(Press-News.org) (San Diego, Calif.--September 10, 2024, 10:35 a.m. PCT) A phase 3 study comparing tusamitamab ravtansine with docetaxel in patients with advanced non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) previously treated with platinum-based chemotherapy and immunotherapy (in combination or sequential), whose tumors highly expressed CEACAM5, is presented today at the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer 2024 World Conference on Lung Cancer in San Diego, Calf., by Dr. Benjamin Besse of Gustave Roussy, in Paris, France. As previously announced by Sanofi in December 2023, the study results did not meet its primary endpoint of improved progression-free survival (PFS).
Tusamitamab ravtansine is an immunoconjugate consisting of anti-carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 5 (CEACAM5) conjugated to a cytotoxic agent, with antineoplastic activity.
The CARMEN-LC03 is a phase 3 open-label, randomized, pivotal, multicenter study evaluating tusamitamab ravtansine (a CEACAM5-directed antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) with cytotoxic payload DM4/ravtansine) versus docetaxel in patients with advanced non-squamous NSCLC previously treated with platinum-based chemotherapy and immunotherapy (in combination or sequential), whose tumors highly expressed CEACAM5. Dr. Besse reported the results from the prespecified final progression-free survival and first interim overall survival (OS) analyses.
The trial randomized adult patients 1:1 to intravenously receive either 100 mg/ m2 tusamitamab ravtansine once every 2 weeks or docetaxel 75 mg/m2 once every 3 weeks. Patients with CEACAM5 positivity (assessed by immunohistochemistry) of greater than or equal to 2+intensity involving ≥50% of tumor cells were included in the study. CEACAM5 is a member of the CEACAM family of 12 glycoproteins and may drive cell adhesion and migration, as well as inhibit apoptosis, and may be overexpressed in many different cancer types.
Dual primary endpoints were PFS and OS. Secondary endpoints were objective response rate (ORR), health-related quality of life (HRQoL), duration of response and safety.
Besse and colleagues randomized 194 patients to receive tusamitamab ravtansine (all patients received treatment) and 195 to docetaxel of whom 177 received treatment. 61 patients (n=36 tusamitamab ravtansine and n=25 docetaxel) remained on treatment. Most patients received 1 or 2 prior lines of therapy, had a median age of 64 years and the majority were males (59.6%). Median follow-up was 7.4 and 18.1 months for PFS (by Independent Radiologic Committee [IRC]) and OS, respectively.
According to data presented by Dr. Besse, results include:
Median progression-free survival as per IRC for tusamitamab ravtansine and docetaxel was 5.4 vs 5.9 months, respectively (hazard ratio [HR]: 1.14; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.86-1.51; p=0.820).
Median overall survival (60% Information Fraction) of tusamitamab ravtansine vs docetaxel was 12.8 vs 11.5 months; HR=0.85 (95% CI [0.64-1.11]; p=0.112).
Similar overall response rate was observed with tusamitamab ravtansine and docetaxel. Time to deterioration of disease related symptoms/physical functioning/role functioning were numerically prolonged with tusamitamab ravtansine.
Grade ≥ 3 treatment-related adverse events and treatment-related serious AEs, TEAE leading to discontinuation and dose reduction were lower with tusamitamab ravtansine; however, dose delay was more frequently required for tusamitamab ravtansine, mainly due to corneal events.
“Despite trends favoring tusamitamab ravtansine on interim overall survival and electronic patient reported outcomes analysis, CARMEN did not meet its co-primary endpoint of improving PFS. The higher median PFS and OS observed with docetaxel was unexpected,” said Dr. Besse. He noted that tusamitamab ravtansine showed better safety data in various important clinical categories.
These exploratory analyses identify patients with advanced non-squamous NSCLC previously treated with immunotherapy and chemotherapy who are likely to derive clinical benefit from CEACAM5-directed therapy and suggest a previously unknown prognostic role for CEACAM5 in NSCLC, Additional research would be needed to corroborate these findings.
About the IASLC:
The International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC) is the only global organization dedicated solely to the study of lung cancer and other thoracic malignancies. Founded in 1974, the association's membership includes more than 10,000 lung cancer specialists across all disciplines in over 100 countries, forming a global network working together to conquer lung and thoracic cancers worldwide. The association also publishes the Journal of Thoracic Oncology, the primary educational and informational publication for topics relevant to the prevention, detection, diagnosis, and treatment of all thoracic malignancies. Visit www.iaslc.org for more information.
About the WCLC:
The World Conference on Lung Cancer (WCLC) is the world’s largest meeting dedicated to lung cancer and other thoracic malignancies, attracting nearly 7,000 researchers, physicians and specialists from more than 100 countries. The goal is to increase awareness, collaboration and understanding of lung cancer, and to help participants implement the latest developments across the globe. The conference will cover a wide range of disciplines and unveil several research studies and clinical trial results. For more information, visit https://wclc2024.iaslc.org.
