Scientists aim to decode the genetic roots of mental illness on a large scale
2024-09-12
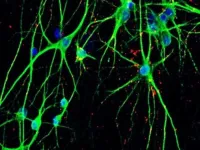
(Press-News.org) Neurodevelopmental and psychiatric disorders (NPD) including schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, autism, and depression are detrimental to individuals, their families and society as a whole, and in many cases still lack effective treatments. It’s becoming more and more clear that genetic mutations in certain genes can increase the likelihood of developing NPD, and several hundreds of those “risk genes” have been identified to date, but their role related to NPD remains a mystery. “Very little is known about the basic function of most of these genes, and what we do know often comes from work in cancer cell lines rather than brain cell types,” says David Panchision, Chief of the Developmental and Genomic Neuroscience Research Branch at the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), who spearheaded the SSPsyGene program aiming to tackle this challenge. “As such, we still don’t have a clear understanding of how alterations in these genes may work individually or in combination to contribute to neurodevelopmental and psychiatric disorders.”
To get to the bottom of this, the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) initiated a consortium called SSPsyGene (sspsygene.ucsc.edu) in 2023, uniting research teams from renowned US universities with the joint goal of characterizing the genetic origins of NPD, focusing on 250 selected high-risk genes. Among the contributors are Jubao Duan, Endeavor Health (formerly NorthShore University Health System) and University of Chicago, USA and Zhiping Pang, Rutgers University, USA with their teams, who developed a method for mutating NPD risk genes in human stem cells at large scale. In the modified cells, a selected NPD risk gene is mutated so that it no longer makes a functional protein. The modified stem cells can subsequently be turned into neurons and other brain cells to model the consequences of risk gene mutations in a simplified, lab-based version of the human brain. In the initial phase of the project, the teams tested 23 NPD risk genes, reported in work published in a recent article in the journal Stem Cell Reports. The resulting stem cell lines will be made available to other researchers worldwide to facilitate research on those risk genes and their contribution to NPD. In future works, Pang, Duan and the other members of the consortium will join forces to generate mutated stem cell lines for a much larger number of risk genes, with the ultimate goal of understanding the genetic causes for NPD and for generating better treatments. “The hope is that this collaborative work will generate a highly impactful resource for the neuroscience and psychiatric research community,” Panchision says.
About Stem Cell Reports
Stem Cell Reports is the open access, peer-reviewed journal of the International Society for Stem Cell Research (ISSCR) for communicating basic discoveries in stem cell research, in addition to translational and clinical studies. Stem Cell Reports focuses on original research with conceptual or practical advances that are of broad interest to stem cell biologists and clinicians. X: @StemCellReports
###
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-09-12
About The Study: This case report describes a woman who presented with bilateral blurry vision a few days after dyeing her hair with hair dye containing aromatic amines.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Nicolas Chirpaz, MD, email nicolas.chirpaz@chu-lyon.fr.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2024.3453)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial ...
2024-09-12
About The Study: This study found that certain social determinants of health affected monitoring for diabetic retinopathy similarly for Black and white patients with diabetes while others affected them differently. Patients living in rural communities, Black patients with preexisting diabetic retinopathy, and Hispanic white patients were not receiving eye care in accordance with clinical practice guidelines, which may contribute to worse outcomes.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Dustin D. French, PhD, email dustin.french@northwestern.edu.
To access the embargoed ...
2024-09-12
About The Study: This single-center cohort study identified substantial overall survival disparity and differing frequencies of driver gene variations by race and ethnicity. Socioeconomic status had the largest contribution but accounted for less than one-third of the disparity, with substantial contribution from tumor molecular features. Further study of the associations of genetic ancestry and the molecular pathogenesis of colorectal cancer with chemotherapy response is needed.
Corresponding ...
2024-09-12
City of Hope and Biopharmaceutical Research Company announce first patient has received BRC-001, a first-in-class cannabinoid therapeutic, in a clinical trial investigating supportive care in breast cancer
Researchers will evaluate whether the cannabinoid therapeutic candidate can address joint pain resulting from cancer treatment using aromatase inhibitors
This side effect has caused many breast cancer patients to discontinue treatment
LOS ANGELES and MONTEREY, Calif. — City of Hope®, one of the largest cancer research and treatment organizations in the United States, and Biopharmaceutical Research ...
2024-09-12
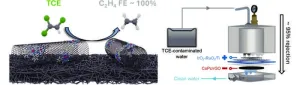
Connecticut, U.S.A -- Some chemicals create environmental problems; others, fortunately, can help clean them up.
Chemists from Yale University and their colleagues have developed an electrochemical catalyst and membrane that offers an efficient and sustainable way to treat water contaminated with trichloroethylene (TCE), a common and persistent environmental pollutant. Their findings highlight the potential for advanced electrochemical treatments in environmental remediation and open the door for further innovations in the field.
Their results were published in Carbon Future ...
2024-09-12
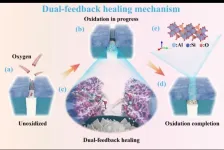
Fiber-reinforced ceramic matrix composites (CMCs) have been the primary choice for radome materials in hypersonic vehicles due to their high toughness, strength, and other advantageous properties. However, oxidation by oxygen in the atmospheric environment at elevated temperatures remains a significant obstacle to their further development. Thermal protection coatings offer a crucial avenue to mitigate this issue. Nonetheless, inherent material differences or fiber orientations within CMCs can lead to disparate thermal expansion rates between the matrix and fibers during temperature variations, inevitably ...
2024-09-12
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [September 12, 2024] — The National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®)—an alliance of leading cancer centers—and the NCCN Foundation® proudly announce plans to make every book in the library of NCCN Guidelines for Patients® available in Spanish; with select editions available in additional languages as well.
NCCN publishes the NCCN Guidelines for Patients library through funding from the NCCN Foundation. It now features more than 70 books with easy-to-understand information about prevention, ...
2024-09-12
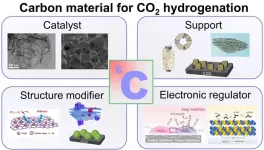
One of the primary drivers of climate change, CO2 emissions, have reached over 35 million tons worldwide. With global annual temperatures still rising, reducing CO2 emissions has become a necessity. To turn this necessity into an opportunity, researchers have been working to find ways to capture the CO2, thereby reducing emissions and then converting that CO2 into valuable chemicals and fuels.
One of the difficulties in working with CO2 is that it is very thermodynamically stable. To overcome this, additional ...
2024-09-12
Gastric cancer remains a formidable adversary, ranking as the fifth most common cancer and the third-leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, with over 1,000,000 new cases and close to 770,000 deaths each year. In Singapore, gastric cancer ranks among the top 10 causes of cancer-related deaths and claims about 300 lives each year.
The peritoneum, the lining of the abdominal cavity, is frequently involved in advanced-stage cancers, including gastric, colon, pancreatic, and ovarian cancers. For gastric cancer, the peritoneum ...
2024-09-12
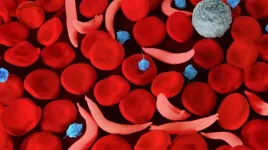
National Institutes of Health (NIH) researchers and collaborators have found that being a carrier for sickle cell disease, known as having sickle cell trait, increases the risk of blood clots, a risk that is the same among diverse human populations that may not traditionally be associated with sickle cell disease. The study provides estimated clinical risks for people with sickle cell trait, which can inform clinical practice guidelines. Researchers examined the largest and most diverse set of people ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Scientists aim to decode the genetic roots of mental illness on a large scale