2-bromopalmitate reduces senescence in human cells: Role of palmitoylation
“For the first time, the present study revealed a critical role for protein palmitoylation in the development of a DNA damage-induced senescence phenotype.”
2024-09-10
(Press-News.org)
“For the first time, the present study revealed a critical role for protein palmitoylation in the development of a DNA damage-induced senescence phenotype.”
BUFFALO, NY- September 10, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science), Volume 16, Issue 16 on August 23, 2024, entitled, “2-Bromopalmitate treatment attenuates senescence phenotype in human adult cells - possible role of palmitoylation.”
As noted in the Abstract of the paper, cells may undergo senescence in response to DNA damage, which is associated with cell cycle arrest, altered gene expression and altered cell morphology. Protein palmitoylation is one of the mechanisms by which the DNA damage response is regulated.
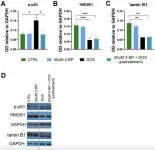
Researchers Adam Krzystyniak, Agata Gluchowska, Agata Pytyś, Magdalena Dudkowska, Tomasz Wójtowicz, Alicja Targonska, Dorota Janiszewska, Ewa Sikora, and Grazyna Mosieniak from the Nencki Institute of Experimental Biology in Warsaw, Poland, hypothesized that protein palmitoylation played a role in regulation of the senescent phenotype. They showed that treatment of senescent human vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) with 2-bromopalmitate (2-BP) - an inhibitor of protein acyltransferases - is associated with changes in different aspects of the senescent phenotype, including the resumption of cell proliferation, a decrease in DNA damage markers and the downregulation of senescence-associated β-galactosidase activity.
“Our data suggest that cell senescence may be regulated by palmitoylation, which provides a new perspective on the role of this posttranslational modification in age-related diseases.”
Continue reading: DOI:https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.206080
Corresponding authors: Grazyna Mosieniak - g.mosieniak@nencki.edu.pl, and Adam Krzystyniak - a.krzystyniak@nencki.edu.pl
Video short: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_y-Qw8ur8r8
Keywords: aging, cell senescence, vascular smooth muscle cell, palmitoylation, 2-BP, DNA damage
Click here to sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article.
About Aging-US
The mission of the journal is to understand the mechanisms surrounding aging and age-related diseases, including cancer as the main cause of death in the modern aged population.
The journal aims to promote 1) treatment of age-related diseases by slowing down aging, 2) validation of anti-aging drugs by treating age-related diseases, and 3) prevention of cancer by inhibiting aging. (Cancer and COVID-19 are age-related diseases.)
Please visit our website at https://www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
Facebook - https://www.facebook.com/AgingUS/
X - https://twitter.com/AgingJrnl
Instagram - https://www.instagram.com/agingjrnl/
YouTube - https://www.youtube.com/@AgingJournal
LinkedIn - https://www.linkedin.com/company/aging/
Pinterest - https://www.pinterest.com/AgingUS/
Spotify - https://open.spotify.com/show/1X4HQQgegjReaf6Mozn6Mc
Click here to subscribe to Aging publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker St., Suite 1
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-09-10
For paleontologists who study animals that lived long ago, fossilized remains tell only part of the story of an animal’s life. While a well-preserved skeleton can provide hints at what an ancient animal ate or how it moved, irrefutable proof of these behaviors is hard to come by. But sometimes, scientists luck out with extraordinary fossils that preserve something beyond the animal’s body. Case in point: in a new study published in the journal Current Biology, researchers found fossilized seeds in the stomachs of one of the earliest birds. This discovery shows that these birds were eating ...
2024-09-10
In a new study published in JAMA Network Open, researchers at Thomas Jefferson University have developed a novel screening tool to measure digital health readiness, which will be critical in addressing barriers to telehealth adoption among diverse patient populations.
The COVID-19 pandemic facilitated many rapid changes in healthcare, including a shift to using telehealth services across the U.S. instead of traditional in-person doctor’s visits. This ensured that patients continued to receive vital care, while only needing access to a mobile device or computer with a webcam. But just because a ...
