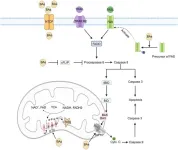
(Press-News.org) CLEVELAND, Ohio (Sept 10, 2024) –Menopausal women are at greater risk of insulin resistance as a result of declining estrogen levels. Previous studies evaluating the potential benefits of hormone therapy on insulin resistance have produced mixed results. However, a new meta-analysis of 17 different randomized, controlled trials suggests hormone therapy can be beneficial. Results of the meta-analysis will be presented at the 2024 Annual Meeting of The Menopause Society in Chicago September 10-14.
Insulin resistance can occur in men or women, but menopausal women are at greater risk because, as estrogen levels fall during the menopause transition, the body can become less responsive to insulin. A diagnosis of insulin resistance is considered serious because it can be a precursor of prediabetes, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic disorders.
A number of studies have previously attempted to determine the potential positive effect of hormone therapy on insulin resistance. However, those studies produced inconsistent results. But in this new metaanalysis of 17 unique randomized, controlled trials that covered more than 29,000 participants between 1998 and 2024, it was found that hormone therapy significantly reduced insulin resistance in healthy postmenopausal women without metabolic diseases including diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular diseases.
Cumulative totals of the 17 different trials included 15,350 participants who were randomized to hormone therapy including estrogen alone or estrogen plus progestogen and 13,937 who were randomized to placebo. The mean age of the study population ranged from 47 to 75 years, and treatment duration ranged from eight weeks to two years.
“Our analysis showed that both types of hormone therapy, including oral and transdermal routes, significantly reduced insulin resistance in healthy postmenopausal women, although estrogen alone was associated with a more prominent reduction when compared to a combination hormone therapy,” says Dr. Xuezhi (Daniel) Jiang, lead researcher from Reading Hospital Tower Health and Drexel University College of Medicine in Pennsylvania.
More detailed results will be discussed at the 2024 Annual Meeting of The Menopause Society as part of the oral abstract presentation titled “Effect of hormone therapy on insulin resistance in healthy postmenopausal women: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials.”
“Hormone therapy is an effective treatment for many bothersome menopause symptoms, including hot flashes,” says Dr. Stephanie Faubion, medical director for The Menopause Society. “This new metaanalysis is important as declining estrogen levels in menopausal women put them at greater risk for insulin resistance and hormone therapy could be beneficial in reducing insulin resistance in these women.”
Drs. Jiang and Faubion are available for interviews in advance of the Annual Meeting.
For more information about menopause and healthy aging, visit the newly redesigned www.menopause.org. The Menopause Society (formerly The North American Menopause Society) is dedicated to empowering healthcare professionals and providing them with the tools and resources to improve the health of women during the menopause transition and beyond. As the leading authority on menopause since 1989, the nonprofit, multidisciplinary organization serves as the independent, evidence-based resource for healthcare professionals, researchers, the media, and the public and leads the conversation about improving women’s health and healthcare experiences. To learn more, visit menopause.org.
END
New meta-analysis shows that hormone therapy can significantly reduce insulin resistance
After years of mixed results, a review of 17 randomized, controlled trials demonstrates benefit of estrogen alone and estrogen plus progesterone in reducing risk of prediabetes
2024-09-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Genomics reveals sled dogs’ Siberian lineage
2024-09-14
ITHACA, N.Y. – New research co-led by Cornell University examines thousands of years of Arctic sled dog ancestry and reveals when and how Siberian and Alaskan sled dogs’ DNA mixed.
“There was a real concern from Siberian breeders – who were mostly racing their dogs – that they were sending out their dogs’ DNA samples for analysis, more for the context of health traits, and they were getting breed ancestry information back that said their dog was not 100% Siberian husky,” said Heather Huson, a former ...
ESMO: Combination therapy reduced agitated delirium in patients with advanced cancers
2024-09-14
ABSTRACT: 1476O
BARCELONA, Spain ― Treatment with a combination of haloperidol and lorazepam reduced symptoms of agitated delirium, a common end-of-life condition for patients with advanced cancers, compared with haloperidol alone, according to a new study led by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. The findings were presented today at the 2024 European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Congress.
Agitated delirium occurs when a patient’s brain function begins to deteriorate as their cancer advances, resulting in many patients beginning to behave aggressively or abnormally. Although the use of medication ...
