(Press-News.org) About The Study: This single-center cohort study identified substantial overall survival disparity and differing frequencies of driver gene variations by race and ethnicity. Socioeconomic status had the largest contribution but accounted for less than one-third of the disparity, with substantial contribution from tumor molecular features. Further study of the associations of genetic ancestry and the molecular pathogenesis of colorectal cancer with chemotherapy response is needed.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, John Paul Shen, MD, email jshen8@mdanderson.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2024.3666)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaoncology/fullarticle/10.1001/jamaoncol.2024.3666?guestAccessKey=68345ab4-be63-495f-92c1-465f42ac77fb&utm_source=for_the_media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=091224
END
Molecular, socioeconomic, and clinical factors affecting racial and ethnic disparities in colorectal cancer survival
JAMA Oncology
2024-09-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
City of Hope and Biopharmaceutical Research Company announce first patient has received BRC-001, a first-in-class cannabinoid therapeutic, in a clinical trial investigating supportive care in breast c
2024-09-12
City of Hope and Biopharmaceutical Research Company announce first patient has received BRC-001, a first-in-class cannabinoid therapeutic, in a clinical trial investigating supportive care in breast cancer
Researchers will evaluate whether the cannabinoid therapeutic candidate can address joint pain resulting from cancer treatment using aromatase inhibitors
This side effect has caused many breast cancer patients to discontinue treatment
LOS ANGELES and MONTEREY, Calif. — City of Hope®, one of the largest cancer research and treatment organizations in the United States, and Biopharmaceutical Research ...
Catalyzing environmental cleanup: A highly active and selective molecular catalyst and electrified membrane
2024-09-12
Connecticut, U.S.A -- Some chemicals create environmental problems; others, fortunately, can help clean them up.
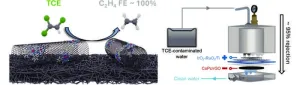
Chemists from Yale University and their colleagues have developed an electrochemical catalyst and membrane that offers an efficient and sustainable way to treat water contaminated with trichloroethylene (TCE), a common and persistent environmental pollutant. Their findings highlight the potential for advanced electrochemical treatments in environmental remediation and open the door for further innovations in the field.
Their results were published in Carbon Future ...
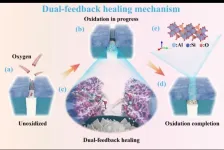
Dual-feedback healing mechanism redefining anti-oxidation coatings in fiber reinforced composites
2024-09-12
Fiber-reinforced ceramic matrix composites (CMCs) have been the primary choice for radome materials in hypersonic vehicles due to their high toughness, strength, and other advantageous properties. However, oxidation by oxygen in the atmospheric environment at elevated temperatures remains a significant obstacle to their further development. Thermal protection coatings offer a crucial avenue to mitigate this issue. Nonetheless, inherent material differences or fiber orientations within CMCs can lead to disparate thermal expansion rates between the matrix and fibers during temperature variations, inevitably ...
NCCN commits to sharing award-winning resources for people with cancer in Spanish and other languages
2024-09-12
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [September 12, 2024] — The National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®)—an alliance of leading cancer centers—and the NCCN Foundation® proudly announce plans to make every book in the library of NCCN Guidelines for Patients® available in Spanish; with select editions available in additional languages as well.
NCCN publishes the NCCN Guidelines for Patients library through funding from the NCCN Foundation. It now features more than 70 books with easy-to-understand information about prevention, ...
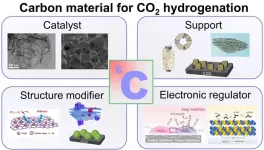
Development strategies for using carbon-based catalysts in CO2 conversion
2024-09-12
One of the primary drivers of climate change, CO2 emissions, have reached over 35 million tons worldwide. With global annual temperatures still rising, reducing CO2 emissions has become a necessity. To turn this necessity into an opportunity, researchers have been working to find ways to capture the CO2, thereby reducing emissions and then converting that CO2 into valuable chemicals and fuels.
One of the difficulties in working with CO2 is that it is very thermodynamically stable. To overcome this, additional ...
Breakthrough research extends hope for gastric cancer patients with peritoneal metasis
2024-09-12
Gastric cancer remains a formidable adversary, ranking as the fifth most common cancer and the third-leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, with over 1,000,000 new cases and close to 770,000 deaths each year. In Singapore, gastric cancer ranks among the top 10 causes of cancer-related deaths and claims about 300 lives each year.
The peritoneum, the lining of the abdominal cavity, is frequently involved in advanced-stage cancers, including gastric, colon, pancreatic, and ovarian cancers. For gastric cancer, the peritoneum ...
Genetic carriers for sickle cell disease have higher risks of blood clots across diverse ancestries
2024-09-12
National Institutes of Health (NIH) researchers and collaborators have found that being a carrier for sickle cell disease, known as having sickle cell trait, increases the risk of blood clots, a risk that is the same among diverse human populations that may not traditionally be associated with sickle cell disease. The study provides estimated clinical risks for people with sickle cell trait, which can inform clinical practice guidelines. Researchers examined the largest and most diverse set of people ...
Study finds unique pattern of blood clots in sickle cell trait, but low overall clot risk
2024-09-12
(WASHINGTON – September 12, 2024) The risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE), or blood clots, in individuals with sickle cell trait (SCT) is higher than in individuals without the trait. However, the risk is lower than for those with heterozygous factor V Leiden (FVL), according to a study published today in Blood Advances that analyzed genetic data from 23andMe research participants.
More than 100 million people worldwide and approximately 7% of Black individuals in the United States have SCT. Unlike sickle cell disease, ...
Deep learning for strain field customization in bioreactor with dielectric elastomer actuator array
2024-09-12
A research paper by scientists at Purdue University presented a deep learning method that enables the customization of complex strain fields according to specific requirements.
The new research paper, published on Aug. 14 in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems, used a deep learning method based on image regression and achieved to predict and customize complex strain fields.
Traditional bioreactors, powered by pneumatic actuators or motors, struggle to generate complex strain fields due to limited control over individual actuators. However, fields like cardiovascular biomechanics and tissue engineering require more advanced customization. “In the field of biomechanics, customizing ...
Killer yeasts may help remedy a craft beer brewing bother
2024-09-12
Highlights:
Diastatic yeasts can spoil craft beer through hyperattenuation, which boosts the alcohol content and causes bottles to explode.
Killer toxins, which are produced by other yeast strains, hint at a remedy.
In a proof-of-concept study, researchers found that killer toxins inhibited up to 95% of diastatic yeasts.
More work is needed to fine tune the recipe, but killer yeasts may help brewers remedy potentially contaminated beers.
Washington, D.C. — Sept. 12, 2024 — When diastatic strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
[Press-News.org] Molecular, socioeconomic, and clinical factors affecting racial and ethnic disparities in colorectal cancer survivalJAMA Oncology