2024-09-10
For more information, contact:
Nicole Fawcett, nfawcett@umich.edu
EMBARGOED for release at 11 a.m. Sept. 10, 2024
New law regulating out-of-pocket drug spending saves cancer patients more than $7,000 a year, study finds
The Inflation Reduction Act’s limit on Medicare Part D spending leads to significant savings for patients prescribed oral chemotherapy
ANN ARBOR, Michigan — As prescription oral chemotherapies have become a common form of cancer treatment, some patients were paying more than $10,000 a year for medications. A new study ...
2024-09-10
About The Study: In this modeling study of racial and ethnic disparities of tuberculosis (TB), these disparities were associated with substantial future health and economic outcomes of TB among U.S.-born persons without interventions beyond current efforts. Actions to eliminate disparities may reduce the excess TB burden among these persons and may contribute to accelerating TB elimination within the U.S.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Nicole A. Swartwood, MSPH, email nswartwood@hsph.harvard.edu.
To ...
2024-09-10
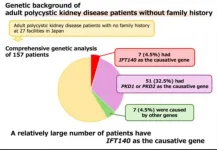
Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) researchers uncover the genetic link in patients with polycystic kidney disease lacking family history
Tokyo, Japan – Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an intractable disorder that causes fluid-filled cysts to grow in the kidneys. It is typically seen in adults. As one of the most prevalent hereditary kidney diseases, the autosomal dominant form of PKD is usually caused by mutations in the PKD1 and PKD2 genes. However, one out of ten patients with this condition typically exhibit no family history of the disease and lack ...
2024-09-10
NEW YORK/TORONTO – September 10, 2024 – Researchers at Klick Labs unveiled a cutting-edge, non-invasive technique that can predict chronic high blood pressure (hypertension) with a high degree of accuracy using just a person's voice. Just published in the peer-reviewed journal IEEE Access, the findings hold tremendous potential for advancing early detection of chronic high blood pressure and showcase yet another novel way to harness vocal biomarkers for better health outcomes.
The ...
2024-09-10
WHO: The Gabriella Miller Kids First Pediatric Research Program (Kids First), an initiative of the National Institutes of Health (NIH)
WHAT: Kids First announces the release of three comprehensive new pediatric research datasets exploring childhood cancers and congenital disorders. New publicly available datasets include:
CHILDHOOD CANCERS
Gabriella Miller Kids First (GMKF) Pediatric Research Program in Susceptibility to Ewing Sarcoma Based on Germline Risk and Familial History of Cancer.
Principal Investigators: Joshua D. Schiffman, MD. Huntsman Cancer Institute, ...
2024-09-10
A new study from Umeå University, Sweden, shows that the body's muscles sense mechanical pressure. This new discovery has important implications for movement neuroscience and may improve the design of training and rehabilitation to relieve stiff muscles.
"The results provide an important piece of the puzzle in understanding what information our nervous system receives from muscles," says Michael Dimitriou, associate professor at the Department of Medical and Translational Biology, ...
2024-09-10
Women who are being treated for asthma are more likely to miscarry and need fertility treatment to get pregnant, according to a large study presented at the European Respiratory Society (ERS) Congress in Vienna, Austria [1]. However, the study also suggests that most women with asthma are able to have babies.
The study was presented by Dr Anne Vejen Hansen from the department of respiratory medicine at Copenhagen University Hospital, Denmark.
She said: “Asthma is common in women of reproductive age. Previous ...
2024-09-10
ABSTRACTS: 510MO, 618MO, 1821MO, 71MO, 995MO
BARCELONA, Spain ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center’s Research Highlights provides a glimpse into recent basic, translational and clinical cancer research from MD Anderson experts. This special edition features upcoming oral presentations by MD Anderson researchers at the 2024 European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Congress focused on clinical advances across a variety of cancer types.
In addition to the studies summarized below, forthcoming press releases will feature the following oral presentations:
Initial results from a first-in-human ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] 2-bromopalmitate reduces senescence in human cells: Role of palmitoylation
“For the first time, the present study revealed a critical role for protein palmitoylation in the development of a DNA damage-induced senescence phenotype.”