(Press-News.org) RESEARCH SUMMARY
Study Title: SOLARIS (Alliance A021703): A multicenter double-blind phase III randomized clinical trial of vitamin D combined with standard chemotherapy plus bevacizumab in patients with previously untreated metastatic colorectal cancer.
Publication: European Society for Medical Oncology 2024 Abstract LBA26
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute authors: Kimmie Ng, MD, MPH, Nadine McCleary, MD, MPH, Jeffrey A. Meyerhardt, MD, MPH
Summary: A double-blind randomized phase 3 clinical trial led by Dana-Farber Cancer Institute researchers and conducted across several hundred cancer centers in the U.S. tested the addition of high-dose vitamin D3 to standard treatment for patients with untreated metastatic colorectal cancer. More than 450 patients received standard chemotherapy plus bevacizumab and were randomized to high-dose or standard dose vitamin D3. The team observed no additional concerning side-effects or toxicities with the addition of high-dose vitamin D3. However, the addition of high-dose vitamin D3 to standard treatment did not delay the progression of cancer more so than standard-dose vitamin D3, according to the team’s analysis after a median 20-month follow up. A potential benefit for high-dose vitamin D3 was observed for patients with left-sided disease (i.e., primary tumors that arise in the descending colon, sigmoid colon, or rectum) and requires further investigation.
Significance: The SOLARIS trial was inspired by previous research suggesting that higher levels of vitamin D in the blood are associated with improved survival for metastatic colorectal cancer and that the addition of high-dose vitamin D3 to standard therapy could potentially improve progression free survival. The SOLARIS results suggest, however, that high-dose vitamin D3 cannot be recommended as a treatment for patients with untreated metastatic colon cancer.
Funding: National Cancer Institute; Pharmavite
Contact: Victoria Warren, victoria_warren@dfci.harvard.edu
END
High-Dose vitamin D3 does not provide benefit for metastatic colorectal cancer
2024-09-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Long-term metastatic melanoma survival dramatically improves on immunotherapy
2024-09-15
Long-term data from a landmark international trial show about half of patients with metastatic melanoma treated with a combination of immune checkpoint inhibitors survive cancer-free for 10 years or more, according to a new report from Weill Cornell Medicine and Dana-Farber Cancer Center investigators and their colleagues.
The 10-year follow-up study, published Sept. 15 in the New England Journal of Medicine, will bring the phase 3 CheckMate 067 trial to a close. The trial, which followed 945 patients treated at 137 sites in 21 countries, demonstrated that combining ...
Contrail avoidance is less likely to damage climate by mistake than previously thought
2024-09-15
A new study allays fears that rerouting flights to avoid forming climate-warming contrails could result in inadvertently making climate warming worse.
Researchers from Sorbonne Universite and the University of Reading found that for most flights that form contrails in the North Atlantic, the climate benefit of avoiding the contrail outweighs the extra carbon dioxide emitted from flying a different route.
Contrail avoidance requires comparing the climate impacts of carbon dioxide and contrails, called CO2 equivalence. Different methods have been proposed, and the choice of which has been largely political. Scientists feared that some choices ...
Breast cancer research: New studies show how post-treatment lifestyle choices shape long-term outcomes after diagnosis
2024-09-15
Young patients can safely breastfeed without increasing the risk of cancer recurrence or new cancer in the opposite breast
Telephone-based intervention can successfully prompt patients who are overweight to exercise more, lowering their weight
BARCELONA, SPAIN – Three studies led by Dana-Farber Cancer Institute researchers have encouraging implications for patients with breast cancer. Two studies focus on breastfeeding after breast cancer diagnosis and treatment. The studies found it was safe and feasible for young patients carrying specific genetic variations to breastfeed without raising their risk of a cancer recurrence or a cancer in the other breast, and that it was safe ...