END
Partial knee replacements for osteoarthritis performed by trainee surgeons last as long as those performed by more experienced consultants, according to data from England and Wales suggesting no difference in rates of subsequent revision surgery
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Medicine: http://journals.plos.org/plosmedicine/article?id=10.1371/journal.pmed.1004445
Article Title: Association between surgeon training grade and the risk of revision following unicompartmental knee replacement: ...
Aotearoa New Zealand’s flightless parrot, the kākāpō, evolved two different color types to potentially help them avoid detection by a now-extinct apex predator, Lara Urban at Helmholtz AI, Germany and colleagues from the Aotearoa New Zealand Department of Conservation and the Māori iwi Ngāi Tahu, report in the open-access journal PLOS Biology, publishing September 10th.
The kākāpō (Strigops habroptilus) is a nocturnal, flightless parrot endemic to New Zealand. It experienced severe population ...
Embargoed until Tuesday September 10 at 19:00 (BST)
Pregnant women who have limited access to affordable, nutritious, and healthy foods have a higher chance of developing both physical and mental health problems.
New research from Newcastle University has found that women who are what is termed “food insecure” are up to four times more likely to have poor mental health - such as stress, anxiety, and depression - than those who don’t struggle to afford or access food.
The mums-to-be are also at increased risk of obesity, developing diabetes during their pregnancy and dental problems, the two studies published ...
Humans, livestock and companion animals benefit from virus-based vaccines and gene therapies, but crops do not. This paradox is highlighted by an international research group led by the Institute of Molecular and Cellular Biology of Plants (IBMCP) within the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC), in an article published in the prestigious journal Nature Reviews Bioengineering. The study proposes a roadmap to use attenuated viruses to enhance performance of crops, making them more resistant to extreme and changing climate ...
About The Study: In 2023, all 3 payer markets (commercial insurance, Medicare Part D, and Medicaid managed care) for pharmacy benefit manager (PBM) services were highly concentrated, but concentration varied and was highest in Medicare Part D. While CVS Caremark held the dominant share in all 3 payer markets, each of the PBMs appeared focused on a different payer: Express Script’s largest share was in the commercial market, while Optum Rx’s and CVS Caremark’s were in Medicare Part D and Medicaid ...
New research published in NEJM and presented at this year’s Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) in Madrid (9-13 Sept) shows that a new class of insulin that is injected once a week is as effective as daily insulin injections for effective and safe blood sugar management in patients with type 2 diabetes. The study is by Dr Carol Wysham, MultiCare Rockwood Center for Diabetes and Endocrinology, Spokane, WA, USA, and colleagues.
When patients with type 2 diabetes find their oral medications alone can no longer control their blood sugar, insulin therapy is added and injection frequency (having daily injections) is among the main factors that can contribute ...
New research published in The Lancet and presented at this year’s Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) in Madrid (9-13 Sept) shows that a new class of insulin that only needs to be injected once weekly is as effective as daily insulin injections for effective blood sugar management in patients with type 1 diabetes. However, higher rates of hypoglycaemia using the new class means vigilance is needed for dose initiation and optimisation. The study is by Dr Richard M Bergenstal, ...
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- When they become fathers, men who have an unhealthy, high-cholesterol diet can cause increased risk of cardiovascular disease, or CVD, in their daughters, a University of California, Riverside-led mouse study has found.
The research, published in the journal JCI Insight, is the first to demonstrate this result seen only in female offspring.
CVD, the leading cause of death globally, is a group of disorders that affects the heart and blood vessels. Hypertension (high blood pressure) is a leading risk factor ...
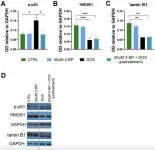
“For the first time, the present study revealed a critical role for protein palmitoylation in the development of a DNA damage-induced senescence phenotype.”
BUFFALO, NY- September 10, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science), Volume 16, Issue 16 on August 23, 2024, entitled, “2-Bromopalmitate treatment attenuates senescence phenotype in human adult cells - possible role of palmitoylation.”
As ...
For paleontologists who study animals that lived long ago, fossilized remains tell only part of the story of an animal’s life. While a well-preserved skeleton can provide hints at what an ancient animal ate or how it moved, irrefutable proof of these behaviors is hard to come by. But sometimes, scientists luck out with extraordinary fossils that preserve something beyond the animal’s body. Case in point: in a new study published in the journal Current Biology, researchers found fossilized seeds in the stomachs of one of the earliest birds. This discovery shows that these birds were eating ...