SOPHiA GENETICS presents ground-breaking multimodal research on AI-driven patient stratification at ESMO 2024
2024-09-14
Boston, MA and Rolle, Switzerland, September 14, 2024 – SOPHiA GENETICS (Nasdaq: SOPH), a cloud-native healthcare technology company and a leader in data-driven medicine, will unveil new research at the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) 2024. The study, conducted in collaboration with AstraZeneca, leverages advanced AI-driven techniques to identify subgroups of stage IV non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients who could most benefit from the addition of tremelimumab to durvalumab and chemotherapy.
The research is a retrospective, multimodal analysis of the POSEIDON Phase 3 clinical trial (NCT03164616). This trial originally demonstrated that the combination of tremelimumab, ...
Mitochondria at the crossroads of cholestatic liver injury: Targeting novel therapeutic avenues
2024-09-14
Bile acids are essential signaling molecules derived from cholesterol metabolism in the liver and are crucial for the digestion and absorption of fats. These molecules undergo further modification in the intestines by the gut microbiome. However, disruptions in bile flow, a condition known as cholestasis, can lead to the pathological accumulation of hydrophobic BAs in the liver and bloodstream. This accumulation not only exacerbates liver damage but also induces significant disturbances in cellular processes. The review focuses on recent developments in understanding how BAs contribute to liver injury by affecting mitochondrial function, endoplasmic reticulum ...
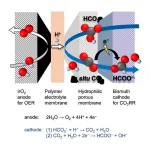
Scientists reveal new design for cells turning carbon dioxide into a green fuel
2024-09-14
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have made strides forward in realizing industrial conversion of bicarbonate solution made from captured carbon to a formate solution, a green fuel. Their new electrochemical cell, with a porous membrane layer in between the electrodes, overcomes major issues suffered in reactive carbon capture (RCC) and achieves performances rivaling energy-hungry gas-fed methods. Processes like theirs directly add value to waste streams and are key to realizing net zero emissions.
Carbon capture technology ...
Paying attention to errors can improve fused remote monitoring of lakes, researchers say
2024-09-14
Lakes can tip the scales from healthy to potential environmental hazard quickly when they become eutrophic. In this state, an abundance of nutrients accelerates algae growth, which then crowd the water’s surface and block light from reaching organisms below. Without light, they can’t make oxygen and life in the water begins to die off. Luckily, researchers can monitor inland lakes for eutrophication with remote sensing technologies; however, those technologies could be adjusted to make more accurate assessments, according to researchers based in China.
The team published their evaluation of the technologies, as well as recommended paths ...
Using training model to map planted and natural forests via satellite image
2024-09-14
While planting trees may seem like an easy win to combat climate change, planted forests often encroach on natural forests, wetlands, and grasslands. This can reduce biodiversity, disturb the natural environment, and disrupt carbon and water cycling. While there has been a global increase in forest cover, it’s hard to know if this forest is the regeneration and growth of natural forests or if it is planting new trees. Accurately mapping these forests with remote sensing technology could help.
However, comprehensive maps of planted forests and natural forests are lacking even though it is possible to distinguish planted forests and natural forests on satellite images ...
Illinois Institute of Technology Architecture Programs earn National Sustainability Designation from U.S. Department of Energy
2024-09-13
CHICAGO—September 13, 2024—The College of Architecture at Illinois Institute of Technology has been awarded the prestigious Zero Energy Design Designation (ZEDD) from the United States Department of Energy (DOE) for it Bachelor of Architecture and Master of Architecture programs. This recognition highlights the college’s commitment to sustainability, carbon neutrality, and zero-energy design practices in a world of escalating extreme weather and climate change.
The ...
Rice research could make weird AI images a thing of the past
2024-09-13
HOUSTON – (Sept. 13, 2024) – Generative artificial intelligence (AI) has notoriously struggled to create consistent images, often getting details like fingers and facial symmetry wrong. Moreover, these models can completely fail when prompted to generate images at different image sizes and resolutions.
Rice University computer scientists’ new method of generating images with pre-trained diffusion models ⎯ a class of generative AI models that “learn” by adding layer after layer of random noise to the images they are trained on and then generate new images by removing the added noise ⎯ could help correct ...
NIH awards establish pandemic preparedness research network
2024-09-13
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) has established a pandemic preparedness research network to conduct research on high-priority pathogens most likely to threaten human health with the goal of developing effective vaccines and monoclonal antibodies. Currently, many of the diseases caused by these pathogens have no available vaccines or therapeutics, and investing in this research is key to preparing for potential public health crises—both in the United States and around the world. NIH’s National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) expects to commit approximately ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
[Press-News.org] New meta-analysis shows that hormone therapy can significantly reduce insulin resistanceAfter years of mixed results, a review of 17 randomized, controlled trials demonstrates benefit of estrogen alone and estrogen plus progesterone in reducing risk of prediabetes