New meta-analysis shows that hormone therapy can significantly reduce insulin resistance
2024-09-14
CLEVELAND, Ohio (Sept 10, 2024) –Menopausal women are at greater risk of insulin resistance as a result of declining estrogen levels. Previous studies evaluating the potential benefits of hormone therapy on insulin resistance have produced mixed results. However, a new meta-analysis of 17 different randomized, controlled trials suggests hormone therapy can be beneficial. Results of the meta-analysis will be presented at the 2024 Annual Meeting of The Menopause Society in Chicago September 10-14.
Insulin resistance can occur in men or women, but menopausal women are at ...
Genomics reveals sled dogs’ Siberian lineage
2024-09-14
ITHACA, N.Y. – New research co-led by Cornell University examines thousands of years of Arctic sled dog ancestry and reveals when and how Siberian and Alaskan sled dogs’ DNA mixed.
“There was a real concern from Siberian breeders – who were mostly racing their dogs – that they were sending out their dogs’ DNA samples for analysis, more for the context of health traits, and they were getting breed ancestry information back that said their dog was not 100% Siberian husky,” said Heather Huson, a former ...
ESMO: Combination therapy reduced agitated delirium in patients with advanced cancers
2024-09-14
ABSTRACT: 1476O
BARCELONA, Spain ― Treatment with a combination of haloperidol and lorazepam reduced symptoms of agitated delirium, a common end-of-life condition for patients with advanced cancers, compared with haloperidol alone, according to a new study led by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. The findings were presented today at the 2024 European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Congress.
Agitated delirium occurs when a patient’s brain function begins to deteriorate as their cancer advances, resulting in many patients beginning to behave aggressively or abnormally. Although the use of medication ...
SOPHiA GENETICS presents ground-breaking multimodal research on AI-driven patient stratification at ESMO 2024
2024-09-14
Boston, MA and Rolle, Switzerland, September 14, 2024 – SOPHiA GENETICS (Nasdaq: SOPH), a cloud-native healthcare technology company and a leader in data-driven medicine, will unveil new research at the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) 2024. The study, conducted in collaboration with AstraZeneca, leverages advanced AI-driven techniques to identify subgroups of stage IV non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients who could most benefit from the addition of tremelimumab to durvalumab and chemotherapy.
The research is a retrospective, multimodal analysis of the POSEIDON Phase 3 clinical trial (NCT03164616). This trial originally demonstrated that the combination of tremelimumab, ...
Mitochondria at the crossroads of cholestatic liver injury: Targeting novel therapeutic avenues
2024-09-14
Bile acids are essential signaling molecules derived from cholesterol metabolism in the liver and are crucial for the digestion and absorption of fats. These molecules undergo further modification in the intestines by the gut microbiome. However, disruptions in bile flow, a condition known as cholestasis, can lead to the pathological accumulation of hydrophobic BAs in the liver and bloodstream. This accumulation not only exacerbates liver damage but also induces significant disturbances in cellular processes. The review focuses on recent developments in understanding how BAs contribute to liver injury by affecting mitochondrial function, endoplasmic reticulum ...
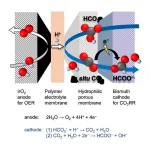
Scientists reveal new design for cells turning carbon dioxide into a green fuel
2024-09-14
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have made strides forward in realizing industrial conversion of bicarbonate solution made from captured carbon to a formate solution, a green fuel. Their new electrochemical cell, with a porous membrane layer in between the electrodes, overcomes major issues suffered in reactive carbon capture (RCC) and achieves performances rivaling energy-hungry gas-fed methods. Processes like theirs directly add value to waste streams and are key to realizing net zero emissions.
Carbon capture technology ...
Paying attention to errors can improve fused remote monitoring of lakes, researchers say
2024-09-14
Lakes can tip the scales from healthy to potential environmental hazard quickly when they become eutrophic. In this state, an abundance of nutrients accelerates algae growth, which then crowd the water’s surface and block light from reaching organisms below. Without light, they can’t make oxygen and life in the water begins to die off. Luckily, researchers can monitor inland lakes for eutrophication with remote sensing technologies; however, those technologies could be adjusted to make more accurate assessments, according to researchers based in China.
The team published their evaluation of the technologies, as well as recommended paths ...