’re interested,” Subak said. “It’s very low risk, and there’s potential for benefit not only for incontinence but also for your general well-being.”
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health (grants R01AG050588, R01DK116712-04S1 and K24AG068601). Researchers from Yale University and San Francisco State University also contributed to the study.
END
Low-impact yoga and exercise found to help older women manage urinary incontinence
2024-09-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Genetic studies reveal new insights into cognitive impairment in schizophrenia
2024-09-06
In a comprehensive review of recent genetic and population studies, published in the peer-reviewed medical journal Genomic Psychiatry (Genomic Press, New York), Professors Michael Owen and Michael O'Donovan of Cardiff University's Centre for Neuropsychiatric Genetics and Genomics present evidence that challenges conventional wisdom about cognitive deficits in schizophrenia. Their analysis reveals that premorbid cognitive impairment – lower IQ and other cognitive deficits present before the onset of psychosis – is largely explained by non-familial factors rather than by the same inherited genetic variants that ...
Researcher develops technology to provide cleaner energy and cleaner water
2024-09-06
As the world transitions to cleaner energy sources, the need for energy-relevant metals and critical minerals has surged dramatically. Driven by the rise of electric vehicles and other green technologies, these essential materials are in high demand across the globe.
Metals, such as lithium, cannot be grown. They must be mined or recycled, making this a top priority for researchers in the mining industry. Traditional methods of mining lithium are expensive and can be harmful to the environment, but researchers at Virginia Tech have found a way to minimize this environment impact. They will optimize and scale up this method with ...
Expect the unexpected: nanoscale silver unveils intrinsic self-healing abilities
2024-09-06
As an innovative concept in materials science and engineering, the inspiration of self-healing materials comes from living organisms that have the innate ability to self-heal. Along with this line, the search for self-healing materials has been generally focused on “soft” materials like polymers and hydrogels. For solid-state metals instead, one may intuitively imagine that any form of self-healing will be much more difficult to achieve.
While a few past studies showcased the self-healing behavior in metals that more or less requires the assistance ...
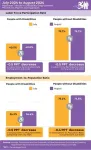
nTIDE September 2024 Jobs Report: Gains in employment for people with disabilities appear to level off after reducing gaps with non-disabled workers
2024-09-06
East Hanover, NJ – September 6, 2024 – Employment and labor force participation trends for people with disabilities appear to be stabilizing after several years of growth that reduced the gaps between individuals with and without disabilities, according to today’s National Trends in Disability Employment – semi-monthly update (nTIDE) issued by Kessler Foundation and the University of New Hampshire’s Institute on Disability (UNH-IOD).
Over the past three months, both groups have seen declines in employment and labor force participation, reflecting a broader workforce ...
Wiley enhances NMR Spectral Library Collection with extensive new databases
2024-09-06
Wiley, one of the world’s largest publishers and a global leader in research and learning, today announced the addition of ten computed CNMR databases totaling over 384,000 records to its KnowItAll NMR Spectral Library collection. With this addition, the KnowItAll NMR collection now provides access to over 1.3 million spectra, making it one of the most comprehensive collections of NMR spectral data available.
“These new databases significantly enhance our ability to support researchers in their quest ...
Renowned psychiatrist Dr. Gustavo Turecki sheds light on depression, suicide, and brain trauma response
2024-09-06
Montreal, Canada - The "Innovators & Ideas: Research Leader" section of Genomic Psychiatry (ISSN: 2997-2388), published by Genomic Press, New York, features an illuminating Genomic Press Interview with Dr. Gustavo Turecki, a trailblazer in psychiatric research at McGill University. The interview delves into Turecki's pioneering work on depression, suicide prevention, and the molecular underpinnings of mental health, offering valuable insights into cutting-edge research shaping our understanding of these critical issues.
Dr. Turecki, who serves as the Chair of the Department of Psychiatry at McGill ...
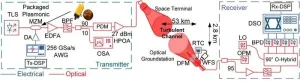
Plasmonic modulators could enable high-capacity space communication
2024-09-06
Researchers have achieved data rates as high as 424Gbit/s across a 53-km turbulent free-space optical link using plasmonic modulators— devices that uses special light waves called surface plasmon polaritons to control and change optical signals. The new research lays the groundwork for high-speed optical communication links that transmit data over open air or space.
Free-space-optical communication networks could aid space exploration because they can provide high-speed, high-capacity data transmission with lower latency and less interference than traditional radio frequency communication systems. ...
UPenn’s Orphan Disease Center to amplify SYNGAP1 research: SynGAP Research Fund’s Million Dollar Bike Ride team raises $74,851 for one-year grant
2024-09-06
Mill Valley, CA – September 5, 2024 – The SynGAP Research Fund 501(c)(3) is proud to announce its continued collaboration with the University of Pennsylvania’s (UPenn) Orphan Disease Center (ODC) through the Million Dollar Bike Ride (MDBR) Pilot Grant Program. ODC is accepting proposals for a grant award of $74,851 to further advance critical research in SYNGAP1-Related Disorders (SRD). Instructions for submitting a letter of interest are available here. Applications are due in two weeks by September 20, 2024.
Why We Participate in This Project
The SynGAP Research ...
Crystallized alternative DNA structure sheds light on insulin and diabetes
2024-09-06
The first crystal structure of an alternative DNA shape from the insulin gene has been revealed by a UCL-led research team.
DNA is widely accepted to be formed of two strands that wind around one another, known as a double helix, but it is possible for DNA to change shape and structure. The new study, published in Nature Communications, reveals the detail in the structure of a type of DNA called i-motif by crystallising it for the first time.
Co-lead author Dr Zoë Waller (UCL School of Pharmacy) ...
Protecting just 0.7% of world’s land could help save a third of most unique and endangered species
2024-09-06
Conservation efforts directed towards just 0.7% of the world’s land mass could help protect one third of the world’s threatened and unique tetrapod (four-limbed vertebrate) species, new research by Imperial College London, On the Edge, and ZSL has shown.
The study, led by researchers at Imperial College London and published this week in Nature Communications, finds that large gains in conservation are possible by focusing on areas home to exceptional biodiversity and species with high levels of evolutionary distinctiveness and global ...